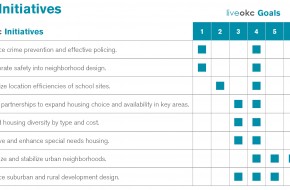
Goals
The goals below are in the form of statements describing ideal future conditions related to neighborhoods that our community has committed to work toward achieving. These goals establish priorities for our city and help community leaders make decisions regarding how our city grows. Clicking on any goal title will reveal the full goal statement and allow viewing of initiatives the City and its partners will undertake to accomplish the goal.
Oklahoma City neighborhoods are safe places to live, work, learn, and play. (jump to section)
We will establish a systematic neighborhood street program, focused on rehabilitation, traffic calming, and safety and functional improvements. Citizens place a high priority on the condition and repair of the existing street system. The streets that affect residents most – local and connector streets – are rarely addressed by normal transportation programs. A systematic neighborhood street program will both provide regular funding for street repair and rehabilitation and completion of special street projects such as traffic calming.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
We will enhance policing and crime prevention programs through partnerships between police and local communities. The term “community policing” has become controversial in some instances, but it is in fact a common sense approach to law enforcement that many cities and towns implement without fanfare. Police departments that practice community-based techniques recognize that police alone cannot deal with neighborhood safety and livability issues, but instead must partner with citizens, businesses, organizations, schools, churches, and others to build safe environments.
Community-based programs establish personal relationships and trust between police and residents. Some police departments describe this approach as a “value system” or even “a way of life” as opposed to a program. In Oklahoma City, effective neighborhood policing will involve greater outreach to residents and businesses, interaction with organizations, working relationships with property owners, and other cooperative efforts. A critical support element will involve direct work with at-risk youth and adequate funding for job training, education, and leadership development programs.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
We will incorporate design and maintenance practices to create safer environments in both established and new neighborhoods. Addressing the impact of the neighborhood environment on public safety will follow two tracks: 1) reviewing new projects (including subdivisions and major new developments) and incorporating safe environmental design standards into their design, and 2) auditing existing neighborhoods for unsafe conditions and correcting problem areas.
Safety evaluation of new projects will start with developing design standards and guidelines, using the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design as a starting point. Our public safety departments should develop specific areas of expertise in these principles and be fully integrated into the City’s project review and approval process.
Established neighborhoods present different challenges. Partnerships between City staff and community organizations will analyze the neighborhood environment and local crime patterns to identify and correct specific problems. The most common issues include overgrown lots, hidden spaces, and vacant and deteriorated buildings. We must be aggressive in such areas as vegetation control and demolition of buildings beyond feasible repair.
Response times when emergencies occur are also an important factor in the interaction between public safety and environmental design. Neighborhood designs should increase the efficiency of public safety operations and ensure that the greatest number of residents can be reached in the shortest amount of time by emergency responders. This should include strategic improvements in existing neighborhoods and efficient design in new neighborhoods.
Systematic evaluation and correction of design aspects of new projects and inherently unsafe environments in established areas will be necessary to ensure a safe environment for all residents of Oklahoma City.
We will correct unsafe building elements and design conditions in public facilities and outdoor spaces. The City should lead in providing safe and secure facilities and properties. This is especially important in distressed neighborhoods, where a public park or center may be seen as a refuge. All publicly accessed properties should be assessed for unsafe conditions, including but not limited to poor lighting, blind spots, and maintenance hazards. Once this inventory has been completed, priorities for repair should be set and incorporated into the capital program.
Graffiti and vandalism in public areas are special and persistent problems. Uncorrected incidents suggest neglect in a neighborhood, which in turn encourages both more vandalism and serious criminal activity. Graffiti can be controlled through an aggressive removal policy, best accomplished in partnership with neighborhood residents. Cooperative action for productive purposes has the secondary benefit of building a sense of neighborhood effectiveness and establishing credibility for improvement efforts all of which help reconstruct the social fabric.
Improve the functionality and efficiency of the street network by:
- Providing direct connections from residential developments to nearby places and to each other.
- Providing street and sidewalk stubs to adjacent vacant land in anticipation of future development.
- Connecting new development to existing street and sidewalk stubs, and to existing trail, open space, and bicycle networks.
- Reducing block sizes and use of dead-end streets.
- Maintaining the existing street grid to preserve connectivity and mobility options.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Evaluate public facilities and public property for unsafe conditions such as poor lighting (quality and quantity); blind spots; poor maintenance conditions; and other unsafe conditions. Prioritize improvements to these facilities and properties based on the following criteria: a) Proximity and condition of nearby neighborhoods; and b) Cost/benefit associated with mitigating the unsafe condition and maintaining the improvement.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Utilize existing natural streams as amenities in public parks, and regularly monitor and maintain stream banks for safety of park users.
Revise subdivision regulations to require development adjacent to parks and public open spaces to maintain open sight lines to parks and public open space. Reduce/limit residential rear yards, fences, walls, and physical and visual enclosures around park and public open space perimeters. Encourage designs that allow homes to face into parks or where side yards are located near parks.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will set neighborhood development priorities by using quantitative evaluation criteria. Available resources are never sufficient to address the problems of struggling neighborhoods. Setting priorities and policy focuses can be addressed by an evaluative process that considers such factors as economic opportunities, educational performance, housing quality, access to commercial and other support services, public safety, and presence of community organizations and institutions. The process should consider positive neighborhood factors that can create the foundations for success, including:
- Existing support capacity from neighborhood associations, local service providers, and area businesses;
- Community institutions like parks, schools, churches, or community centers; and,
- Connections to surrounding neighborhoods.
We will expand rehabilitation and redevelopment programs to stabilize the physical fabric of neighborhoods. The physical condition of a neighborhood and its buildings is critical to its ability to function as a community. Residential rehabilitation programs should be expanded to both meet the needs of existing residents and serve future generations. Rehabilitation should focus items that directly affect health and safety, secure the basic building envelope, and add economic value to the surrounding area. Programs in which community development corporations acquire, rehabilitate, and either sell or rent units on a “turnkey” basis at moderate costs have been particularly effective in adding value, preserving housing, and introducing new owners and potential leaders into a neighborhood.
But housing rehabilitation is only part of the picture. Vacant sites and dilapidated buildings depress both property values and community momentum. Programs to accelerate the redevelopment of dilapidated properties should be tied closely to the priority evaluation process. Funds should be targeted to areas and projects that create a critical mass that in turn catalyzes private market investment and creates a self-sustaining community. Mechanisms like landbanks and land trusts have also proven effective in gaining control over vacant properties and returning them to productive use. Often, a high priority or visibility project at a strategic location can produce an unexpectedly powerful private reaction as neighbors gain confidence in their future.
We will create, enhance, and maintain community spaces where residents interact positively and advance the social fabric. Successful neighborhoods include spaces where people see and greet each other, and work and play together in a common enterprise. These spaces open a neighborhood, and increase the level of positive interaction that is the essence of a living neighborhood. Yet, hidden or neglected public spaces have the opposite effect, attracting nuisances and sometimes crime, and being scary or off-putting places that people avoid. Good community spaces can take many forms – a well-maintained public park surrounded and watched over by residents; a community garden; the median of a parkway; or a school or community center site.
Strengthening these community places begins with inventorying and analyzing their operations. This can be done in cooperation with neighbors and community organizations. Volunteer work, business participation, and other public and private support can provide the means to reclaim existing spaces and develop new ones, and to provide adequate resources for continued support and maintenance.
Facilities like community gardens and groceries are particularly attractive as community spaces because they are self-supporting; become natural and productive attractors of people, and address other key concerns such as access to healthy food. Efforts at a neighborhood level to secure sites and organize gardens should be expanded and educational institutions should provide technical help to gardeners. Public development incentives should have a special focus on attracting grocery stores to skipped over areas with viable consumer markets, and should encourage inclusion of public space in project design.
We will coordinate public infrastructure projects and community revitalization. In an effort to create tangible catalysts for revitalizing urban communities, the City will use the analysis described in this section as well as those located throughout planokc, to inform its capital improvements program.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Prioritize neighborhoods for revitalization and re-investment in order to reverse the decline associated with poor maintenance of public infrastructure and other property by using the following objective criteria:
- Low economic opportunity;
- Low educational attainment;
- Poor health outcomes;
- Poor housing environments;
- Low neighborhood quality; and,
- Existing capacity to support the revitalization efforts; and other important indicators.
Increase the City’s capacity to participate in targeted programs that strengthen neighborhood infrastructure and other assets.
Increase and/or re-assign City staff to support targeted neighborhoods and coalitions.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
We will institute neighborhood design guidelines and practices that build community in lower-density settings. We recognize that different people have different preferences. Many people seek new houses but still want the diversity and neighborliness of the best of established neighborhoods. Others seek the bigger lots and greater personal space offered by low-density development. But almost everyone wants an attractive living environment, a sense of belonging to a community, public space, and connection. As we move toward new standards that implement the land use plan, we should ensure that new development designs reflect patterns that create better communities. These include such items as encouraging lot clusters to maintain open space, even in low-density development; street connections for both community contact and public safety access; trail and pathway systems; and housing variety where appropriate. Planned unit developments should be used in their intended way, to encourage creative design by looking at developments in their entirety.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Change subdivision regulations to determine the number of entries into a residential development based on number of lots in order to improve connectivity of the roadway network and emergency response.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will continue and expand our program to locate, plan, and build our parks for safety. When new parks are developed, their initial planning should include an assessment of security needs. Locations should have good street exposure and visibility. Park design and programming should be guided by the Crime Prevention through Environmental Design principles, which uses design to maximize public safety.
Create a standards for trails based on industry standards, “Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design” principles, expected use, and surrounding land uses.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Evaluate public facilities and public property for unsafe conditions such as poor lighting (quality and quantity); blind spots; poor maintenance conditions; and other unsafe conditions. Prioritize improvements to these facilities and properties based on the following criteria: a) Proximity and condition of nearby neighborhoods; and b) Cost/benefit associated with mitigating the unsafe condition and maintaining the improvement.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Utilize existing natural streams as amenities in public parks, and regularly monitor and maintain stream banks for safety of park users.
Protect the health of park visitors by utilizing the most environmentally friendly least toxic means available of reducing weeds and other pests to acceptable levels.
Revise subdivision regulations to require development adjacent to parks and public open spaces to maintain open sight lines to parks and public open space. Reduce/limit residential rear yards, fences, walls, and physical and visual enclosures around park and public open space perimeters. Encourage designs that allow homes to face into parks or where side yards are located near parks.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
We will reduce crime and improve the sense of security throughout the city. We will establish and expand crime prevention partnerships with neighborhoods, visible patrols with a high degree of community contact and interaction in targeted areas, and youth programs. Other components of this effort should include regular evaluation of police staffing needs and expansion of such preventive measures as elimination of nuisances like abandoned buildings and integration of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design in the project review process. The liveokc and serveokc elements also provide initiatives that address public safety issues.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will provide incentives and investments that produce a favorable environment for private investment on underutilized sites. In Oklahoma City, we have tended to view land as an inexhaustible and disposable resource, reducing the desirability of older areas and decreasing land values, while expanding the city’s boundaries outward. The surveys and process of planokc show that this view is also changing, as citizens place a high value on using existing infrastructure and urban land effectively and rebuilding established neighborhoods. Preferences are also changing, as many families appreciate active urban places like Midtown and Automobile Alley that provide living, shopping, entertainment, and work places with good walking, bike, and transit access. Effective use of existing land resources is a central principle of Chapter Two’s land use vision.
Redevelopment and infill depend on major private investment. City policy and action can create the conditions that help this private investment occur.
Directions for these policies include:
- Site assembly. Multiple property owners, often absent or very difficult to find, can make it impossible to put together sites for redevelopment. The City can help private developers by helping them assemble sites.
- Infrastructure and street improvement. While redevelopment and infill sites usually have infrastructure, these facilities are sometime obsolete and require improvement. Redevelopment can provide the impetus for making necessary public investments in these assets.
- Public investments. Parks, schools, civic facilities, pedestrian and bicycle facilities, streetscapes, and other amenities can provide anchors that are proven to generate private development. The Bricktown Canal is an excellent example of a public amenity that has paid for itself many times over in private investment. Similarly, the new MAPS 3 Park will inevitably become the catalyst for the Core to Shore redevelopment.
- Code improvement and proactive enforcement. Poor property maintenance, unattractive and cluttered signs, and public or operating nuisances can degrade the value of surrounding property and discourage reinvestment. Updated ordinances and consistent, enforcement will minimize these disincentives and create momentum for new private development.
Establish new incentives and raise awareness of existing incentives that stimulate the preservation and rehabilitation of historic resources. Incentives could include:
- Preservation easements, low-interest or forgivable rehabilitation loans, and Tax Increment Financing Districts for historic buildings, sites, and districts.
- Tools and practices for public/private partnerships to ensure the preservation and retention of top-priority historic resources whose deterioration or demolition would present an irreparable and highly significant loss to the City and beyond.
- Existing city, state, and federal tools and incentives for rehabilitation, including state and federal tax credits for certified rehabilitation.
- Expedited review process for projects involving infill sites.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
Prioritize and concentrate development where facilities, infrastructure, and services have capacity and in areas where the Police and Fire Departments are best able to respond. Guide the location and timing of development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will incorporate crime prevention principles into the City’s design regulations and guidelines. Previous elements of the plan, including playokc and liveokc, introduced the concept of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles (CPTED), which use common-sense design features to minimize opportunities for criminal activity. CPTED principles apply on a wide range of scales, from individual site vegetation choices to citywide development patterns.
