Goals
The goals below are in the form of statements describing ideal future conditions related to economic development that our community has committed to work toward achieving. These goals establish priorities for our city and help community leaders make decisions regarding how our city grows and improves. Clicking on any goal title will reveal the full goal statement and allow viewing of initiatives the City and its partners will undertake to accomplish the goal.
Oklahoma City has a growing and diverse economy that fosters vigorous job growth and self-sufficient citizens.
We will begin a cooperative study with the Burlington Northern & Santa Fe (BNSF) Railway and other involved railroads to expand freight and passenger capacity in the north-south corridor. In view of increased freight traffic projections on the BNSF, it will be important to develop a plan to increase capacity in this service corridor. The public has a significant stake in addition to increasing Oklahoma City’s ability to position itself as a freight transportation hub. Increased length and frequency of trains can degrade traffic flow at this line’s relatively frequent grade crossings. Also, from a regional transportation perspective, increased freight traffic on this single line may make commuter rail or additional Amtrak service impossible. A study will examine alternatives that could include an additional track, improved technology, or a freight bypass.
We will work to establish Oklahoma City as a principal intermodal center, beginning with a study to consider the demand, feasibility, and measures necessary to develop such a facility. Oklahoma City, at the intersection of major road, railroad, and air facilities, appears well-positioned to expand its role as a major focus for intermodal freight and distribution. The impact of such a center can be very beneficial in terms of new jobs, investment, and even redevelopment of brownfields industrial sites. One of the newest intermodal facilities, the BNSF’s Kansas City Intermodal Facility and the associated Logistics Park, is opening with about one million square feet of warehousing space and is projected to attract up to 15 million square feet of warehousing, distribution, and associated industry, with employment in excess of 2,000 people. The private and public sectors of our community should examine the feasibility of such a facility, potential sites, potential developers, and steps necessary to execute the concept.
Identify and prioritize freight infrastructure projects that are needed to maintain mobility and enhance the city’s (and region’s) economic competitiveness.
Initiate a long-range planning process for the expansion of the BNSF freight corridor.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
We will create development-ready sites with access to infrastructure in strategic areas.
An adequate and ongoing supply of immediately developable land provides the ability to respond nimbly to economic opportunities. Meeting the recommendation of the Employment Land Needs Assessment and Action Plan for maintaining a constant inventory of 1,000 acres of development-ready land involves a two-part strategy that:
- Protects land appropriate for major employment development from short-term encroachment by other uses.
- Extends services and infrastructure to this land so that major employers can build with minimum delay.
The Employment (EM) LUTA is specifically designed to preserve the integrity of land best suited for large-scale employment growth. Through the development approval process, the City can avoid compromising these sites by approving uses that will prove incompatible with future major employment centers. This may require creation of public or community-based development groups with the patience and ability to hold large assemblages of land for industrial, business park, or office headquarters uses.
The other leg of the strategy involves preparing this land for timely development by financing and installing (or being immediately prepared to install) infrastructure. Accomplishing this will require mobilization of existing agencies such as the Urban Renewal Authority, the Oklahoma Industries Authority, and the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust. It will also require establishing a reliable and repeatable method of funding capital investments that may include tax increment financing, general obligation limited tax bonds, and other public sources.
We will continue to provide incentives to major employers, targeted to specific industry clusters and locations. The City will continue to provide direct financial incentives to attract and retain major employers. These incentives should be targeted to:
- Industrial and employer clusters whose requirements are matched to our attributes and who move in the direction of greater economic diversification. These natural affinities for Oklahoma City include aerospace, aviation, defense, bio-science and other high-technology industries, renewable energy, new-to-market company headquarters, and advanced manufacturing.
- Sites where major community investments have been made in land, infrastructure, amenities, and other capital improvements; major redevelopment areas; or other desirable sites where these facilities are already available.
We will update public incentive programs to provide maximum leverage per dollar spent. The City provides incentives to businesses through its Strategic Investment Program. This incentive structure will be reviewed and optimized to provide the greatest community benefit and return on investment. This update should include specific evaluation criteria and objective measures of benefit. Preferred investments should move in the direction of private, front-end investment with incentive reimbursement tied to meeting performance criteria such as job creation and greater retail activity.
We will support locally-owned businesses and existing assets. Locally-owned businesses can have greater multiplier effects on the local economy than similar businesses that are non-local. This includes even the smallest businesses, such as home businesses, mobile food vendors, pop-up retail or vendors at farmer’s markets. The City can support locally-owned businesses and entrepreneurs through favorable tax policies, flexible regulations, and partnerships with local educational institutions to support business incubators and other programs that encourage business start-ups. We must also look carefully at measures that level the playing field among retail entities and allow local retailers to compete on at least an equal footing with on-line and out-of-city competitors.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Create and promote development-ready sites in Employment (EM) areas using the following strategies:
- Task the Oklahoma Industries Authority (OIA) and/or the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust (OCICFT) to help public and private entities create development-ready sites.