Oklahoma City should incorporate CPTED principles into its design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. Some cities (including Wichita, Kansas) have established ordinances that officially integrate CPTED principles into their design standards, while others use them as guidelines and adapt for their own use.
The City can encourage the use of CPTED principles through:
- Encouraging land use planning that mixes uses and extends hours of activity and “eyes on the street.”
- Establishing neighborhood territoriality by which adjacent residents and businesses can monitor activity in the public realm. a mixture of uses in neighborhoods.
- Lighting and building design guidelines.
- Landscaping guidelines that avoid hidden places.
- Building code enforcement and resolution and elimination of chronic vacancy and structural deterioration.
The City’s project review and approval process should include Police Department participation to provide specific public safety recommendations. The department should maintain an officer on staff with a specialty in CPTED and its principles. This staff member should also provide outreach to the development community to provide special training to builders, developers, and design professionals on safe community design.
Create a standards for trails based on industry standards, “Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design” principles, expected use, and surrounding land uses.
Establish access management requirements that limit driveways on arterials and collectors and increase connections between uses to improve safety and traffic efficiency.
Limit driveways on arterials and collectors and increase connections between uses to improve safety and traffic efficiency.
Ensure proper access to and between subdivisions in order to offer a choice in routes for residents, multiple access points for emergency responders, and to reduce vehicle congestion at arterial intersections. Contiguous developments should share access whenever feasible.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure that planokc is periodically updated to coordinate/correspond with the City’s Emergency Operation Plan and vice versa.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Encourage the integration and mixing of land uses in urban areas.
In order to promote compatibility between different uses, establish standards and guidelines that ensure all developments are pedestrian-friendly and human scale at street frontages and property lines.
2: Increase partnerships between police and communities to minimize conditions that encourage crime.
We will implement cooperative programs with neighborhoods that both build local trust and engage and redirect at-risk youth. Public safety partnerships begin by working with neighborhoods to address and remove signs of neglect and alienation, both in the physical and human environments. It continues with building on the natural allegiances between a police department whose commitment is to protect and serve its citizens and citizens who need the security of safe neighborhoods to live and prosper. Finally, and perhaps most importantly, it involves the creativity and imagination to see young people as potential leaders rather than potential criminals. People often live up or down to expectations. Youth should be engaged in the process of becoming leaders, improving themselves and their neighborhoods. Law enforcement officers, in partnership with other organizations, are in an ideal position to lead that process.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Seek ways to improve efficiency of positions in the Police Department, such as directing responsibility for analyzing and proactively addressing crime from uniformed officers to trained analysts.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Oklahoma City area schools are neighborhood assets and sources of pride.
We will establish partnerships between the City and school districts to assist in non-educational functions. School districts deal with a variety of non-educational or indirectly educational functions on a regular basis. This includes siting of new schools, redeveloping closed schools, addressing crime and crime prevention, and other community outreach functions. By working together, funding should be leveraged and resources used efficiently to strengthen neighborhoods, making them viable choices for young households.
We will co-locate new public projects in coordination with local school districts. Strong civic institutions strengthen neighborhood identify, social interaction and appeal to investors. Co-locating public projects such as libraries, fire stations, parks, recreation centers, and schools create neighborhood activity centers and realize efficiencies through joint use arrangements.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
We will support our schools in improving student performance. Low academic performance is a problem in our city, and especially within Oklahoma City Public Schools, as measured by the State Department of Education. Our entire community must address this issue aggressively. Some solutions involve long-term and continuing efforts, such as creating and sustaining healthy, mixed-income neighborhoods that provide the secure environments necessary to nurture learning and achievement. Recommendations that help create these types of neighborhoods are found throughout planokc, from land use initiatives to neighborhood reinvestment and housing variety. Other specific efforts, involving concerted action by the public and private sectors and school districts can provide more immediate results. These educational support programs can include scholarship programs that offer post-secondary grants to students in inner-city schools and districts, expanded early childhood education, after- school programs, mentoring, specialized educational tracks, teacher skills training, or financial incentives for high-performing schools and teachers.
The City will also assist the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce in efforts to adapt the education and training offered by local institutions to match the current and future needs of local companies. This includes both K-12 schools and secondary schools.
Educational issues and programs represent a convergence of different perspectives. This element approaches good educational programming from a workforce and economic development framework; liveokc from a neighborhood development viewpoint; and serveokc from a public service and community quality point of view. However, all point in the same direction, highlighting the importance of increasing achievement and learning.
Facilitate communication among the 23 school districts in order to develop more arts education opportunities for the children in our community.
Establish development standards and design guidelines for new cultural, civic, and sporting facilities that address site design, architecture, compatibility, pedestrian-orientation and access, landscaping, and the inclusion of public art.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Coordinate with Strong Neighborhoods Initiative to provide recreational, fire safety, public safety, and character building programs in schools.
Identify ways to establish/strengthen relationships and partnerships between schools and the business community as one method to improve student education and outcomes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Work with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce to recommend adaptations to local education and training opportunities to match the current and projected needs of local companies.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Avoid concentrations of apartment complexes. Instead, integrate multifamily units into neighborhoods with mixes of housing types or in mixed-use developments.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Oklahoma City's neighborhoods thrive because they contain quality housing choices to meet the diverse needs of the population.
We will create public/private partnerships that fill critical demands like workforce housing that are not normally satisfied by the private market. The Housing Market Preference and Demand Study defined housing preferences for different age and income groups, including residential types and locations. This information provides valuable guidance to city agencies, community organizations, builders, and developers that can help all parties make policy and business decisions. However, these data rapidly become outdated. Regular updates, funded by a mutually beneficial partnership of public and private sectors, can ensure that this information remains relevant and useful.
But information must be put to use. The 2013 housing study identified a major demand for “workforce” housing – equity and rental units affordable to people in a range from 60% to 120% of the citywide median household income. The normal private market has difficulty producing housing for much of this income range because of perceived risk and small profit. Partnerships between the public, private, and nonprofit sectors, including employers, can develop programs that remove obstacles to workforce housing production and marketing. Options include site acquisition, landbanking, interim financing, appraisals, mortgage financing, neighborhood infrastructure, and streamlined development reviews.
Collaborate with local development and real estate professionals to prepare a city-wide Housing Demand Market Study every 5 years which includes analyses and recommendations related to:
- Projected demand and trends in supply;
- Special needs housing;
- Housing conditions;
- Work force housing and its associated program; and,
- Overall health of the housing market, including owner-occupied and renter-occupied.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Ensure that new publicly financed developments – those which directly use or receive public dollars – with more than 100 units or with densities greater than 10 units/acre are located where they have easy access to frequent transit service.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
We will create forces that produce housing diversity through implementation of the land use plan. Development markets are conservative in the sense that builders become familiar with a certain housing type and build to their specialization. The land use plan is built on the principle of mixing uses and densities, and greater housing variety is a beneficial outcome of this new approach. Moving the local housing industry into the new territory of mixed products and densities is a gradual process that requires the cooperation of both regulators and builders.
Implementation of the Land Use Plan will include new regulations that both allow and support a variety of housing types. In addition to permitting variety, guidelines and review procedures may be developed that require mixes of lot sizes and housing configurations in large projects. Additionally, redevelopment should be encouraged through incentives like density bonuses, fee waivers, and assistance with site preparation and infrastructure.
Major new concepts will require close consultation with the development sector.
We will create more opportunities for income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods. Greater income diversity can be achieved in a variety of ways, but one of the most effective ways is to ensure a variety of housing styles and sizes. Additionally, financing tools like direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds, and other public/private partnerships should be used to develop new or redevelop existing mixed-income projects in the urban and downtown land use typologies. The capacity of nonprofit developers like Community Development Corporations and Community Housing Development Organizations should also be expanded to provide mixed-income housing in targeted areas.
Collaborate with local development and real estate professionals to prepare a city-wide Housing Demand Market Study every 5 years which includes analyses and recommendations related to:
- Projected demand and trends in supply;
- Special needs housing;
- Housing conditions;
- Work force housing and its associated program; and,
- Overall health of the housing market, including owner-occupied and renter-occupied.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Develop design standards that incorporate ‘universal design’ principles or other design considerations that make a space easy to use for people with mobility restrictions.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
Avoid concentrations of apartment complexes. Instead, integrate multifamily units into neighborhoods with mixes of housing types or in mixed-use developments.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
Revise subdivision and zoning regulations to allow increased densities as appropriate. For example, density potential could be increased by allowing “cottage” or “pocket” neighborhoods and accessory dwelling units (additional dwelling units allowed on owner-occupied properties) where appropriate.
We will create opportunities that can increase housing for special needs populations. The need for housing that accommodates special needs populations, including the aging and people with physical or mental disabilities, is growing. Diversity in housing also includes providing environments for people who cannot fully live independently. Policies and regulations should encourage group settings and shelters in places with convenient access to transit, community facilities, daily needs, and support services. Universal design standards should be required within larger projects. Universal design involves designing spaces that can be used by the widest range of people and abilities.
We will address homelessness by applying a Continuum of Care model. Homelessness should be addressed through a two-point approach. The needs of people who are currently without homes should be met by building additional accommodations, including emergency shelter, transitional housing, and permanent supportive housing. A Continuum of Care model can identify and develop strategies adapted to Oklahoma City’s specific needs. In addition to supplying more housing, this approach prevents homelessness by including rent or mortgage assistance, housing counseling, medical or health counseling, and budget counseling.
Increase the supply of housing for residents with enhanced needs, (including but not limited to the elderly and persons with disabilities or behavioral health concerns), in locations convenient to transit, community facilities, daily needs, and appropriate supportive services.
Increase housing opportunities for the homeless or displaced, ranging from emergency shelter to transitional housing to permanent housing.
Prevent homelessness by early identification of homelessness risk factors such as recent unemployment of low-income householder, mental health challenges, or others and employ appropriate interventions such as rent or mortgage assistance, housing counseling, medical or health counseling, and budget counseling.
Develop design standards that incorporate ‘universal design’ principles or other design considerations that make a space easy to use for people with mobility restrictions.
We will institute neighborhood design guidelines and practices that build community in lower-density settings. We recognize that different people have different preferences. Many people seek new houses but still want the diversity and neighborliness of the best of established neighborhoods. Others seek the bigger lots and greater personal space offered by low-density development. But almost everyone wants an attractive living environment, a sense of belonging to a community, public space, and connection. As we move toward new standards that implement the land use plan, we should ensure that new development designs reflect patterns that create better communities. These include such items as encouraging lot clusters to maintain open space, even in low-density development; street connections for both community contact and public safety access; trail and pathway systems; and housing variety where appropriate. Planned unit developments should be used in their intended way, to encourage creative design by looking at developments in their entirety.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Change subdivision regulations to determine the number of entries into a residential development based on number of lots in order to improve connectivity of the roadway network and emergency response.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will promote redevelopment of vacant or under-used sites. Infill development on vacant, under-utilized, and brownfield sites should receive special attention through changes to land use regulations, infrastructure upgrades in target neighborhoods, incentives, favorable tax policies, expedited processing, and greater flexibility. The City recently produced a study on vacant and abandoned buildings to help address this issue and will continue to pursue implementation of the recommendations of that study.
We will encourage diversity in our neighborhoods. The City should use its housing and land use policies to encourage neighborhoods that have a diverse range of home sizes and types, and avoid concentration of low income households. Diversity builds unique and resilient neighborhoods, increases community involvement, and expands support for neighborhood schools. From an economic development point of view, housing and price-point diversity provides solid, affordable residential areas for members of the labor force at all levels of income and tends to encourage upward mobility.
We will support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative. The City should continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and consider permanent funding for the Neighborhood Stabilization Program to help reverse decline and create valuable places.
We will require good neighborhood design. Good neighborhood design can increase citizens’ access to jobs, housing, schools, and daily needs. It will also contribute to positive perceptions of neighborhoods, thereby encouraging investment.
New citywide site design and building regulations should establish basic functional requirements for features that produce good urban places. These include encouraging active transportation; integrating residential areas and activity centers; implementing good basic standards for signage, building materials, and site planning; and developing public spaces designed for desirable person to person contact.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will build housing and neighborhoods that address the needs of citizens at all stages of their lives. Oklahoma City’s citizens and their households have characteristics such as family size, income, age, and tastes that require diverse housing choices. In the past, the majority of new housing development has been single-family, detached, and owner-occupied on relatively large lots. We have also tended to separate housing by type and cost, encouraged by our zoning and subdivision ordinances. However, the private market and resident needs are moving toward greater diversification – different designs, densities, and prices, connected together into neighborhoods. Most housing is built privately, and builders, who respond to markets, cannot be forced to build certain kinds of products. City decisions should encourage both diversity and integration of housing types to the maximum degree possible. Implementing the LUTA concept will help remove statutory obstacles to projects that include diverse housing types and relate them to each other. Updated subdivision regulations will also require the street, pedestrian, and bicycle connectivity, common space, and housing variety needed to turn “pods” into communities.
Design standards can establish a baseline for quality development that respects the needs for both privacy and civic life, and incentives should reward builders and developers who innovate to build diverse, active communities.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Avoid concentrations of apartment complexes. Instead, integrate multifamily units into neighborhoods with mixes of housing types or in mixed-use developments.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
Oklahoma City's neighborhoods are vibrant because they have high occupancy rates, a diverse housing stock, and well-maintained properties.
We will establish programs for the rehabilitation or redevelopment of deteriorated structures. Vacant and abandoned properties threaten good community appearance. liveokc presents policies that address vacant buildings. When vacant properties have historic or architectural significance, preservation incentives should be especially focused on their reuse.
We will expand efforts to increase public awareness and participation in neighborhood clean-up efforts. These efforts may include training in property maintenance skills, development of volunteer programs (i.e. adopt a street), or publicizing such programs as Bulk Waste Days. Community education programs and materials should increase access to resources and knowledge, and publicize the level of property maintenance expected of citizens of Oklahoma City.
Enhance existing development standards and establish design guidelines for areas outside of the City’s existing Design Review Overlay Districts. Development standards and design guidelines could include the following provisions:
- Minimize views and prominence of parking lots in relation to structures on a site.
- Sense of proportion (street width to building height, human scale)
- Pedestrian orientation of structures and architectural detailing/fenestration
- Terminated vistas
- Reduce the predominance of residential garages in the design of the front facades of single-family residences.
- Inclusion of front porches into the design of residential structures.
- Internal orientation of parking facilities and garages in multi-family developments.
- Improved pedestrian safety and enhanced pedestrian access through parking lots.
Establish a list of preferred and discouraged building materials for all zoning districts.
Develop distinctive standards for different types and categories of walls and fences, emphasizing durability, aesthetics, and visual continuity in materials and design with particular consideration of zoning classification.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Initiate efforts to educate the public regarding programs that provide assistance for neighborhood clean-up efforts. Such efforts could include the following:
- Provide assistance to residents to make housing and neighborhood improvements and provide training in property maintenance skills.
- Develop and organize volunteer programs (such as adopt-a-street, adopt-a-park, and neighborhood clean-up days) and/or coordinate efforts to obtain grant funding to establish community clean-up programs in neighborhoods where inadequate property maintenance is prevalent.
- Publicize Bulk Waste Days and/or explore the possibility of adding more days/increased frequency.
- Develop a list of outside funding sources that could be used for property maintenance and make this information available to all citizens, especially those in targeted low-income areas.
- Establish public educational programs and advertising campaigns to discourage littering. Education should begin at the elementary level and continue through the adult level.
Intensify code enforcement in areas where specific and/or chronic violations have detrimental impacts on community appearance. Such efforts could include:
- Implement stricter enforcement of property maintenance regulations and consider more significant penalties for violations.
- Increase emphasis on the enforcement of littering laws. Impose fines against littering in a uniform and consistent manner to reinforce a public perception that littering does carry a definite risk.
- Immediately report and ensure expedient removal of graffiti that is visible from interstate highways and other important/designated viewshed corridors.
Revise ordinances for design districts and design review procedures to ensure consistency in the treatment of historic properties, including the assessment of demolition proposals, the identification of historic or significant properties, and the consideration of the impact that the alteration or demolition of individual properties has on the context and continuity of the surrounding environment.
Incorporate natural features (such as ponds, lakes, streams, rock outcroppings, stands of mature trees, and/or sizable individual trees) into the design of all residential, commercial, and industrial projects rather than eliminating, hiding, or limiting access to those features.
Establish streetscape standards requiring attractive entry features and the provision of accessible common open space in new neighborhoods.
Enhance the City’s Landscape Ordinance by accomplishing the following objectives:
- Add guidelines and recommendations for landscape design that minimizes the need for supplemental irrigation.
- Clarify responsibilities and standards for landscape maintenance, including within public rights-of-way.
- Incentivize the use of drought-tolerant and native plants.
- Restrict the use of turf grass to the greatest extent feasible.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards for parking lots and consider making revisions that would result in more landscape buffering on parking lot fringes and more internal landscaping.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards to determine whether new standards should be adopted to help screen or buffer parking structures.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards in comparison to best practices and peer cities to determine whether minimum site landscaping standards should be revised and/or restructured to result in increased landscaping.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Establish a funded beautification program and source of funding to provide facade and landscaping enhancements along targeted industrial corridors.
Establish policy or adopt ordinance language to ensure that City-owned or controlled historic buildings are appropriately recognized, maintained and repaired, or rehabilitated. Potential methods to be considered could include:
- Attach a preservation restriction or easement to historic properties that are surplused by the City.
- Assess the historic status of City-owned or controlled properties in order to follow through with formal HP/HL zoning, National Register listing, or other historic designation as appropriate.
- Incorporate early and substantive review of city improvement projects to assess potential impacts on historic buildings, and adopt alternatives that minimize or eliminate the impacts when necessary.
Improve landscape design, installation, and landscape maintenance compliance through the following actions:
- Produce informational materials and work with local media to publicize the benefits of limiting turf areas (e.g. reduced water use, less mowing) and highlight the positive effects on property values and aesthetics that result from proper installation and maintenance of landscaping.
- Develop a program, including informational outreach, to inform property owners of their responsibilities to maintain right-of-way areas, the procedures for enforcement, and the applicable fines.
- Identify specific corridors with the worst landscape maintenance conditions and initiate coordinated clean-up programs in those locations.
- Install demonstration gardens/landscapes in select civic/public locations to provide practical examples of how to integrate drought tolerant and low maintenance plants in commercial and residential installations.
- Improve efficiency and effectiveness of the process for reporting, citing, and proactive enforcement violations for maintenance and compliance with landscape requirements.
- Explore the establishment of landscape improvement/maintenance districts where property owners are assessed a pro-rata share of the costs to properly and uniformly maintain landscaping within the district boundaries.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Increase proactive code enforcement efforts, including litter control, and graffiti clean-up in targeted areas (e.g., SNI areas, and special districts).
We will enhance policing and crime prevention programs through partnerships between police and local communities. The term “community policing” has become controversial in some instances, but it is in fact a common sense approach to law enforcement that many cities and towns implement without fanfare. Police departments that practice community-based techniques recognize that police alone cannot deal with neighborhood safety and livability issues, but instead must partner with citizens, businesses, organizations, schools, churches, and others to build safe environments.
Community-based programs establish personal relationships and trust between police and residents. Some police departments describe this approach as a “value system” or even “a way of life” as opposed to a program. In Oklahoma City, effective neighborhood policing will involve greater outreach to residents and businesses, interaction with organizations, working relationships with property owners, and other cooperative efforts. A critical support element will involve direct work with at-risk youth and adequate funding for job training, education, and leadership development programs.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
We will incorporate design and maintenance practices to create safer environments in both established and new neighborhoods. Addressing the impact of the neighborhood environment on public safety will follow two tracks: 1) reviewing new projects (including subdivisions and major new developments) and incorporating safe environmental design standards into their design, and 2) auditing existing neighborhoods for unsafe conditions and correcting problem areas.
Safety evaluation of new projects will start with developing design standards and guidelines, using the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design as a starting point. Our public safety departments should develop specific areas of expertise in these principles and be fully integrated into the City’s project review and approval process.
Established neighborhoods present different challenges. Partnerships between City staff and community organizations will analyze the neighborhood environment and local crime patterns to identify and correct specific problems. The most common issues include overgrown lots, hidden spaces, and vacant and deteriorated buildings. We must be aggressive in such areas as vegetation control and demolition of buildings beyond feasible repair.
Response times when emergencies occur are also an important factor in the interaction between public safety and environmental design. Neighborhood designs should increase the efficiency of public safety operations and ensure that the greatest number of residents can be reached in the shortest amount of time by emergency responders. This should include strategic improvements in existing neighborhoods and efficient design in new neighborhoods.
Systematic evaluation and correction of design aspects of new projects and inherently unsafe environments in established areas will be necessary to ensure a safe environment for all residents of Oklahoma City.
We will correct unsafe building elements and design conditions in public facilities and outdoor spaces. The City should lead in providing safe and secure facilities and properties. This is especially important in distressed neighborhoods, where a public park or center may be seen as a refuge. All publicly accessed properties should be assessed for unsafe conditions, including but not limited to poor lighting, blind spots, and maintenance hazards. Once this inventory has been completed, priorities for repair should be set and incorporated into the capital program.
Graffiti and vandalism in public areas are special and persistent problems. Uncorrected incidents suggest neglect in a neighborhood, which in turn encourages both more vandalism and serious criminal activity. Graffiti can be controlled through an aggressive removal policy, best accomplished in partnership with neighborhood residents. Cooperative action for productive purposes has the secondary benefit of building a sense of neighborhood effectiveness and establishing credibility for improvement efforts all of which help reconstruct the social fabric.
Improve the functionality and efficiency of the street network by:
- Providing direct connections from residential developments to nearby places and to each other.
- Providing street and sidewalk stubs to adjacent vacant land in anticipation of future development.
- Connecting new development to existing street and sidewalk stubs, and to existing trail, open space, and bicycle networks.
- Reducing block sizes and use of dead-end streets.
- Maintaining the existing street grid to preserve connectivity and mobility options.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Evaluate public facilities and public property for unsafe conditions such as poor lighting (quality and quantity); blind spots; poor maintenance conditions; and other unsafe conditions. Prioritize improvements to these facilities and properties based on the following criteria: a) Proximity and condition of nearby neighborhoods; and b) Cost/benefit associated with mitigating the unsafe condition and maintaining the improvement.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Utilize existing natural streams as amenities in public parks, and regularly monitor and maintain stream banks for safety of park users.
Revise subdivision regulations to require development adjacent to parks and public open spaces to maintain open sight lines to parks and public open space. Reduce/limit residential rear yards, fences, walls, and physical and visual enclosures around park and public open space perimeters. Encourage designs that allow homes to face into parks or where side yards are located near parks.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will establish partnerships between the City and school districts to assist in non-educational functions. School districts deal with a variety of non-educational or indirectly educational functions on a regular basis. This includes siting of new schools, redeveloping closed schools, addressing crime and crime prevention, and other community outreach functions. By working together, funding should be leveraged and resources used efficiently to strengthen neighborhoods, making them viable choices for young households.
We will co-locate new public projects in coordination with local school districts. Strong civic institutions strengthen neighborhood identify, social interaction and appeal to investors. Co-locating public projects such as libraries, fire stations, parks, recreation centers, and schools create neighborhood activity centers and realize efficiencies through joint use arrangements.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
We will create public/private partnerships that fill critical demands like workforce housing that are not normally satisfied by the private market. The Housing Market Preference and Demand Study defined housing preferences for different age and income groups, including residential types and locations. This information provides valuable guidance to city agencies, community organizations, builders, and developers that can help all parties make policy and business decisions. However, these data rapidly become outdated. Regular updates, funded by a mutually beneficial partnership of public and private sectors, can ensure that this information remains relevant and useful.
But information must be put to use. The 2013 housing study identified a major demand for “workforce” housing – equity and rental units affordable to people in a range from 60% to 120% of the citywide median household income. The normal private market has difficulty producing housing for much of this income range because of perceived risk and small profit. Partnerships between the public, private, and nonprofit sectors, including employers, can develop programs that remove obstacles to workforce housing production and marketing. Options include site acquisition, landbanking, interim financing, appraisals, mortgage financing, neighborhood infrastructure, and streamlined development reviews.
Collaborate with local development and real estate professionals to prepare a city-wide Housing Demand Market Study every 5 years which includes analyses and recommendations related to:
- Projected demand and trends in supply;
- Special needs housing;
- Housing conditions;
- Work force housing and its associated program; and,
- Overall health of the housing market, including owner-occupied and renter-occupied.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Ensure that new publicly financed developments – those which directly use or receive public dollars – with more than 100 units or with densities greater than 10 units/acre are located where they have easy access to frequent transit service.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
We will create forces that produce housing diversity through implementation of the land use plan. Development markets are conservative in the sense that builders become familiar with a certain housing type and build to their specialization. The land use plan is built on the principle of mixing uses and densities, and greater housing variety is a beneficial outcome of this new approach. Moving the local housing industry into the new territory of mixed products and densities is a gradual process that requires the cooperation of both regulators and builders.
Implementation of the Land Use Plan will include new regulations that both allow and support a variety of housing types. In addition to permitting variety, guidelines and review procedures may be developed that require mixes of lot sizes and housing configurations in large projects. Additionally, redevelopment should be encouraged through incentives like density bonuses, fee waivers, and assistance with site preparation and infrastructure.
Major new concepts will require close consultation with the development sector.
We will create more opportunities for income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods. Greater income diversity can be achieved in a variety of ways, but one of the most effective ways is to ensure a variety of housing styles and sizes. Additionally, financing tools like direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds, and other public/private partnerships should be used to develop new or redevelop existing mixed-income projects in the urban and downtown land use typologies. The capacity of nonprofit developers like Community Development Corporations and Community Housing Development Organizations should also be expanded to provide mixed-income housing in targeted areas.
Collaborate with local development and real estate professionals to prepare a city-wide Housing Demand Market Study every 5 years which includes analyses and recommendations related to:
- Projected demand and trends in supply;
- Special needs housing;
- Housing conditions;
- Work force housing and its associated program; and,
- Overall health of the housing market, including owner-occupied and renter-occupied.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Develop design standards that incorporate ‘universal design’ principles or other design considerations that make a space easy to use for people with mobility restrictions.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
Avoid concentrations of apartment complexes. Instead, integrate multifamily units into neighborhoods with mixes of housing types or in mixed-use developments.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
Revise subdivision and zoning regulations to allow increased densities as appropriate. For example, density potential could be increased by allowing “cottage” or “pocket” neighborhoods and accessory dwelling units (additional dwelling units allowed on owner-occupied properties) where appropriate.
We will create opportunities that can increase housing for special needs populations. The need for housing that accommodates special needs populations, including the aging and people with physical or mental disabilities, is growing. Diversity in housing also includes providing environments for people who cannot fully live independently. Policies and regulations should encourage group settings and shelters in places with convenient access to transit, community facilities, daily needs, and support services. Universal design standards should be required within larger projects. Universal design involves designing spaces that can be used by the widest range of people and abilities.