- Partner with the State School Land Trust to prepare their sites located in EM areas for development.
- Pursue public purchase or optioning of key properties in EM areas in cooperation with the Urban Renewal Authority, the Oklahoma Industries Authority (OIA), and/or the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust (OCICFT).
- Conduct a market analysis and feasibility study for a new business park.
- Facilitate development of EM sites by providing:
- Infrastructure financing options, such as tax-increment financing,
- Prioritized delivery of infrastructure, and
- Accelerated or facilitated permitting.
Provide adequate infrastructure for new or expanding companies by giving priority to Capital Improvements in ER areas. Additionally, consider the implementation of impact fees for infrastructure in order to provide infrastructure in a timely manner and to better coordinate with private development.
Consider updating the City’s Strategic Investment Program and retail incentive guidelines to maximize public benefit and return on investment from business recruitment and retention incentive structures according to the following order of preference:
- The prospective company pays for infrastructure and/or amenities and is reimbursed by the City as performance standards are achieved.
- The City pays for infrastructure and/or amenities, which the prospective company must repay if performance standards are not met.
- Direct, performance-based payments are made to the prospective company.
Continue providing direct financial incentives on a limited basis to attract and retain large, well-paying employers in areas where public infrastructure and amenities are already adequate. Financial incentives may include:
- Payments from general obligation limited tax bonds
- Performance-based rebate of all or a portion of future impact fees (if implemented)
- Revolving loan fund for small business starts/expansions
- Industrial revenue bonds
Increase economic diversity by supporting development of industry clusters such as aerospace, aviation, defense, bioscience (and other high-technology industries), renewable energy, new-to-market company headquarters, and advanced manufacturing. Strategies can include:
- Prioritizing incentives administered by the Oklahoma City Economic Development Trust for these industries
- Prioritizing installation of infrastructure to support aviation-related industrial development on the east side of the Will Rogers Airport
- Engaging ODOT in discussions to make improvements to I-44 in the vicinity of the Will Rogers Airport to relieve congestion and improve access to the airport-owned lands from I-44
- Protecting Airports and Tinker Air Force Base from encroachment by incompatible uses by analyzing the effectiveness of current Airport Environs overlay zoning districts and implementing necessary changes
- Facilitating expansion of Tinker-related operations to the east and south by prioritizing improvements to transportation, water, and sewer infrastructure
- Coordinating with the Chamber of Commerce to prepare sector acceleration plans for targeted industries
Support locally-owned businesses and entrepreneurs, which have greater multiplier effects on the local economy, by the following actions:
- Establish online sales taxes to correct a competitive imbalance currently suffered by local “brick and mortar” merchants.
- Facilitate entrepreneurial growth by working with local companies and universities and supporting business incubators.
- Consider amending the Strategic Investment Program guidelines to give higher priority to locally-owned businesses.
- Consider creating incentives and/or easing regulations for small, locally-owned businesses such as home businesses, farmers’ markets, mobile food vendors, pop-up retail, etc.
Support development of land designated for large employers and employment centers within the Employment Reserve LUTA, using the following strategies:
- When major infrastructure is extended to allow specific properties to develop in an Employment Reserve area, the City should place a condition on the land (through a development agreement) limiting future development to employment uses.
- Guide employment land development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure to accomplish the large-site employment land inventory objectives outlined in the Employment Land Needs Assessment & Action Plan.
We will support our schools in improving student performance. Low academic performance is a problem in our city, and especially within Oklahoma City Public Schools, as measured by the State Department of Education. Our entire community must address this issue aggressively. Some solutions involve long-term and continuing efforts, such as creating and sustaining healthy, mixed-income neighborhoods that provide the secure environments necessary to nurture learning and achievement. Recommendations that help create these types of neighborhoods are found throughout planokc, from land use initiatives to neighborhood reinvestment and housing variety. Other specific efforts, involving concerted action by the public and private sectors and school districts can provide more immediate results. These educational support programs can include scholarship programs that offer post-secondary grants to students in inner-city schools and districts, expanded early childhood education, after- school programs, mentoring, specialized educational tracks, teacher skills training, or financial incentives for high-performing schools and teachers.
The City will also assist the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce in efforts to adapt the education and training offered by local institutions to match the current and future needs of local companies. This includes both K-12 schools and secondary schools.
Educational issues and programs represent a convergence of different perspectives. This element approaches good educational programming from a workforce and economic development framework; liveokc from a neighborhood development viewpoint; and serveokc from a public service and community quality point of view. However, all point in the same direction, highlighting the importance of increasing achievement and learning.
Facilitate communication among the 23 school districts in order to develop more arts education opportunities for the children in our community.
Establish development standards and design guidelines for new cultural, civic, and sporting facilities that address site design, architecture, compatibility, pedestrian-orientation and access, landscaping, and the inclusion of public art.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Coordinate with Strong Neighborhoods Initiative to provide recreational, fire safety, public safety, and character building programs in schools.
Identify ways to establish/strengthen relationships and partnerships between schools and the business community as one method to improve student education and outcomes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Work with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce to recommend adaptations to local education and training opportunities to match the current and projected needs of local companies.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Avoid concentrations of apartment complexes. Instead, integrate multifamily units into neighborhoods with mixes of housing types or in mixed-use developments.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
We will continue to create and enhance amenities such as parks, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. The MAPS programs have generated tremendous momentum for our city, but we cannot rest on past accomplishments. Instead we must continue our efforts to create great places at neighborhood, citywide, and street levels. In the future, these amenities will include public spaces, street corridors, transit facilities, cultural and recreational attractions, special districts, and community gateways.
Connections like the Bricktown Canal connecting Bricktown and the riverfront, the SkyDance Bridge, the riverfront greenway and in the near future the modern streetcar and trails projects have been as important as individual destinations. Signature transportation corridors are also vital parts of the cityscape. To this end, the City will explore the feasibility of installing and maintaining landscaping and public art along key transportation corridors to enhance the City’s appearance, image, and sense of place. Features like gateways can mark the transition from one district to another, and help emphasize the distinctiveness of Oklahoma City’s special districts.
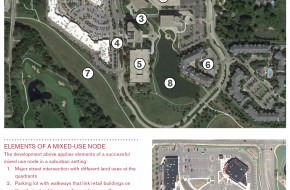
We will build on the success of our special districts to attract residents and businesses. Downtown, Bricktown, Midtown, the Plaza, Deep Deuce, the Paseo, Stockyards City, Automobile Alley, Heritage Hills, and others are important districts that contribute strongly to Oklahoma City’s sense of place and identity. Future districts like Core to Shore will contribute to Oklahoma City’s collection of urban places. The City will continue to invest in features that make these existing and future places centerpieces of our community by catalyzing development, increasing land use diversity, building quality of life amenities, and promoting family-friendly features.
Catalyzing development. Urban housing has proven to be a staple of downtown and urban district revitalization. Residential development not only creates a market for more local services but also creates a comfortable environment that brings other people in from around the city and region. The City will continue to guide housing development to urban districts to increase activity and support demand for new retailing. Special focuses will include Downtown and surrounding areas and the new Core to Shore neighborhood. The City should also place a priority on establishing a signature retail development or a retail/housing mixed-use development.
Diversifying land use. Increasing land use diversity in urban districts will help attract and retain visitors and support development momentum. For example, Bricktown’s first development phases concentrated on offices, bars, and restaurants. But the historic district has become more vital with nearby housing, retailing at different scales, and hospitality uses, and this type of diversification should accelerate. In special districts, City policy should attract a balance of retail, residential, employment, and recreational uses.
Investing in amenities and activities. The City can strengthen downtown’s and other districts’ senses of place and increase activity by encouraging and investing in more public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Building family-friendliness. We can help attract and retain a variety of households to downtown and other urban districts by promoting and enhancing them as family-friendly places to live and play. Attention to street design, land uses (particularly around the downtown school) and public safety can help promote this image.
We will establish a place-making program. The City will establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city and promote both the economic and quality-of-life value of place-making investments. The program will establish partnerships and provide funding on a regular basis, including attention to small, neighborhood-scaled projects.
A significant part of this program is communicating the message of Oklahoma City’s places to the outside world. This both benefits businesses directly through promotion and supports city marketing and talent recruitment efforts. The Chamber of Commerce and Convention and Visitors Bureau are major partners in this effort.
We will designate additional special districts. The City will foster more specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to promote diversity and improve perceptions of the city. For example, Capitol Hill could grow as the center of an emerging Hispanic/Latino district, with appeal to people throughout the region. New special districts would include thematic infrastructure, amenities, design, public art, and streetscape improvements. Appropriate areas should be identified for special districts, followed by preparation of plans that establish design guidelines and strategies to capitalize on cultural meaning.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city. The program should promote the economic and quality-of-life benefits of place-making investments and should:
- Establish and maintain partnerships between the City, the private sector, and “place management” organizations.
- Provide funding and City staff support for “place management” organizations.
Create specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to enhance the diversity and perceptions of the city. Identify appropriate areas and create master plans with urban design guidelines specialized to the cultural history on display. For example, one special district could be themed for the Hispanic/Latino community. Such a district would include associated thematic infrastructure, amenity, design, public art, and streetscape improvements.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
Attract and retain young professionals to downtown and its environs to support and enhance place-making efforts and investments.
- Explore the possibility of the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce contracting with the City to facilitate and promote civic engagement and social opportunities for young professionals.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Strengthen downtown’s sense of place and activity levels by encouraging more housing, retail, public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Encourage the use of special service districts with enhanced levels of service.