We will address homelessness by applying a Continuum of Care model. Homelessness should be addressed through a two-point approach. The needs of people who are currently without homes should be met by building additional accommodations, including emergency shelter, transitional housing, and permanent supportive housing. A Continuum of Care model can identify and develop strategies adapted to Oklahoma City’s specific needs. In addition to supplying more housing, this approach prevents homelessness by including rent or mortgage assistance, housing counseling, medical or health counseling, and budget counseling.
Increase the supply of housing for residents with enhanced needs, (including but not limited to the elderly and persons with disabilities or behavioral health concerns), in locations convenient to transit, community facilities, daily needs, and appropriate supportive services.
Increase housing opportunities for the homeless or displaced, ranging from emergency shelter to transitional housing to permanent housing.
Prevent homelessness by early identification of homelessness risk factors such as recent unemployment of low-income householder, mental health challenges, or others and employ appropriate interventions such as rent or mortgage assistance, housing counseling, medical or health counseling, and budget counseling.
Develop design standards that incorporate ‘universal design’ principles or other design considerations that make a space easy to use for people with mobility restrictions.
We will set neighborhood development priorities by using quantitative evaluation criteria. Available resources are never sufficient to address the problems of struggling neighborhoods. Setting priorities and policy focuses can be addressed by an evaluative process that considers such factors as economic opportunities, educational performance, housing quality, access to commercial and other support services, public safety, and presence of community organizations and institutions. The process should consider positive neighborhood factors that can create the foundations for success, including:
- Existing support capacity from neighborhood associations, local service providers, and area businesses;
- Community institutions like parks, schools, churches, or community centers; and,
- Connections to surrounding neighborhoods.
We will expand rehabilitation and redevelopment programs to stabilize the physical fabric of neighborhoods. The physical condition of a neighborhood and its buildings is critical to its ability to function as a community. Residential rehabilitation programs should be expanded to both meet the needs of existing residents and serve future generations. Rehabilitation should focus items that directly affect health and safety, secure the basic building envelope, and add economic value to the surrounding area. Programs in which community development corporations acquire, rehabilitate, and either sell or rent units on a “turnkey” basis at moderate costs have been particularly effective in adding value, preserving housing, and introducing new owners and potential leaders into a neighborhood.
But housing rehabilitation is only part of the picture. Vacant sites and dilapidated buildings depress both property values and community momentum. Programs to accelerate the redevelopment of dilapidated properties should be tied closely to the priority evaluation process. Funds should be targeted to areas and projects that create a critical mass that in turn catalyzes private market investment and creates a self-sustaining community. Mechanisms like landbanks and land trusts have also proven effective in gaining control over vacant properties and returning them to productive use. Often, a high priority or visibility project at a strategic location can produce an unexpectedly powerful private reaction as neighbors gain confidence in their future.
We will create, enhance, and maintain community spaces where residents interact positively and advance the social fabric. Successful neighborhoods include spaces where people see and greet each other, and work and play together in a common enterprise. These spaces open a neighborhood, and increase the level of positive interaction that is the essence of a living neighborhood. Yet, hidden or neglected public spaces have the opposite effect, attracting nuisances and sometimes crime, and being scary or off-putting places that people avoid. Good community spaces can take many forms – a well-maintained public park surrounded and watched over by residents; a community garden; the median of a parkway; or a school or community center site.
Strengthening these community places begins with inventorying and analyzing their operations. This can be done in cooperation with neighbors and community organizations. Volunteer work, business participation, and other public and private support can provide the means to reclaim existing spaces and develop new ones, and to provide adequate resources for continued support and maintenance.
Facilities like community gardens and groceries are particularly attractive as community spaces because they are self-supporting; become natural and productive attractors of people, and address other key concerns such as access to healthy food. Efforts at a neighborhood level to secure sites and organize gardens should be expanded and educational institutions should provide technical help to gardeners. Public development incentives should have a special focus on attracting grocery stores to skipped over areas with viable consumer markets, and should encourage inclusion of public space in project design.
We will coordinate public infrastructure projects and community revitalization. In an effort to create tangible catalysts for revitalizing urban communities, the City will use the analysis described in this section as well as those located throughout planokc, to inform its capital improvements program.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Prioritize neighborhoods for revitalization and re-investment in order to reverse the decline associated with poor maintenance of public infrastructure and other property by using the following objective criteria:
- Low economic opportunity;
- Low educational attainment;
- Poor health outcomes;
- Poor housing environments;
- Low neighborhood quality; and,
- Existing capacity to support the revitalization efforts; and other important indicators.
Increase the City’s capacity to participate in targeted programs that strengthen neighborhood infrastructure and other assets.
Increase and/or re-assign City staff to support targeted neighborhoods and coalitions.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
We will institute neighborhood design guidelines and practices that build community in lower-density settings. We recognize that different people have different preferences. Many people seek new houses but still want the diversity and neighborliness of the best of established neighborhoods. Others seek the bigger lots and greater personal space offered by low-density development. But almost everyone wants an attractive living environment, a sense of belonging to a community, public space, and connection. As we move toward new standards that implement the land use plan, we should ensure that new development designs reflect patterns that create better communities. These include such items as encouraging lot clusters to maintain open space, even in low-density development; street connections for both community contact and public safety access; trail and pathway systems; and housing variety where appropriate. Planned unit developments should be used in their intended way, to encourage creative design by looking at developments in their entirety.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Change subdivision regulations to determine the number of entries into a residential development based on number of lots in order to improve connectivity of the roadway network and emergency response.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will promote redevelopment of vacant or under-used sites. Infill development on vacant, under-utilized, and brownfield sites should receive special attention through changes to land use regulations, infrastructure upgrades in target neighborhoods, incentives, favorable tax policies, expedited processing, and greater flexibility. The City recently produced a study on vacant and abandoned buildings to help address this issue and will continue to pursue implementation of the recommendations of that study.
We will encourage diversity in our neighborhoods. The City should use its housing and land use policies to encourage neighborhoods that have a diverse range of home sizes and types, and avoid concentration of low income households. Diversity builds unique and resilient neighborhoods, increases community involvement, and expands support for neighborhood schools. From an economic development point of view, housing and price-point diversity provides solid, affordable residential areas for members of the labor force at all levels of income and tends to encourage upward mobility.
We will support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative. The City should continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and consider permanent funding for the Neighborhood Stabilization Program to help reverse decline and create valuable places.
We will require good neighborhood design. Good neighborhood design can increase citizens’ access to jobs, housing, schools, and daily needs. It will also contribute to positive perceptions of neighborhoods, thereby encouraging investment.
New citywide site design and building regulations should establish basic functional requirements for features that produce good urban places. These include encouraging active transportation; integrating residential areas and activity centers; implementing good basic standards for signage, building materials, and site planning; and developing public spaces designed for desirable person to person contact.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will develop and implement new land development regulations that support the Land Use Typology Area system of integrated uses and greater flexibility and efficiency. Our current development ordinances date from a time when we valued low density and separation of different land uses higher than city life. The fact that low density increases the cost of services and infrastructure gives us pause. That, combined with our successes at building places that people want to experience has moved us in new directions. The zoning code, which divides the city into 26 single-use “base” districts, 7 special districts, and 16 overlay districts, discourages the trends toward new development forms. We must modernize these codes to implement the LUTA concept and provide both the flexibility and protection that benefit contemporary developers and their neighbors alike.
Despite its large number of specific districts, our zoning ordinance does not provide adequate protections for neighborhoods or guarantees to approving agencies on actual performance or design of projects. This forces the Planning Commission and City Council to use Planned Unit Developments (PUDs), tying developers to a specific project and building design. PUDs are actually intended for a different purpose – to encourage innovative, comprehensively planned developments– and are overly rigid when applied to more routine projects.
Revisions to Oklahoma City’s land development regulations could move in several directions, from modifying existing zoning districts with new performance and design standards to establishing a new structure that uses the Land Use Typology Areas as the basic development districts for the city. The LUTAs, as presented in Chapter Two, permit a variety of uses, but establish permitted ranges of development intensity. The LUTA system achieves compatibility between different types or intensities of uses by implementing performance standards, design guidelines, and transitional methods. These techniques give specific and predictable guidance to builders and developers, and address such areas as operating effects, traffic, parking, design, scale, and safety, avoiding the unnecessary overuse of PUDs. A LUTA-based system would incorporate the criteria for locations and supporting transportation and infrastructure established by this plan for individual land uses.
We will execute a smooth transition between the existing zoning code and new land development ordinances. Development ordinances are complicated and difficult to change because people have become accustomed to them, rough spots and all. Migrating to an alternative concept will take time and care. In the meantime, the City will evaluate using a hybrid approach, mixing the existing zoning districts with the LUTA/mixed use concept. One way of accomplishing this is to group the zoning districts that are consistent with the intensity and use ranges of LUTAs, and apply compatibility policies and design standards to developments within them. The existing zoning ordinance could then be modified to include these compatibility standards. New rezoning requests would be evaluated for consistency with the LUTA in which they are located. If the new project is adjacent to a different land use, the compatibility policies and standards would apply to the design of that project.
Coordinate the design, development, expansion, and/or investment in transportation projects with the Land Use Typology map.
Require the construction of new streets, streetscapes, and street widening projects to implement the design components of the assigned street typologies established in this plan.
Revise Subdivision Regulations and development standards to reflect the street typology standards.
Routinely assess the City’s development standards, design guidelines, and development review procedures to ensure that they reflect current trends in best-practice and allow for innovative design techniques and evolving methods in low-impact development.
Enhance existing development standards and establish design guidelines for areas outside of the City’s existing Design Review Overlay Districts. Development standards and design guidelines could include the following provisions:
- Minimize views and prominence of parking lots in relation to structures on a site.
- Sense of proportion (street width to building height, human scale)
- Pedestrian orientation of structures and architectural detailing/fenestration
- Terminated vistas
- Reduce the predominance of residential garages in the design of the front facades of single-family residences.
- Inclusion of front porches into the design of residential structures.
- Internal orientation of parking facilities and garages in multi-family developments.
- Improved pedestrian safety and enhanced pedestrian access through parking lots.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration and mixing of land uses in urban areas.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
In order to promote compatibility between different uses, establish standards and guidelines that ensure all developments are pedestrian-friendly and human scale at street frontages and property lines.
Prioritize and concentrate development where facilities, infrastructure, and services have capacity and in areas where the Police and Fire Departments are best able to respond. Guide the location and timing of development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure.
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Ensure the ongoing compatibility and appropriateness of development in Planned Unit Developments (PUDs) and Simplified Planned Unit Developments (SPUDs) by:
- Exploring the establishment of expiration dates for PUDs and SPUDs that have not been initiated after a certain period of time;
- Establish a procedure to ensure PUDs build-out according to approved plans.
Enable increased densities as appropriate to individual land use typology areas by addressing financial incentives and disincentives through evaluating the feasibility of strategies such as:
- Impact fees and/or transportation utility fees that vary by district according to actual cost;
- Assessing solid waste charges according to actual cost;
- Private solid waste services where it is impractical for the City to provide service such as in rural areas.
Encourage unified planning for all adjoining land owned or controlled by a project’s developer to ensure proper circulation and land use relationships.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
Revise subdivision and zoning regulations to allow increased densities as appropriate. For example, density potential could be increased by allowing “cottage” or “pocket” neighborhoods and accessory dwelling units (additional dwelling units allowed on owner-occupied properties) where appropriate.
We will provide incentives and investments that produce a favorable environment for private investment on underutilized sites. In Oklahoma City, we have tended to view land as an inexhaustible and disposable resource, reducing the desirability of older areas and decreasing land values, while expanding the city’s boundaries outward. The surveys and process of planokc show that this view is also changing, as citizens place a high value on using existing infrastructure and urban land effectively and rebuilding established neighborhoods. Preferences are also changing, as many families appreciate active urban places like Midtown and Automobile Alley that provide living, shopping, entertainment, and work places with good walking, bike, and transit access. Effective use of existing land resources is a central principle of Chapter Two’s land use vision.
Redevelopment and infill depend on major private investment. City policy and action can create the conditions that help this private investment occur.
Directions for these policies include:
- Site assembly. Multiple property owners, often absent or very difficult to find, can make it impossible to put together sites for redevelopment. The City can help private developers by helping them assemble sites.
- Infrastructure and street improvement. While redevelopment and infill sites usually have infrastructure, these facilities are sometime obsolete and require improvement. Redevelopment can provide the impetus for making necessary public investments in these assets.
- Public investments. Parks, schools, civic facilities, pedestrian and bicycle facilities, streetscapes, and other amenities can provide anchors that are proven to generate private development. The Bricktown Canal is an excellent example of a public amenity that has paid for itself many times over in private investment. Similarly, the new MAPS 3 Park will inevitably become the catalyst for the Core to Shore redevelopment.
- Code improvement and proactive enforcement. Poor property maintenance, unattractive and cluttered signs, and public or operating nuisances can degrade the value of surrounding property and discourage reinvestment. Updated ordinances and consistent, enforcement will minimize these disincentives and create momentum for new private development.
Establish new incentives and raise awareness of existing incentives that stimulate the preservation and rehabilitation of historic resources. Incentives could include:
- Preservation easements, low-interest or forgivable rehabilitation loans, and Tax Increment Financing Districts for historic buildings, sites, and districts.
- Tools and practices for public/private partnerships to ensure the preservation and retention of top-priority historic resources whose deterioration or demolition would present an irreparable and highly significant loss to the City and beyond.
- Existing city, state, and federal tools and incentives for rehabilitation, including state and federal tax credits for certified rehabilitation.
- Expedited review process for projects involving infill sites.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
Prioritize and concentrate development where facilities, infrastructure, and services have capacity and in areas where the Police and Fire Departments are best able to respond. Guide the location and timing of development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Citizens have easy access to a variety of affordable healthy food options.
We will establish an awareness of agriculture in and around the city as important to both food security and open space preservation. We tend to think of farming around cities as a temporary use that disappears when development takes over. Yet our city includes rural land that is likely to remain in agricultural use. This gives us the unique ability to integrate farming into the structure of the city. We can build public awareness and appreciation of agriculture’s environmental, economic, open space, and food security benefits and provide assistance to farmers that address the challenges of agriculture within the corporate limits of a big city.
We will maintain the ability of agricultural operations to exist and thrive at different scales, from large farms to small urban gardens. Land use policies should support and encourage farming and gardening activities in rural parts of Oklahoma City and on small parcels in the city. The directions and policies contained in the Land Use Plan and the sustainokc element cluster rural residential development and discourage the spread of very low-density residential acreages into agricultural areas, preserving the integrity of farms. Similarly, we should discourage conversion of land designated as Prime Farmland to non-agricultural use, and ensure that these uses support agriculture and reinforce the rural quality of the landscape. Within the city, we should encourage use of vacant or underused sites for raising food, at least on a temporary basis, and identify sites where more permanent urban gardens may be established on civic land.
We will maximize healthy food options for all neighborhoods and citizens. We cannot require people to eat certain kinds of foods or restrict access to the wide range of items that the food industry produces. However, people should not be forced into unhealthy diets by gaps in the food supply system or lack of knowledge. Our strategies addressing the food system should follow two paths. On the supply side, we should increase the number of places that provide affordable healthy food options in under-served neighborhoods. On the demand side, we should increase awareness and knowledge of citizens about diet, health, and practical ways that they can incorporate healthy eating habits into their routine.
A HEALTHY FOOD AWARENESS CAMPAIGN
An effective and far-reaching campaign that introduces people to the benefits of healthy eating and makes healthy food options available and affordable to all can help develop a market that the private and community sectors can economically satisfy. Elements of this campaign may include:
- Strategies for selection and preparation of healthy food that is cost-and time-competitive with manufactured food.
- Selecting and preparing nutritious food for use in schools, recreation centers, senior centers, technical/trade schools, farmers markets, and anywhere people might go to learn.
- Linking training for unemployed people and welfare-to-work programs with opportunities for living wage jobs in urban food-related businesses.
- “Edible Schoolyards”, a school-based program that integrates nutrition and gardening to connect healthy food choices and locally grown fresh produce.
- Farm-to-school programs.
- Farm-to-institution programs that offer healthy food choices to hospitals, universities, prisons, and businesses.
Establish development regulations to help protect Oklahoma City’s water resources through standards that:
- Require buffers, setbacks, and vegetation conservation requirements to protect riparian and littoral zones and filter waterborne pollutants from development activities and storm water runoff. Buffer widths should be based on water quality function and wildlife habitat needs.
- Encourage natural drainage systems and methods for onsite infiltration and onsite sediment retention.
- Require new developments to maintain or decrease the site’s pre-development runoff rate.
- Allow low-impact development design features such as pervious pavement, rain gardens, landscaped parkways, and alternative curbing designs.
- Reduce the amount of impervious surfaces allowed in buffer zones around Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
- Restore watershed features such as forest, wetlands, and natural stream channels.
Raise the level of public awareness of agriculture’s value to ecology, economy, open space, culture, and local food security by the following actions:
- Organize training activities in a variety of settings (schools, colleges, health care facilities, continuing education programs) that demonstrate the history, importance and value of agricultural operations.
- Improve the knowledge of current growers and motivate potential new growers.
- Promote incentives offered by governments, banks, land-grant universities, and private businesses such as start-up capital, credit, crop insurance, horticultural and financial advice, soil testing, markets, subsidies, tools, and inputs such as seeds and soil alterations.
- Promote farms as a destination stop for tourists and visitors.
Revise city codes and ordinances to allow urban agricultural operations and sales, including the following provisions:
- Define types of urban agriculture.
- Allow urban agriculture types in appropriate zoning districts.
- Establish standards for operations within different zoning districts.
- Allow a variety of retail options for locally grown produce.
Protect the ability of agricultural operations to exist and thrive at different scales, from large farms to small urban gardens through the following actions:
- Protect land suitable for agriculture by maintaining parcels large enough to sustain agricultural production, and discourage conversion of existing agricultural lands to non-agricultural uses.
- Encourage dwellings and other non-agricultural development to be ancillary to and compatible with agricultural uses. Such uses should be limited in size and grouped together to minimize disturbance to agricultural production.
- Create incentives to protect soils designated as Prime Farmland by the U.S. Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS).
- Facilitate the use of vacant and under-used urban lands for raising food.
- Identify public lands in urban parks, and around municipal buildings, schools, public housing, hospitals, and other civic spaces, that may be used for food production with plantings of fruit trees, edible landscaping, and vegetable gardens.
Promote local and urban agricultural operations by establishing programs and partnerships to:
- Lease publicly-owned land to farmers for sustainable urban agricultural use.
- Encourage land tenure methods such as land trusts, leases, and policy initiatives to secure long-term commitment for community gardens, entrepreneurial farms, and other urban agriculture ventures.
- Develop community-based farming infrastructure such as tool banks with equipment and supplies, community kitchens and other shared processing facilities, farmers’ markets, community supported agriculture projects, funding opportunities, and technical service providers.
- Construct and operate a demonstration urban farm for education, outreach, and local food production.
- Encourage the local agricultural economy and improve access to local foods by allowing city property (parks, city facilities, etc.) to be used for farmers markets and other public markets.
Strengthen the local food system and increase access to healthy food options using strategies such as:
- Increasing the effectiveness of community gardens, especially in underserved areas.
- Reducing access to low nutrition food (e.g. junk food, fast food).
- Preserving agricultural lands for purposes of producing food, fiber, and fuel.
- Participating in a local or regional food policy council.
- Develop an incentive program that will assist convenience stores with providing fresh fruits, vegetables, and other healthy food items.
- Develop a land bank to convert tax-reverted, vacant, and abandoned properties into community gardens or “satellite farms.”
- Prioritize underserved areas when locating new grocery stores, farmer’s markets, and mobile grocers. Use financial incentives, technical assistance, and other services to improve the quality and selection of healthy foods available to underserved areas.
Create a Healthy Food Awareness campaign that includes:
- Strategies for selection and preparation of healthy food that is cost- and time- competitive with manufactured food.
- A uniform curriculum associated with selecting and preparing nutritious food for use in schools, recreation centers, senior centers, technical/trade schools, farmers markets, and anywhere people might go to learn.
- Strategies to link training for unemployed people and welfare-to-work work programs with opportunities for living wage jobs in urban food-related businesses.
- “Edible Schoolyards”, a school-based program which integrates nutrition and gardening to raise awareness about the connection between healthy food choices and locally grown fresh produce.
- Expansion of farm-to-school programs.
- Farm-to-institution programs that offer healthy food choices to hospitals, universities, prisons, and businesses.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
We will set neighborhood development priorities by using quantitative evaluation criteria. Available resources are never sufficient to address the problems of struggling neighborhoods. Setting priorities and policy focuses can be addressed by an evaluative process that considers such factors as economic opportunities, educational performance, housing quality, access to commercial and other support services, public safety, and presence of community organizations and institutions. The process should consider positive neighborhood factors that can create the foundations for success, including:
- Existing support capacity from neighborhood associations, local service providers, and area businesses;
- Community institutions like parks, schools, churches, or community centers; and,
- Connections to surrounding neighborhoods.
We will expand rehabilitation and redevelopment programs to stabilize the physical fabric of neighborhoods. The physical condition of a neighborhood and its buildings is critical to its ability to function as a community. Residential rehabilitation programs should be expanded to both meet the needs of existing residents and serve future generations. Rehabilitation should focus items that directly affect health and safety, secure the basic building envelope, and add economic value to the surrounding area. Programs in which community development corporations acquire, rehabilitate, and either sell or rent units on a “turnkey” basis at moderate costs have been particularly effective in adding value, preserving housing, and introducing new owners and potential leaders into a neighborhood.
But housing rehabilitation is only part of the picture. Vacant sites and dilapidated buildings depress both property values and community momentum. Programs to accelerate the redevelopment of dilapidated properties should be tied closely to the priority evaluation process. Funds should be targeted to areas and projects that create a critical mass that in turn catalyzes private market investment and creates a self-sustaining community. Mechanisms like landbanks and land trusts have also proven effective in gaining control over vacant properties and returning them to productive use. Often, a high priority or visibility project at a strategic location can produce an unexpectedly powerful private reaction as neighbors gain confidence in their future.
We will create, enhance, and maintain community spaces where residents interact positively and advance the social fabric. Successful neighborhoods include spaces where people see and greet each other, and work and play together in a common enterprise. These spaces open a neighborhood, and increase the level of positive interaction that is the essence of a living neighborhood. Yet, hidden or neglected public spaces have the opposite effect, attracting nuisances and sometimes crime, and being scary or off-putting places that people avoid. Good community spaces can take many forms – a well-maintained public park surrounded and watched over by residents; a community garden; the median of a parkway; or a school or community center site.
Strengthening these community places begins with inventorying and analyzing their operations. This can be done in cooperation with neighbors and community organizations. Volunteer work, business participation, and other public and private support can provide the means to reclaim existing spaces and develop new ones, and to provide adequate resources for continued support and maintenance.
Facilities like community gardens and groceries are particularly attractive as community spaces because they are self-supporting; become natural and productive attractors of people, and address other key concerns such as access to healthy food. Efforts at a neighborhood level to secure sites and organize gardens should be expanded and educational institutions should provide technical help to gardeners. Public development incentives should have a special focus on attracting grocery stores to skipped over areas with viable consumer markets, and should encourage inclusion of public space in project design.
We will coordinate public infrastructure projects and community revitalization. In an effort to create tangible catalysts for revitalizing urban communities, the City will use the analysis described in this section as well as those located throughout planokc, to inform its capital improvements program.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Prioritize neighborhoods for revitalization and re-investment in order to reverse the decline associated with poor maintenance of public infrastructure and other property by using the following objective criteria:
- Low economic opportunity;
- Low educational attainment;
- Poor health outcomes;
- Poor housing environments;
- Low neighborhood quality; and,
- Existing capacity to support the revitalization efforts; and other important indicators.
Increase the City’s capacity to participate in targeted programs that strengthen neighborhood infrastructure and other assets.
Increase and/or re-assign City staff to support targeted neighborhoods and coalitions.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
We will institute neighborhood design guidelines and practices that build community in lower-density settings. We recognize that different people have different preferences. Many people seek new houses but still want the diversity and neighborliness of the best of established neighborhoods. Others seek the bigger lots and greater personal space offered by low-density development. But almost everyone wants an attractive living environment, a sense of belonging to a community, public space, and connection. As we move toward new standards that implement the land use plan, we should ensure that new development designs reflect patterns that create better communities. These include such items as encouraging lot clusters to maintain open space, even in low-density development; street connections for both community contact and public safety access; trail and pathway systems; and housing variety where appropriate. Planned unit developments should be used in their intended way, to encourage creative design by looking at developments in their entirety.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Change subdivision regulations to determine the number of entries into a residential development based on number of lots in order to improve connectivity of the roadway network and emergency response.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
Citizens have access to a variety of transportation choices to serve their daily needs.
We will ensure that street improvements and expansions to the network serve the development vision of planokc. The Land Use Plan, the foundation of planokc, is based on efficient use of land resources, and incremental, market-based extensions of urban development. Road construction projects in undeveloped areas can have the opposite effect by encouraging decentralized development. Both city and regional road plans should reinforce the vision of efficiency by focusing on enhancing the existing network, addressing areas of congestion and poor operation, increasing network connectivity and route choice, and using new street extensions to guide development in desirable directions.
We will implement the street typology concept. The street typologies combine the function and context of streets to produce design standards. Our subdivision ordinances and design practices should be amended to be consistent with these standards. Different land uses and intensities of development also require streets with the ability to handle the traffic they generate. Therefore, new development should be located on streets of appropriate type and capacity, or include measures necessary to supply the required capacity.
Coordinate the design, development, expansion, and/or investment in transportation projects with the Land Use Typology map.
Require traffic impact analyses with all comprehensive plan amendments requests to change to a higher intensity LUTA.
Require the construction of new streets, streetscapes, and street widening projects to implement the design components of the assigned street typologies established in this plan.
Share parking among contiguous developments.
Revise Subdivision Regulations and development standards to reflect the street typology standards.
Identify and prioritize freight infrastructure projects that are needed to maintain mobility and enhance the city’s (and region’s) economic competitiveness.
Undertake targeted parking studies to determine existing parking capacity and develop appropriate parking standards based on land use, location, and demand.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Maintain historical lot and block sizes where possible and appropriate.
Assess the need for additional funds for citywide road maintenance beyond past average annual expenditures. If additional funds are needed for street maintenance, explore the feasibility of:
- Implementing a transportation utility fee; or
- Increasing the proportion of G.O. Bond money spent on street maintenance over past levels.