Ensure adequate funds to maintain enhanced levels of service (including staffing) in places that have been or will be designated as special districts.
Initiate an effort to create and publicize a brand and image for the city. Examples of specific outcomes include:
- Coordinate with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber to advertise the city’s quality of life to national and regional audiences during major events such as the NBA playoffs, and at other appropriate times and places, and in appropriate media.
- Overhaul of City logo (buses, police cars, streetcar)
- Overhaul of City Website
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Enhance Downtown Oklahoma City’s prominence by maintaining and increasing its role as the major business center, establishing it as a major urban residential center, and focusing on developing retail, office, entertainment, and arts and cultural uses.
Work to establish a critical mass of retail uses in the downtown area. A lifestyle center or mixed-use town center presents the most viable option for a major infusion of retail into downtown.
We will reduce crime and improve the sense of security throughout the city. We will establish and expand crime prevention partnerships with neighborhoods, visible patrols with a high degree of community contact and interaction in targeted areas, and youth programs. Other components of this effort should include regular evaluation of police staffing needs and expansion of such preventive measures as elimination of nuisances like abandoned buildings and integration of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design in the project review process. The liveokc and serveokc elements also provide initiatives that address public safety issues.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
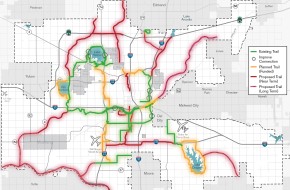
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
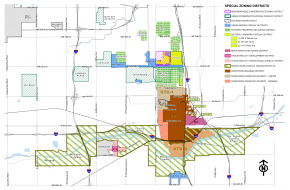
We will ensure that new and expanding industries have places to locate and grow in Oklahoma City. The Employment Reserve LUTA designates areas that are especially suitable for major industrial and office development. Public/private partnerships should provide adequate infrastructure and transportation services to these strategic areas. This typology area also recognizes that all land uses do not mix well with each other. Industries must have space to operate responsibly, but have operating characteristics that often are incompatible with other uses. Because industrial and office development may require holding large areas for long periods of time, owners often attempt to realize short-term returns by splitting off parts of sites for commercial or residential uses. If established, these uses can limit industrial and office options. Uses that could compromise future industrial and office growth should not be permitted to encroach on prime land with access to transportation infrastructure that is designated for major employment.
We will reduce the level of land use conflict between industrial and non-industrial uses. Protecting industrial land from non-industrial encroachment is part of a strategy to maintain a sufficient inventory. Reducing the potential for conflict between industrial and other uses also helps maintain the industrial land supply. Industrial development standards and guidelines should include landscaping and screening along major streets and edges of industrial areas, locating higher intensity industries away from neighboring uses, and standards that address building appearance and placement, outdoor storage, and buffering of high-impact site elements.
Create and promote development-ready sites in Employment (EM) areas using the following strategies:
- Task the Oklahoma Industries Authority (OIA) and/or the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust (OCICFT) to help public and private entities create development-ready sites.
- Partner with the State School Land Trust to prepare their sites located in EM areas for development.
- Pursue public purchase or optioning of key properties in EM areas in cooperation with the Urban Renewal Authority, the Oklahoma Industries Authority (OIA), and/or the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust (OCICFT).
- Conduct a market analysis and feasibility study for a new business park.
- Facilitate development of EM sites by providing:
- Infrastructure financing options, such as tax-increment financing,
- Prioritized delivery of infrastructure, and
- Accelerated or facilitated permitting.
Support development of land designated for large employers and employment centers within the Employment Reserve LUTA, using the following strategies:
- When major infrastructure is extended to allow specific properties to develop in an Employment Reserve area, the City should place a condition on the land (through a development agreement) limiting future development to employment uses.
- Guide employment land development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure to accomplish the large-site employment land inventory objectives outlined in the Employment Land Needs Assessment & Action Plan.
Develop design standards and guidelines for industrial development. Standards and guidelines should address: sensitive design and placement of buildings; screening or prohibiting outdoor storage; parcel sizes which allow for long term expansion for individual users; special landscaping requirements addressing screening and landscaping adjacent to residential areas and along highway and arterial streets; standards for the suitable location, orientation and screening of loading bays; and buffering treatments for truck access points.
Avoid placing heavy industrial uses on borders of industrial areas to avoid conflicts with adjacent development.
Direct oil drilling in industrial areas to locate equipment and facilities near major streets so as to keep interior areas free of obstructions that could hinder industrial development.
The quality and reputation of Oklahoma City area schools attract and retain residents and employers.