We will incorporate all appropriate forms of transportation into major street and land use corridors. Major corridors provide access to important community destinations, including shopping centers, civic institutions, and employment centers. Multi-modal corridors do not require every form of transportation on every major street. Rather, the corridor taken broadly provides access for all modes of transportation to destinations along the way. For example, service roads, local streets, trails, or other paths parallel to arterials can accommodate local transit, pedestrians, and bicyclists comfortably. The concept of multi-modal corridors also requires that projects that change or expand the motor vehicle capacity of major streets and roads accommodate transit and active modes in the final design and during the construction process.
Set level of service goals and adopt standards to improve the performance of pedestrian, bicycle, and transit facilities. Emphasize pedestrian, bicycle and transit infrastructure in street widening designs.
Require the construction of new streets, streetscapes, and street widening projects to implement the design components of the assigned street typologies established in this plan.
When approving projects that improve the level of service for vehicular traffic, ensure they do not negatively impact the walkability or bikeability of the area.
Locate, design and upgrade City facilities and infrastructure in a manner that supports neighborhood revitalization and redevelopment.
We will develop facilities that encourage people to use other means of transportation to travel to transit stops and stations. The traditional service area around a transit route is a 1/4 mile walking distance. We should maintain clear and continuous pedestrian routes within that service area to transit stops or stations. Safe, comfortable, and attractive shelters and waiting areas should be located at strategic points along routes. Providing features that encourage people to bike or drive to stops and stations can extend these service areas and increase the number of potential riders. These features can include:
- Connections from trails to transit stops.
- Bike parking, lockers, and potentially rental stations at major transit stops and hubs.
- Park and ride facilities such as lots and structures, integrated into transit-oriented developments or at appropriate commuter sites.
Develop design standards for bus stops and transit stations that consider location, make connections to sidewalks and bicycle routes/trails, and provide safe, comfortable, and attractive waiting areas for riders.
Locate, design and upgrade City facilities and infrastructure in a manner that supports neighborhood revitalization and redevelopment.
We will incorporate transit access into street design standards and projects on appropriate corridors. As streets that carry transit routes are improved or modified, their design should include features that specifically encourage amenities, pedestrian access, and smoother operations. These features may include enhanced pedestrian access and street crossings at transit stops; signal cycles that give pedestrians time to cross streets; space for shelters; signal controls; and reserved lanes or “JUMP” lanes for bus rapid transit. In addition, street typology standards that include transit-friendly features should be implemented.
We will implement standards that provide good transit access and user connections to major projects on transit routes. The length and nature of the path between a transit stop and the entrance to a major destination determines whether a project really has adequate transit service. For example, a stop should not require people to find their way across a large parking lot to enter the development. New design standards for large projects with transit potential should provide safe and comfortable links from the transit stop, or provide routes into the project for transit use.
Revise development standards to require sidewalks and transit stops along existing and planned transit routes.
Develop design standards for bus stops and transit stations that consider location, make connections to sidewalks and bicycle routes/trails, and provide safe, comfortable, and attractive waiting areas for riders.
Ensure that new publicly financed developments – those which directly use or receive public dollars – with more than 100 units or with densities greater than 10 units/acre are located where they have easy access to frequent transit service.
We will design and implement a bicycle route system based on getting people to priority destinations. The current Bicycle Transportation Plan provides a two-phased network of potential bike routes. This network is based on evaluating various streets for bicycle suitability, and provides a solid foundation for implementation. The system should now be refined by considering destinations and designing routes that assemble on-street segments and trails into an entire network that serves multiple destinations.
We will incorporate appropriate support features such as bike parking and wayfinding signage into the system. On and off-street facilities function best with relatively inexpensive support facilities like parking and information graphics. Zoning ordinances and cost-sharing programs can both require, and encourage through incentives, bike parking for appropriate land uses, like major commercial, multi-family, and mixed use development. Desirable city actions include installing bike parking in public parking structures and business districts and encouraging bike “corrals” in which one parking space is dedicated to bike parking in neighborhood business districts.
Identify areas that could be used to establish a greenbelt network throughout the City that connect major employment centers, commercial sites, parks, and key locations within major residential neighborhoods. Use the greenbelt as the backbone for a bicycle trails network which all other bicycle trails feed into.
Create and implement a citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan that addresses riders of all levels.
Require the placement of secure, properly positioned bicycle parking within multi-family and commercial development, and in all public parking garages.
We will design or retrofit trails to provide convenient and barrier-free access to adjacent streets and major destinations. A trail that provides miles but does not connect to its surroundings may provide benefits to people seeking workouts, but it fails in its transportation mission to move people to places. In addition, poor access or visibility to and from surroundings can create public safety problems as well. We must design new trails and retrofit existing trails to provide frequent and comfortable access to wayside destinations and streets, with clear signage that helps orient users to their location.
Create a standards for trails based on industry standards, “Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design” principles, expected use, and surrounding land uses.
Acquire easements in new and existing developments to develop and connect trails.
Establish connections between parks, residential areas, and other points of interest by constructing additional bike routes, trails and pedestrian paths to meet the growing demands for recreation and alternative transportation routes.
Require that new development tie into the park and trail system by providing linkages to existing parks or dedicating new park land. Connect existing parks and neighborhoods to create a continuous system of open spaces, for example along stream corridors.
We will set neighborhood development priorities by using quantitative evaluation criteria. Available resources are never sufficient to address the problems of struggling neighborhoods. Setting priorities and policy focuses can be addressed by an evaluative process that considers such factors as economic opportunities, educational performance, housing quality, access to commercial and other support services, public safety, and presence of community organizations and institutions. The process should consider positive neighborhood factors that can create the foundations for success, including:
- Existing support capacity from neighborhood associations, local service providers, and area businesses;
- Community institutions like parks, schools, churches, or community centers; and,
- Connections to surrounding neighborhoods.
We will expand rehabilitation and redevelopment programs to stabilize the physical fabric of neighborhoods. The physical condition of a neighborhood and its buildings is critical to its ability to function as a community. Residential rehabilitation programs should be expanded to both meet the needs of existing residents and serve future generations. Rehabilitation should focus items that directly affect health and safety, secure the basic building envelope, and add economic value to the surrounding area. Programs in which community development corporations acquire, rehabilitate, and either sell or rent units on a “turnkey” basis at moderate costs have been particularly effective in adding value, preserving housing, and introducing new owners and potential leaders into a neighborhood.
But housing rehabilitation is only part of the picture. Vacant sites and dilapidated buildings depress both property values and community momentum. Programs to accelerate the redevelopment of dilapidated properties should be tied closely to the priority evaluation process. Funds should be targeted to areas and projects that create a critical mass that in turn catalyzes private market investment and creates a self-sustaining community. Mechanisms like landbanks and land trusts have also proven effective in gaining control over vacant properties and returning them to productive use. Often, a high priority or visibility project at a strategic location can produce an unexpectedly powerful private reaction as neighbors gain confidence in their future.
We will create, enhance, and maintain community spaces where residents interact positively and advance the social fabric. Successful neighborhoods include spaces where people see and greet each other, and work and play together in a common enterprise. These spaces open a neighborhood, and increase the level of positive interaction that is the essence of a living neighborhood. Yet, hidden or neglected public spaces have the opposite effect, attracting nuisances and sometimes crime, and being scary or off-putting places that people avoid. Good community spaces can take many forms – a well-maintained public park surrounded and watched over by residents; a community garden; the median of a parkway; or a school or community center site.
Strengthening these community places begins with inventorying and analyzing their operations. This can be done in cooperation with neighbors and community organizations. Volunteer work, business participation, and other public and private support can provide the means to reclaim existing spaces and develop new ones, and to provide adequate resources for continued support and maintenance.
Facilities like community gardens and groceries are particularly attractive as community spaces because they are self-supporting; become natural and productive attractors of people, and address other key concerns such as access to healthy food. Efforts at a neighborhood level to secure sites and organize gardens should be expanded and educational institutions should provide technical help to gardeners. Public development incentives should have a special focus on attracting grocery stores to skipped over areas with viable consumer markets, and should encourage inclusion of public space in project design.
We will coordinate public infrastructure projects and community revitalization. In an effort to create tangible catalysts for revitalizing urban communities, the City will use the analysis described in this section as well as those located throughout planokc, to inform its capital improvements program.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Prioritize neighborhoods for revitalization and re-investment in order to reverse the decline associated with poor maintenance of public infrastructure and other property by using the following objective criteria:
- Low economic opportunity;
- Low educational attainment;
- Poor health outcomes;
- Poor housing environments;
- Low neighborhood quality; and,
- Existing capacity to support the revitalization efforts; and other important indicators.
Increase the City’s capacity to participate in targeted programs that strengthen neighborhood infrastructure and other assets.
Increase and/or re-assign City staff to support targeted neighborhoods and coalitions.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
We will institute neighborhood design guidelines and practices that build community in lower-density settings. We recognize that different people have different preferences. Many people seek new houses but still want the diversity and neighborliness of the best of established neighborhoods. Others seek the bigger lots and greater personal space offered by low-density development. But almost everyone wants an attractive living environment, a sense of belonging to a community, public space, and connection. As we move toward new standards that implement the land use plan, we should ensure that new development designs reflect patterns that create better communities. These include such items as encouraging lot clusters to maintain open space, even in low-density development; street connections for both community contact and public safety access; trail and pathway systems; and housing variety where appropriate. Planned unit developments should be used in their intended way, to encourage creative design by looking at developments in their entirety.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Change subdivision regulations to determine the number of entries into a residential development based on number of lots in order to improve connectivity of the roadway network and emergency response.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will provide complete sidewalk networks to serve local parks. People within the realistic walking radius (or “walkshed”) of a local park should have pedestrian facilities – sidewalks, paths, or trails – that connect to that park. Creating such a pedestrian web around parks includes:
- Analyzing sidewalk coverage within the walkshed, (½ mile for neighborhood parks and one mile for community parks) for interruptions and barriers.
- Evaluating current park access points and their relationship to the pedestrian system.
- Establishing priority routes to parks and focusing funding on closing gaps and removing barriers, including intersection design issues.
- Providing signage and wayfinding information to direct users to parks destinations.
- Within new developments, require street patterns and pedestrian links that provide direct routes to private parks, school parks, and public trails.
We will complete trails to serve all parts of Oklahoma City to meet the community priority placed on trails and increase access to parks. As discussed in connectokc, trails are both a recreational and transportation resource. The basic trail system identified by the Parks Master Plan included four major phases of trail development:
- The existing trail system.
- Programmed trails, including the MAPS 3 trails and a Katy Trail extension.
- Near-term off-street trails, connecting the trail core to outlying parts of the urban area.
- Long-term off-street trails, extending the city system to the periphery of Oklahoma City.
The programmed system should be completed by 2020, by which time priorities should be set for completion of the longer-term system components. The ability to provide park access should be a strong factor in setting priorities.
Other trail-related actions should include:
- Designating on-street routes that connect neighborhoods to trail access points. These routes should focus on low-volume, direct streets that include continuous sidewalks and pavement markings.
- Requiring developments to dedicate trail segments designated by the trails master plan.
- Enhancing the recreational trail experience with landscaping, fitness facilities, wayfinding signage, rest areas, and other amenities.
We will improve the usefulness of transit as a way of getting to parks. Parks can be hard to serve by transit because they rarely generate the trip volume at specific times that help support service. However, we can take steps that help transit service adapt to park needs. Directions include increasing service on potential high-volume routes that serve major park and recreation facilities, and locating new investments, such as multi-generational centers, on sites with good transit service. We also should be open to transportation solutions other than fixed route transit. Examples are special services or brokering of other transportation providers to serve time specific needs, such as after school service to a major recreation facility.
Modify Subdivision Regulations to require new development adjacent to public trails to provide sufficient connections to the trails.
Update, implement, and maintain the currency of the 1997 Oklahoma City Trails Master Plan.
Enhance the safety and walkability of the sidewalk network through:
- Establishing a citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan that includes an inventory of sidewalk locations and conditions, and priorities for enhancement.
- Implementing sidewalk improvements through future bond issues, CIP projects or other sources of funding as prioritized in the citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan.
- Maintaining currency of the citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan.
- Explore the feasibility of the City assuming responsibility for sidewalk maintenance.
Develop a downtown park master plan that identifies the following:
- Opportunities for providing private parks and open space while still maintaining a dense, urban environment (such as vest pocket parks, rooftop gardens, plazas and courtyards);
- Linkages and connections between public and private parks;
- Programming and amenities that complement and support parks in the system; and
- Funding for operations and maintenance.
Ensure all homes are within walking distance of a park based on level of service standards for each urban land use typology by updating codes and regulations for new construction and by improving connections and access between existing parks and neighborhoods.
Acquire easements in new and existing developments to develop and connect trails.
Establish connections between parks, residential areas, and other points of interest by constructing additional bike routes, trails and pedestrian paths to meet the growing demands for recreation and alternative transportation routes.
Require that new development tie into the park and trail system by providing linkages to existing parks or dedicating new park land. Connect existing parks and neighborhoods to create a continuous system of open spaces, for example along stream corridors.
Prioritize capital improvement to construct linkages and connections from the existing urban parks and open space system to neighborhoods, commercial areas, employment centers, and community facilities.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
People have a number of places to gather and socialize that are easily accessible from and within neighborhoods.
We will provide good street connections within and between neighborhoods to provide a choice of routes and separate local traffic from major arterials. Good street connectivity has many benefits. By providing alternative routes for short distance trips, it indirectly increases the capacity of arterial streets. It also provides better quiet street opportunities for pedestrians and bicyclists, and improves the efficiency of delivering emergency access and city services.
Maintain the traditional grid street pattern where it currently exists, reconnect it where possible, and keep alleys open and functioning. When improving older streets in neighborhoods, maintain original street widths and curb radii.
Improve the functionality and efficiency of the street network by:
- Providing direct connections from residential developments to nearby places and to each other.
- Providing street and sidewalk stubs to adjacent vacant land in anticipation of future development.
- Connecting new development to existing street and sidewalk stubs, and to existing trail, open space, and bicycle networks.
- Reducing block sizes and use of dead-end streets.
- Maintaining the existing street grid to preserve connectivity and mobility options.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Change subdivision regulations to determine the number of entries into a residential development based on number of lots in order to improve connectivity of the roadway network and emergency response.
Maintain existing alleys or construct new alleys where feasible to provide trash collection service and parking behind primary buildings and minimize curb cuts along the primary street frontage.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
We will establish a systematic neighborhood street program, focused on rehabilitation, traffic calming, and safety and functional improvements. Citizens place a high priority on the condition and repair of the existing street system. The streets that affect residents most – local and connector streets – are rarely addressed by normal transportation programs. A systematic neighborhood street program will both provide regular funding for street repair and rehabilitation and completion of special street projects such as traffic calming.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
We will develop and implement a strategic plan for the city’s pedestrian network, building on the foundation of the 2013 Sidewalk Master Plan for MAPS 3. The 2013 Sidewalk Master Plan was a significant step forward, including an analysis of pedestrian demand in different parts of the city. However, its primary purpose was to identify priority projects for a specific sidewalk construction category of MAPS 3. Many of these projects supply new sidewalks along major corridors with high demand, based on a systematic rating system. These are extremely important, but many other problems remain, including:
- Neighborhood sidewalks on local streets that provide access to destinations such as schools and transit stops.
- Barriers to pedestrian travel such as major intersections, long arterial street crossings, and signal timing.
- Relationship of sidewalks to other parts of the active transportation network, including multi-modal streets, bicycle facilities, transit, connections to adjacent development, and trail access.
These issues require an expanded pedestrian system plan that:
- Identifies a Complete Streets Network prioritizing pedestrian corridors that should be developed and funded as part of the city’s transportation program. The MAPS 3 and previous bond issue study provide a starting point for this network.
- Establishes standards for local sidewalk coverage and a process to evaluate pedestrian service on a neighborhood by neighborhood basis. An example of such a standard would be provision of a complete and well-maintained web of sidewalks within a 1/2 mile walking radius of elementary and middle schools.
- Identifies key pedestrian barriers that obstruct access for important user groups, including children and older adults. This effort should include standards and techniques to minimize these barriers.
- Relates other active modes or facilities to the sidewalk network.
- Provides a phased implementation program that may include individual categories of funding, such as neighborhood target areas and major network investments.
Enhance the safety and walkability of the sidewalk network through:
- Establishing a citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan that includes an inventory of sidewalk locations and conditions, and priorities for enhancement.
- Implementing sidewalk improvements through future bond issues, CIP projects or other sources of funding as prioritized in the citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan.
- Maintaining currency of the citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan.
- Explore the feasibility of the City assuming responsibility for sidewalk maintenance.
Establish requirements for providing alternate pedestrian routes when construction activity prohibits use of existing facilities.
We will enhance policing and crime prevention programs through partnerships between police and local communities. The term “community policing” has become controversial in some instances, but it is in fact a common sense approach to law enforcement that many cities and towns implement without fanfare. Police departments that practice community-based techniques recognize that police alone cannot deal with neighborhood safety and livability issues, but instead must partner with citizens, businesses, organizations, schools, churches, and others to build safe environments.
Community-based programs establish personal relationships and trust between police and residents. Some police departments describe this approach as a “value system” or even “a way of life” as opposed to a program. In Oklahoma City, effective neighborhood policing will involve greater outreach to residents and businesses, interaction with organizations, working relationships with property owners, and other cooperative efforts. A critical support element will involve direct work with at-risk youth and adequate funding for job training, education, and leadership development programs.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
We will incorporate design and maintenance practices to create safer environments in both established and new neighborhoods. Addressing the impact of the neighborhood environment on public safety will follow two tracks: 1) reviewing new projects (including subdivisions and major new developments) and incorporating safe environmental design standards into their design, and 2) auditing existing neighborhoods for unsafe conditions and correcting problem areas.
Safety evaluation of new projects will start with developing design standards and guidelines, using the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design as a starting point. Our public safety departments should develop specific areas of expertise in these principles and be fully integrated into the City’s project review and approval process.
Established neighborhoods present different challenges. Partnerships between City staff and community organizations will analyze the neighborhood environment and local crime patterns to identify and correct specific problems. The most common issues include overgrown lots, hidden spaces, and vacant and deteriorated buildings. We must be aggressive in such areas as vegetation control and demolition of buildings beyond feasible repair.
Response times when emergencies occur are also an important factor in the interaction between public safety and environmental design. Neighborhood designs should increase the efficiency of public safety operations and ensure that the greatest number of residents can be reached in the shortest amount of time by emergency responders. This should include strategic improvements in existing neighborhoods and efficient design in new neighborhoods.
Systematic evaluation and correction of design aspects of new projects and inherently unsafe environments in established areas will be necessary to ensure a safe environment for all residents of Oklahoma City.
We will correct unsafe building elements and design conditions in public facilities and outdoor spaces. The City should lead in providing safe and secure facilities and properties. This is especially important in distressed neighborhoods, where a public park or center may be seen as a refuge. All publicly accessed properties should be assessed for unsafe conditions, including but not limited to poor lighting, blind spots, and maintenance hazards. Once this inventory has been completed, priorities for repair should be set and incorporated into the capital program.
Graffiti and vandalism in public areas are special and persistent problems. Uncorrected incidents suggest neglect in a neighborhood, which in turn encourages both more vandalism and serious criminal activity. Graffiti can be controlled through an aggressive removal policy, best accomplished in partnership with neighborhood residents. Cooperative action for productive purposes has the secondary benefit of building a sense of neighborhood effectiveness and establishing credibility for improvement efforts all of which help reconstruct the social fabric.
Improve the functionality and efficiency of the street network by:
- Providing direct connections from residential developments to nearby places and to each other.
- Providing street and sidewalk stubs to adjacent vacant land in anticipation of future development.
- Connecting new development to existing street and sidewalk stubs, and to existing trail, open space, and bicycle networks.
- Reducing block sizes and use of dead-end streets.
- Maintaining the existing street grid to preserve connectivity and mobility options.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Evaluate public facilities and public property for unsafe conditions such as poor lighting (quality and quantity); blind spots; poor maintenance conditions; and other unsafe conditions. Prioritize improvements to these facilities and properties based on the following criteria: a) Proximity and condition of nearby neighborhoods; and b) Cost/benefit associated with mitigating the unsafe condition and maintaining the improvement.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Utilize existing natural streams as amenities in public parks, and regularly monitor and maintain stream banks for safety of park users.
Revise subdivision regulations to require development adjacent to parks and public open spaces to maintain open sight lines to parks and public open space. Reduce/limit residential rear yards, fences, walls, and physical and visual enclosures around park and public open space perimeters. Encourage designs that allow homes to face into parks or where side yards are located near parks.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will establish partnerships between the City and school districts to assist in non-educational functions. School districts deal with a variety of non-educational or indirectly educational functions on a regular basis. This includes siting of new schools, redeveloping closed schools, addressing crime and crime prevention, and other community outreach functions. By working together, funding should be leveraged and resources used efficiently to strengthen neighborhoods, making them viable choices for young households.
We will co-locate new public projects in coordination with local school districts. Strong civic institutions strengthen neighborhood identify, social interaction and appeal to investors. Co-locating public projects such as libraries, fire stations, parks, recreation centers, and schools create neighborhood activity centers and realize efficiencies through joint use arrangements.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
We will create public/private partnerships that fill critical demands like workforce housing that are not normally satisfied by the private market. The Housing Market Preference and Demand Study defined housing preferences for different age and income groups, including residential types and locations. This information provides valuable guidance to city agencies, community organizations, builders, and developers that can help all parties make policy and business decisions. However, these data rapidly become outdated. Regular updates, funded by a mutually beneficial partnership of public and private sectors, can ensure that this information remains relevant and useful.
But information must be put to use. The 2013 housing study identified a major demand for “workforce” housing – equity and rental units affordable to people in a range from 60% to 120% of the citywide median household income. The normal private market has difficulty producing housing for much of this income range because of perceived risk and small profit. Partnerships between the public, private, and nonprofit sectors, including employers, can develop programs that remove obstacles to workforce housing production and marketing. Options include site acquisition, landbanking, interim financing, appraisals, mortgage financing, neighborhood infrastructure, and streamlined development reviews.
Collaborate with local development and real estate professionals to prepare a city-wide Housing Demand Market Study every 5 years which includes analyses and recommendations related to:
- Projected demand and trends in supply;
- Special needs housing;
- Housing conditions;
- Work force housing and its associated program; and,
- Overall health of the housing market, including owner-occupied and renter-occupied.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Ensure that new publicly financed developments – those which directly use or receive public dollars – with more than 100 units or with densities greater than 10 units/acre are located where they have easy access to frequent transit service.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
We will set neighborhood development priorities by using quantitative evaluation criteria. Available resources are never sufficient to address the problems of struggling neighborhoods. Setting priorities and policy focuses can be addressed by an evaluative process that considers such factors as economic opportunities, educational performance, housing quality, access to commercial and other support services, public safety, and presence of community organizations and institutions. The process should consider positive neighborhood factors that can create the foundations for success, including:
- Existing support capacity from neighborhood associations, local service providers, and area businesses;
- Community institutions like parks, schools, churches, or community centers; and,
- Connections to surrounding neighborhoods.
We will expand rehabilitation and redevelopment programs to stabilize the physical fabric of neighborhoods. The physical condition of a neighborhood and its buildings is critical to its ability to function as a community. Residential rehabilitation programs should be expanded to both meet the needs of existing residents and serve future generations. Rehabilitation should focus items that directly affect health and safety, secure the basic building envelope, and add economic value to the surrounding area. Programs in which community development corporations acquire, rehabilitate, and either sell or rent units on a “turnkey” basis at moderate costs have been particularly effective in adding value, preserving housing, and introducing new owners and potential leaders into a neighborhood.
But housing rehabilitation is only part of the picture. Vacant sites and dilapidated buildings depress both property values and community momentum. Programs to accelerate the redevelopment of dilapidated properties should be tied closely to the priority evaluation process. Funds should be targeted to areas and projects that create a critical mass that in turn catalyzes private market investment and creates a self-sustaining community. Mechanisms like landbanks and land trusts have also proven effective in gaining control over vacant properties and returning them to productive use. Often, a high priority or visibility project at a strategic location can produce an unexpectedly powerful private reaction as neighbors gain confidence in their future.
We will create, enhance, and maintain community spaces where residents interact positively and advance the social fabric. Successful neighborhoods include spaces where people see and greet each other, and work and play together in a common enterprise. These spaces open a neighborhood, and increase the level of positive interaction that is the essence of a living neighborhood. Yet, hidden or neglected public spaces have the opposite effect, attracting nuisances and sometimes crime, and being scary or off-putting places that people avoid. Good community spaces can take many forms – a well-maintained public park surrounded and watched over by residents; a community garden; the median of a parkway; or a school or community center site.
Strengthening these community places begins with inventorying and analyzing their operations. This can be done in cooperation with neighbors and community organizations. Volunteer work, business participation, and other public and private support can provide the means to reclaim existing spaces and develop new ones, and to provide adequate resources for continued support and maintenance.
Facilities like community gardens and groceries are particularly attractive as community spaces because they are self-supporting; become natural and productive attractors of people, and address other key concerns such as access to healthy food. Efforts at a neighborhood level to secure sites and organize gardens should be expanded and educational institutions should provide technical help to gardeners. Public development incentives should have a special focus on attracting grocery stores to skipped over areas with viable consumer markets, and should encourage inclusion of public space in project design.
We will coordinate public infrastructure projects and community revitalization. In an effort to create tangible catalysts for revitalizing urban communities, the City will use the analysis described in this section as well as those located throughout planokc, to inform its capital improvements program.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Prioritize neighborhoods for revitalization and re-investment in order to reverse the decline associated with poor maintenance of public infrastructure and other property by using the following objective criteria:
- Low economic opportunity;
- Low educational attainment;
- Poor health outcomes;
- Poor housing environments;
- Low neighborhood quality; and,
- Existing capacity to support the revitalization efforts; and other important indicators.
Increase the City’s capacity to participate in targeted programs that strengthen neighborhood infrastructure and other assets.
Increase and/or re-assign City staff to support targeted neighborhoods and coalitions.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
We will institute neighborhood design guidelines and practices that build community in lower-density settings. We recognize that different people have different preferences. Many people seek new houses but still want the diversity and neighborliness of the best of established neighborhoods. Others seek the bigger lots and greater personal space offered by low-density development. But almost everyone wants an attractive living environment, a sense of belonging to a community, public space, and connection. As we move toward new standards that implement the land use plan, we should ensure that new development designs reflect patterns that create better communities. These include such items as encouraging lot clusters to maintain open space, even in low-density development; street connections for both community contact and public safety access; trail and pathway systems; and housing variety where appropriate. Planned unit developments should be used in their intended way, to encourage creative design by looking at developments in their entirety.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Change subdivision regulations to determine the number of entries into a residential development based on number of lots in order to improve connectivity of the roadway network and emergency response.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Modify codes to allow residential clustering in rural land use typology areas, provided water supply and sewage disposal requirements are met, and permanently preserve nearby open space through means such as conservation easements.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will continue to create and enhance amenities such as parks, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. The MAPS programs have generated tremendous momentum for our city, but we cannot rest on past accomplishments. Instead we must continue our efforts to create great places at neighborhood, citywide, and street levels. In the future, these amenities will include public spaces, street corridors, transit facilities, cultural and recreational attractions, special districts, and community gateways.