We will support our schools in improving student performance. Low academic performance is a problem in our city, and especially within Oklahoma City Public Schools, as measured by the State Department of Education. Our entire community must address this issue aggressively. Some solutions involve long-term and continuing efforts, such as creating and sustaining healthy, mixed-income neighborhoods that provide the secure environments necessary to nurture learning and achievement. Recommendations that help create these types of neighborhoods are found throughout planokc, from land use initiatives to neighborhood reinvestment and housing variety. Other specific efforts, involving concerted action by the public and private sectors and school districts can provide more immediate results. These educational support programs can include scholarship programs that offer post-secondary grants to students in inner-city schools and districts, expanded early childhood education, after- school programs, mentoring, specialized educational tracks, teacher skills training, or financial incentives for high-performing schools and teachers.
The City will also assist the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce in efforts to adapt the education and training offered by local institutions to match the current and future needs of local companies. This includes both K-12 schools and secondary schools.
Educational issues and programs represent a convergence of different perspectives. This element approaches good educational programming from a workforce and economic development framework; liveokc from a neighborhood development viewpoint; and serveokc from a public service and community quality point of view. However, all point in the same direction, highlighting the importance of increasing achievement and learning.
Facilitate communication among the 23 school districts in order to develop more arts education opportunities for the children in our community.
Establish development standards and design guidelines for new cultural, civic, and sporting facilities that address site design, architecture, compatibility, pedestrian-orientation and access, landscaping, and the inclusion of public art.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Coordinate with Strong Neighborhoods Initiative to provide recreational, fire safety, public safety, and character building programs in schools.
Identify ways to establish/strengthen relationships and partnerships between schools and the business community as one method to improve student education and outcomes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Work with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce to recommend adaptations to local education and training opportunities to match the current and projected needs of local companies.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Avoid concentrations of apartment complexes. Instead, integrate multifamily units into neighborhoods with mixes of housing types or in mixed-use developments.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
We will promote redevelopment of vacant or under-used sites. Infill development on vacant, under-utilized, and brownfield sites should receive special attention through changes to land use regulations, infrastructure upgrades in target neighborhoods, incentives, favorable tax policies, expedited processing, and greater flexibility. The City recently produced a study on vacant and abandoned buildings to help address this issue and will continue to pursue implementation of the recommendations of that study.
We will encourage diversity in our neighborhoods. The City should use its housing and land use policies to encourage neighborhoods that have a diverse range of home sizes and types, and avoid concentration of low income households. Diversity builds unique and resilient neighborhoods, increases community involvement, and expands support for neighborhood schools. From an economic development point of view, housing and price-point diversity provides solid, affordable residential areas for members of the labor force at all levels of income and tends to encourage upward mobility.
We will support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative. The City should continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and consider permanent funding for the Neighborhood Stabilization Program to help reverse decline and create valuable places.
We will require good neighborhood design. Good neighborhood design can increase citizens’ access to jobs, housing, schools, and daily needs. It will also contribute to positive perceptions of neighborhoods, thereby encouraging investment.
New citywide site design and building regulations should establish basic functional requirements for features that produce good urban places. These include encouraging active transportation; integrating residential areas and activity centers; implementing good basic standards for signage, building materials, and site planning; and developing public spaces designed for desirable person to person contact.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will reduce crime and improve the sense of security throughout the city. We will establish and expand crime prevention partnerships with neighborhoods, visible patrols with a high degree of community contact and interaction in targeted areas, and youth programs. Other components of this effort should include regular evaluation of police staffing needs and expansion of such preventive measures as elimination of nuisances like abandoned buildings and integration of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design in the project review process. The liveokc and serveokc elements also provide initiatives that address public safety issues.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will provide incentives and investments that produce a favorable environment for private investment on underutilized sites. In Oklahoma City, we have tended to view land as an inexhaustible and disposable resource, reducing the desirability of older areas and decreasing land values, while expanding the city’s boundaries outward. The surveys and process of planokc show that this view is also changing, as citizens place a high value on using existing infrastructure and urban land effectively and rebuilding established neighborhoods. Preferences are also changing, as many families appreciate active urban places like Midtown and Automobile Alley that provide living, shopping, entertainment, and work places with good walking, bike, and transit access. Effective use of existing land resources is a central principle of Chapter Two’s land use vision.
Redevelopment and infill depend on major private investment. City policy and action can create the conditions that help this private investment occur.
Directions for these policies include:
- Site assembly. Multiple property owners, often absent or very difficult to find, can make it impossible to put together sites for redevelopment. The City can help private developers by helping them assemble sites.
- Infrastructure and street improvement. While redevelopment and infill sites usually have infrastructure, these facilities are sometime obsolete and require improvement. Redevelopment can provide the impetus for making necessary public investments in these assets.
- Public investments. Parks, schools, civic facilities, pedestrian and bicycle facilities, streetscapes, and other amenities can provide anchors that are proven to generate private development. The Bricktown Canal is an excellent example of a public amenity that has paid for itself many times over in private investment. Similarly, the new MAPS 3 Park will inevitably become the catalyst for the Core to Shore redevelopment.
- Code improvement and proactive enforcement. Poor property maintenance, unattractive and cluttered signs, and public or operating nuisances can degrade the value of surrounding property and discourage reinvestment. Updated ordinances and consistent, enforcement will minimize these disincentives and create momentum for new private development.
Establish new incentives and raise awareness of existing incentives that stimulate the preservation and rehabilitation of historic resources. Incentives could include:
- Preservation easements, low-interest or forgivable rehabilitation loans, and Tax Increment Financing Districts for historic buildings, sites, and districts.
- Tools and practices for public/private partnerships to ensure the preservation and retention of top-priority historic resources whose deterioration or demolition would present an irreparable and highly significant loss to the City and beyond.
- Existing city, state, and federal tools and incentives for rehabilitation, including state and federal tax credits for certified rehabilitation.
- Expedited review process for projects involving infill sites.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
Prioritize and concentrate development where facilities, infrastructure, and services have capacity and in areas where the Police and Fire Departments are best able to respond. Guide the location and timing of development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Oklahoma City’s workforce is well-educated, highly skilled, motivated, creative, healthy, and culturally diverse.
We will develop new site and building design guidelines and regulations and increase property maintenance standards and enforcement. Better community appearance is largely based on raising people’s expectations of how they should both develop and maintain their own property. New standards will establish better minimum expectations for how buildings and sites should look and function. These new standards should not add burdens or excessive costs, but should establish new basic assumptions about how we build, whether our projects are small convenience stores or a large mixed use developments. We often judge community appearance by the routine rather than the unique.
The same holds true for private property maintenance. Maintenance quality is contagious – care produces more care, and neglect produces more neglect. Again, our standards, technical assistance programs, and ultimately enforcement should move toward a higher level of care in our own individual environments.
We will improve the appearance of our streets. The public environment, all too often viewed as nobody’s responsibility, should in fact lead the way in creating upgraded appearance standards. In the planokc Business Survey, local businesses overwhelmingly cited “improving the appearance of major commercial streets” as the most important way to improve the appearance of the city.
After 2007 Bond Election resurfacing projects are complete, the City will assess the need for additional funds for citywide road maintenance beyond average annual expenditures. The assessment will be based on citizen satisfaction surveys, traffic volumes, and street condition data maintained by the Public Works Department. The City will also explore the feasibility of burying existing utility lines where possible and requiring all new utility lines to be buried. These efforts toward improving the quality of basic street appearance will continue and will encourage adjacent property owners to follow suit.
We will reduce litter and graffiti. The City will enhance litter and graffiti control through public awareness efforts and stricter laws and enforcement. Active code enforcement should be increased in targeted areas, including retail plan areas, special districts, and areas that are part of the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative (SNI).
We will reduce the impact of sign pollution. The City will update the sign code to reduce the visual impact of signs. Good standards actually improve readability and communicate business messages better than a cacophony of competing signs. The City can also explore reduction of sign pollution through amortization (gradual elimination as the service lives of signs expires) of existing signs that do not conform with new requirements.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Initiate efforts to educate the public regarding programs that provide assistance for neighborhood clean-up efforts. Such efforts could include the following:
- Provide assistance to residents to make housing and neighborhood improvements and provide training in property maintenance skills.
- Develop and organize volunteer programs (such as adopt-a-street, adopt-a-park, and neighborhood clean-up days) and/or coordinate efforts to obtain grant funding to establish community clean-up programs in neighborhoods where inadequate property maintenance is prevalent.
- Publicize Bulk Waste Days and/or explore the possibility of adding more days/increased frequency.
- Develop a list of outside funding sources that could be used for property maintenance and make this information available to all citizens, especially those in targeted low-income areas.
- Establish public educational programs and advertising campaigns to discourage littering. Education should begin at the elementary level and continue through the adult level.
Intensify code enforcement in areas where specific and/or chronic violations have detrimental impacts on community appearance. Such efforts could include:
- Implement stricter enforcement of property maintenance regulations and consider more significant penalties for violations.
- Increase emphasis on the enforcement of littering laws. Impose fines against littering in a uniform and consistent manner to reinforce a public perception that littering does carry a definite risk.
- Immediately report and ensure expedient removal of graffiti that is visible from interstate highways and other important/designated viewshed corridors.
Incorporate natural features (such as ponds, lakes, streams, rock outcroppings, stands of mature trees, and/or sizable individual trees) into the design of all residential, commercial, and industrial projects rather than eliminating, hiding, or limiting access to those features.
Develop and adopt new standards to minimize the detrimental appearance of accessory utility equipment (i.e. transformers, cable cabinets, telephone cabinets, utility meters, valves, etc.) by integrating them into less prominent areas of the site design or by screening them with landscaping, artistic features, or architectural materials compatible with the primary structures. If not encouraged, artistic embellishment (creating urban ambiance with imaginatively designed/painted screens) should not be prohibited. Ensure that such facilities are situated so that they do not impede pedestrian access.