Connections like the Bricktown Canal connecting Bricktown and the riverfront, the SkyDance Bridge, the riverfront greenway and in the near future the modern streetcar and trails projects have been as important as individual destinations. Signature transportation corridors are also vital parts of the cityscape. To this end, the City will explore the feasibility of installing and maintaining landscaping and public art along key transportation corridors to enhance the City’s appearance, image, and sense of place. Features like gateways can mark the transition from one district to another, and help emphasize the distinctiveness of Oklahoma City’s special districts.
We will build on the success of our special districts to attract residents and businesses. Downtown, Bricktown, Midtown, the Plaza, Deep Deuce, the Paseo, Stockyards City, Automobile Alley, Heritage Hills, and others are important districts that contribute strongly to Oklahoma City’s sense of place and identity. Future districts like Core to Shore will contribute to Oklahoma City’s collection of urban places. The City will continue to invest in features that make these existing and future places centerpieces of our community by catalyzing development, increasing land use diversity, building quality of life amenities, and promoting family-friendly features.
Catalyzing development. Urban housing has proven to be a staple of downtown and urban district revitalization. Residential development not only creates a market for more local services but also creates a comfortable environment that brings other people in from around the city and region. The City will continue to guide housing development to urban districts to increase activity and support demand for new retailing. Special focuses will include Downtown and surrounding areas and the new Core to Shore neighborhood. The City should also place a priority on establishing a signature retail development or a retail/housing mixed-use development.
Diversifying land use. Increasing land use diversity in urban districts will help attract and retain visitors and support development momentum. For example, Bricktown’s first development phases concentrated on offices, bars, and restaurants. But the historic district has become more vital with nearby housing, retailing at different scales, and hospitality uses, and this type of diversification should accelerate. In special districts, City policy should attract a balance of retail, residential, employment, and recreational uses.
Investing in amenities and activities. The City can strengthen downtown’s and other districts’ senses of place and increase activity by encouraging and investing in more public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Building family-friendliness. We can help attract and retain a variety of households to downtown and other urban districts by promoting and enhancing them as family-friendly places to live and play. Attention to street design, land uses (particularly around the downtown school) and public safety can help promote this image.
We will establish a place-making program. The City will establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city and promote both the economic and quality-of-life value of place-making investments. The program will establish partnerships and provide funding on a regular basis, including attention to small, neighborhood-scaled projects.
A significant part of this program is communicating the message of Oklahoma City’s places to the outside world. This both benefits businesses directly through promotion and supports city marketing and talent recruitment efforts. The Chamber of Commerce and Convention and Visitors Bureau are major partners in this effort.
We will designate additional special districts. The City will foster more specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to promote diversity and improve perceptions of the city. For example, Capitol Hill could grow as the center of an emerging Hispanic/Latino district, with appeal to people throughout the region. New special districts would include thematic infrastructure, amenities, design, public art, and streetscape improvements. Appropriate areas should be identified for special districts, followed by preparation of plans that establish design guidelines and strategies to capitalize on cultural meaning.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city. The program should promote the economic and quality-of-life benefits of place-making investments and should:
- Establish and maintain partnerships between the City, the private sector, and “place management” organizations.
- Provide funding and City staff support for “place management” organizations.
Create specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to enhance the diversity and perceptions of the city. Identify appropriate areas and create master plans with urban design guidelines specialized to the cultural history on display. For example, one special district could be themed for the Hispanic/Latino community. Such a district would include associated thematic infrastructure, amenity, design, public art, and streetscape improvements.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
Attract and retain young professionals to downtown and its environs to support and enhance place-making efforts and investments.
- Explore the possibility of the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce contracting with the City to facilitate and promote civic engagement and social opportunities for young professionals.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Strengthen downtown’s sense of place and activity levels by encouraging more housing, retail, public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Encourage the use of special service districts with enhanced levels of service.
Ensure adequate funds to maintain enhanced levels of service (including staffing) in places that have been or will be designated as special districts.
Initiate an effort to create and publicize a brand and image for the city. Examples of specific outcomes include:
- Coordinate with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber to advertise the city’s quality of life to national and regional audiences during major events such as the NBA playoffs, and at other appropriate times and places, and in appropriate media.
- Overhaul of City logo (buses, police cars, streetcar)
- Overhaul of City Website
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Enhance Downtown Oklahoma City’s prominence by maintaining and increasing its role as the major business center, establishing it as a major urban residential center, and focusing on developing retail, office, entertainment, and arts and cultural uses.
Work to establish a critical mass of retail uses in the downtown area. A lifestyle center or mixed-use town center presents the most viable option for a major infusion of retail into downtown.
We will develop and implement new land development regulations that support the Land Use Typology Area system of integrated uses and greater flexibility and efficiency. Our current development ordinances date from a time when we valued low density and separation of different land uses higher than city life. The fact that low density increases the cost of services and infrastructure gives us pause. That, combined with our successes at building places that people want to experience has moved us in new directions. The zoning code, which divides the city into 26 single-use “base” districts, 7 special districts, and 16 overlay districts, discourages the trends toward new development forms. We must modernize these codes to implement the LUTA concept and provide both the flexibility and protection that benefit contemporary developers and their neighbors alike.
Despite its large number of specific districts, our zoning ordinance does not provide adequate protections for neighborhoods or guarantees to approving agencies on actual performance or design of projects. This forces the Planning Commission and City Council to use Planned Unit Developments (PUDs), tying developers to a specific project and building design. PUDs are actually intended for a different purpose – to encourage innovative, comprehensively planned developments– and are overly rigid when applied to more routine projects.
Revisions to Oklahoma City’s land development regulations could move in several directions, from modifying existing zoning districts with new performance and design standards to establishing a new structure that uses the Land Use Typology Areas as the basic development districts for the city. The LUTAs, as presented in Chapter Two, permit a variety of uses, but establish permitted ranges of development intensity. The LUTA system achieves compatibility between different types or intensities of uses by implementing performance standards, design guidelines, and transitional methods. These techniques give specific and predictable guidance to builders and developers, and address such areas as operating effects, traffic, parking, design, scale, and safety, avoiding the unnecessary overuse of PUDs. A LUTA-based system would incorporate the criteria for locations and supporting transportation and infrastructure established by this plan for individual land uses.
We will execute a smooth transition between the existing zoning code and new land development ordinances. Development ordinances are complicated and difficult to change because people have become accustomed to them, rough spots and all. Migrating to an alternative concept will take time and care. In the meantime, the City will evaluate using a hybrid approach, mixing the existing zoning districts with the LUTA/mixed use concept. One way of accomplishing this is to group the zoning districts that are consistent with the intensity and use ranges of LUTAs, and apply compatibility policies and design standards to developments within them. The existing zoning ordinance could then be modified to include these compatibility standards. New rezoning requests would be evaluated for consistency with the LUTA in which they are located. If the new project is adjacent to a different land use, the compatibility policies and standards would apply to the design of that project.
Coordinate the design, development, expansion, and/or investment in transportation projects with the Land Use Typology map.
Require the construction of new streets, streetscapes, and street widening projects to implement the design components of the assigned street typologies established in this plan.
Revise Subdivision Regulations and development standards to reflect the street typology standards.
Routinely assess the City’s development standards, design guidelines, and development review procedures to ensure that they reflect current trends in best-practice and allow for innovative design techniques and evolving methods in low-impact development.
Enhance existing development standards and establish design guidelines for areas outside of the City’s existing Design Review Overlay Districts. Development standards and design guidelines could include the following provisions:
- Minimize views and prominence of parking lots in relation to structures on a site.
- Sense of proportion (street width to building height, human scale)
- Pedestrian orientation of structures and architectural detailing/fenestration
- Terminated vistas
- Reduce the predominance of residential garages in the design of the front facades of single-family residences.
- Inclusion of front porches into the design of residential structures.
- Internal orientation of parking facilities and garages in multi-family developments.
- Improved pedestrian safety and enhanced pedestrian access through parking lots.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Encourage the integration and mixing of land uses in urban areas.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
In order to promote compatibility between different uses, establish standards and guidelines that ensure all developments are pedestrian-friendly and human scale at street frontages and property lines.
Prioritize and concentrate development where facilities, infrastructure, and services have capacity and in areas where the Police and Fire Departments are best able to respond. Guide the location and timing of development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure.
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Ensure the ongoing compatibility and appropriateness of development in Planned Unit Developments (PUDs) and Simplified Planned Unit Developments (SPUDs) by:
- Exploring the establishment of expiration dates for PUDs and SPUDs that have not been initiated after a certain period of time;
- Establish a procedure to ensure PUDs build-out according to approved plans.
Enable increased densities as appropriate to individual land use typology areas by addressing financial incentives and disincentives through evaluating the feasibility of strategies such as:
- Impact fees and/or transportation utility fees that vary by district according to actual cost;
- Assessing solid waste charges according to actual cost;
- Private solid waste services where it is impractical for the City to provide service such as in rural areas.
Encourage unified planning for all adjoining land owned or controlled by a project’s developer to ensure proper circulation and land use relationships.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
Revise subdivision and zoning regulations to allow increased densities as appropriate. For example, density potential could be increased by allowing “cottage” or “pocket” neighborhoods and accessory dwelling units (additional dwelling units allowed on owner-occupied properties) where appropriate.
We will continue the process of creating a mixed-use, intensively developed, human-scaled, and experience-rich downtown. American downtowns declined as the number of reasons that brought people downtown decreased. Recently, downtowns have achieved success as places to live and visit as well as work. This evolution in Oklahoma City began in Bricktown and surrounding areas, where the canal and ballpark anchored adaptive reuse of historic buildings and the addition of new restaurants, entertainment venues, hotels, offices, and homes. This transformation continued with the addition of one of the National Basketball Association’s premier franchises, the Civic Center restoration, major office projects, and new housing. While the growth and development of downtown will always be ongoing, these accomplishments provide the foundation for building a great 21st century downtown.
Land use and development targets and policies will be instrumental in guiding this future. Major land use focuses will include a range of housing types and costs to serve a complete cross-section of the Oklahoma City market; services and retailing that support a larger resident population, including child care, educational facilities, and neighborhood commercial uses like a grocery store; integration of multiple uses into new and existing buildings; and public parks and open spaces for both programmed and informal activity. Much of this future development will occur on currently under-used sites such as the Core to Shore redevelopment area, the future Boulevard on the former I-40 right-of-way; existing surface parking lots, and vacant sites. Initial steps in meeting these needs include revisions of regulations to accelerate desirable uses and market research to demonstrate and quantify markets for specific project types.
As Downtown continues to develop, it must also evolve as a great urban place that offers a superb experience to its residents, workers, and visitors. The history of the urban renewal era in Oklahoma City tells us that investment dollars and big projects alone do not create a living and vibrant city center. A secure, populated, human-scaled environment requires family-friendly amenities, windows on the street, buildings with details scaled to people, pedestrian environments that engage the eye and mind, and an overall sense of welcoming and even festivity. These features have the power to attract the life that is characteristic of great downtowns.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
Attract and retain young professionals to downtown and its environs to support and enhance place-making efforts and investments.
- Explore the possibility of the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce contracting with the City to facilitate and promote civic engagement and social opportunities for young professionals.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Strengthen downtown’s sense of place and activity levels by encouraging more housing, retail, public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
In order to promote compatibility between different uses, establish standards and guidelines that ensure all developments are pedestrian-friendly and human scale at street frontages and property lines.
Enhance Downtown Oklahoma City’s prominence by maintaining and increasing its role as the major business center, establishing it as a major urban residential center, and focusing on developing retail, office, entertainment, and arts and cultural uses.
Continue to pursue a full scale downtown grocery store or a natural food grocer by:
- Increasing the amount of downtown housing
- Conducting a market study to quantify existing and future potential
- Promoting downtown to potential store operators
- Providing incentives such as land, infrastructure, or sales tax rebates, and allowing for mixed-use (vertical) integration with other uses including, but not limited to, residential.
Encourage development of new educational and childcare facilities downtown to accommodate families with children that work and/or live downtown.
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
We will coordinate library service planning with investments in City facilities and neighborhood planning. Oklahoma City should partner with the Metropolitan Library System and the State Department of Libraries to coordinate facility expansions, improvements, and new facility locations with other types of civic investments, such as schools, fire stations, and parks. This could allow for efficiencies through facility sharing or co-location.
New and remodeled libraries should support neighborhood planning goals by integrating themselves into their surroundings. The City should adopt design standards for both new and remodeled libraries that focus on integrating the building and site into the surrounding neighborhoods, thus increasing access to the libraries by walking, biking, and transit.
Form a working partnership with the library system, both the Metropolitan Library System and the Oklahoma Department of Libraries, to coordinate timing of facility expansions, improvements, and new facility siting with other types of civic resources, such as schools, fire stations, parks, and projected growth and demand for those resources. This should also include identifying a mechanism to provide library services in Canadian County.
Adopt design standards applicable to both new and remodeled libraries focusing on integrating the building and the site into existing neighborhoods and urban fabric, reducing their dependence on automobiles and increasing their access by other modes, especially walking, biking, and transit.
























 Download PDF
Download PDF