Facilitate and coordinate burial of overhead power and communications distribution lines.
Develop standards/guidelines that require architectural articulation, variety, and interest on large structures adjacent to public streets by limiting long stretches of unbroken wall planes.
Use light fixtures and street furniture in the public right-of-way that complement established or evolving cultural or design districts.
Establish a funded beautification program and source of funding to provide facade and landscaping enhancements along targeted industrial corridors.
Establish incentives such as a simplified permitting process, reduced application fees, and special recognition for projects that:
- Utilize best management practices or other low-impact development methods for storm water management.
- Bring buried streams to the surface and restore riparian habitat.
- Install bridge systems instead of culverts for stream crossings to help maintain the natural ecosystem associated with the stream.
Revise the landscape ordinance to include the following:
- Define terms such as invasive species, exotic/non-native species, and native/indigenous species
- Require removal of invasive species from existing sites, and prohibit such species from being planted or maintained in new development.
- Provide a reference list of native plants and drought-tolerant plants.
- Provide incentives for using native and drought-tolerant plants and disincentives for using high-water plants and turf grass.
- Establish requirements for using design practices that minimize the need for supplemental irrigation.
Develop and adopt a tree preservation ordinance that achieves the following:
- Defines methods of preservation;
- Defines situations where preservation of trees is mandatory versus optional;
- Establishes incentives for tree preservation;
- Establishes mitigation options if preservation cannot be accomplished; and
- Establishes penalties for unauthorized tree removal.
Preserve mature healthy trees and incorporate them into the design of new development or redevelopment projects to the greatest extent possible. Include provisions and best management practices to ensure proper tree protection throughout the construction process. Best management practices include but are not limited to:
- The use of proper pruning techniques;
- Appropriate watering;
- Installation of protective fencing at the drip lines of trees or groups of trees;
- Designated material storage areas; and
- Approved equipment and vehicle parking and maintenance areas.
Modify development and subdivision regulations, and City policies to minimize alteration of natural landforms and native vegetation and maximize retention of distinctive natural features for public and private projects.
Preserve overall landscape character and natural landforms (rolling hills, native vegetation, etc.) to the greatest extent possible.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Increase proactive code enforcement efforts, including litter control, and graffiti clean-up in targeted areas (e.g., SNI areas, and special districts).
Require all new utility lines to be buried and bury existing utility lines when possible (e.g., when roads are widened).
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
Commercial buildings should be built at the street rather than behind a parking lot in order to promote pedestrian circulation, multipurpose shopping trips, and walkable and attractive streetscapes. Large-scale commercial buildings with parking in front should screen parking lots with the coordinated development of out-parcels (pad sites) and with landscaping.
Amend the landscape ordinance to increase the number of trees and landscaped islands required in parking lots.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
We will continue to create and enhance amenities such as parks, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. The MAPS programs have generated tremendous momentum for our city, but we cannot rest on past accomplishments. Instead we must continue our efforts to create great places at neighborhood, citywide, and street levels. In the future, these amenities will include public spaces, street corridors, transit facilities, cultural and recreational attractions, special districts, and community gateways.
Connections like the Bricktown Canal connecting Bricktown and the riverfront, the SkyDance Bridge, the riverfront greenway and in the near future the modern streetcar and trails projects have been as important as individual destinations. Signature transportation corridors are also vital parts of the cityscape. To this end, the City will explore the feasibility of installing and maintaining landscaping and public art along key transportation corridors to enhance the City’s appearance, image, and sense of place. Features like gateways can mark the transition from one district to another, and help emphasize the distinctiveness of Oklahoma City’s special districts.
We will build on the success of our special districts to attract residents and businesses. Downtown, Bricktown, Midtown, the Plaza, Deep Deuce, the Paseo, Stockyards City, Automobile Alley, Heritage Hills, and others are important districts that contribute strongly to Oklahoma City’s sense of place and identity. Future districts like Core to Shore will contribute to Oklahoma City’s collection of urban places. The City will continue to invest in features that make these existing and future places centerpieces of our community by catalyzing development, increasing land use diversity, building quality of life amenities, and promoting family-friendly features.
Catalyzing development. Urban housing has proven to be a staple of downtown and urban district revitalization. Residential development not only creates a market for more local services but also creates a comfortable environment that brings other people in from around the city and region. The City will continue to guide housing development to urban districts to increase activity and support demand for new retailing. Special focuses will include Downtown and surrounding areas and the new Core to Shore neighborhood. The City should also place a priority on establishing a signature retail development or a retail/housing mixed-use development.
Diversifying land use. Increasing land use diversity in urban districts will help attract and retain visitors and support development momentum. For example, Bricktown’s first development phases concentrated on offices, bars, and restaurants. But the historic district has become more vital with nearby housing, retailing at different scales, and hospitality uses, and this type of diversification should accelerate. In special districts, City policy should attract a balance of retail, residential, employment, and recreational uses.
Investing in amenities and activities. The City can strengthen downtown’s and other districts’ senses of place and increase activity by encouraging and investing in more public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Building family-friendliness. We can help attract and retain a variety of households to downtown and other urban districts by promoting and enhancing them as family-friendly places to live and play. Attention to street design, land uses (particularly around the downtown school) and public safety can help promote this image.
We will establish a place-making program. The City will establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city and promote both the economic and quality-of-life value of place-making investments. The program will establish partnerships and provide funding on a regular basis, including attention to small, neighborhood-scaled projects.
A significant part of this program is communicating the message of Oklahoma City’s places to the outside world. This both benefits businesses directly through promotion and supports city marketing and talent recruitment efforts. The Chamber of Commerce and Convention and Visitors Bureau are major partners in this effort.
We will designate additional special districts. The City will foster more specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to promote diversity and improve perceptions of the city. For example, Capitol Hill could grow as the center of an emerging Hispanic/Latino district, with appeal to people throughout the region. New special districts would include thematic infrastructure, amenities, design, public art, and streetscape improvements. Appropriate areas should be identified for special districts, followed by preparation of plans that establish design guidelines and strategies to capitalize on cultural meaning.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city. The program should promote the economic and quality-of-life benefits of place-making investments and should:
- Establish and maintain partnerships between the City, the private sector, and “place management” organizations.
- Provide funding and City staff support for “place management” organizations.
Create specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to enhance the diversity and perceptions of the city. Identify appropriate areas and create master plans with urban design guidelines specialized to the cultural history on display. For example, one special district could be themed for the Hispanic/Latino community. Such a district would include associated thematic infrastructure, amenity, design, public art, and streetscape improvements.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
Attract and retain young professionals to downtown and its environs to support and enhance place-making efforts and investments.
- Explore the possibility of the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce contracting with the City to facilitate and promote civic engagement and social opportunities for young professionals.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Strengthen downtown’s sense of place and activity levels by encouraging more housing, retail, public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Encourage the use of special service districts with enhanced levels of service.
Ensure adequate funds to maintain enhanced levels of service (including staffing) in places that have been or will be designated as special districts.
Initiate an effort to create and publicize a brand and image for the city. Examples of specific outcomes include:
- Coordinate with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber to advertise the city’s quality of life to national and regional audiences during major events such as the NBA playoffs, and at other appropriate times and places, and in appropriate media.
- Overhaul of City logo (buses, police cars, streetcar)
- Overhaul of City Website
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Enhance Downtown Oklahoma City’s prominence by maintaining and increasing its role as the major business center, establishing it as a major urban residential center, and focusing on developing retail, office, entertainment, and arts and cultural uses.
Work to establish a critical mass of retail uses in the downtown area. A lifestyle center or mixed-use town center presents the most viable option for a major infusion of retail into downtown.
We will promote redevelopment of vacant or under-used sites. Infill development on vacant, under-utilized, and brownfield sites should receive special attention through changes to land use regulations, infrastructure upgrades in target neighborhoods, incentives, favorable tax policies, expedited processing, and greater flexibility. The City recently produced a study on vacant and abandoned buildings to help address this issue and will continue to pursue implementation of the recommendations of that study.
We will encourage diversity in our neighborhoods. The City should use its housing and land use policies to encourage neighborhoods that have a diverse range of home sizes and types, and avoid concentration of low income households. Diversity builds unique and resilient neighborhoods, increases community involvement, and expands support for neighborhood schools. From an economic development point of view, housing and price-point diversity provides solid, affordable residential areas for members of the labor force at all levels of income and tends to encourage upward mobility.
We will support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative. The City should continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and consider permanent funding for the Neighborhood Stabilization Program to help reverse decline and create valuable places.
We will require good neighborhood design. Good neighborhood design can increase citizens’ access to jobs, housing, schools, and daily needs. It will also contribute to positive perceptions of neighborhoods, thereby encouraging investment.
New citywide site design and building regulations should establish basic functional requirements for features that produce good urban places. These include encouraging active transportation; integrating residential areas and activity centers; implementing good basic standards for signage, building materials, and site planning; and developing public spaces designed for desirable person to person contact.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will form partnerships and implement efforts that create settings that advance educational achievement. The challenges facing Oklahoma City’s public education system are daunting. The stakes of success are great, given the need to capitalize on the potential of our youth and the importance of quality schools in achieving this plan’s overall goals. School policy and curriculum are far beyond the scope of planokc. But City policy can help provide safe and nurturing environments that remove at least some of the pressures and distractions that keep kids from learning. Both this element and liveokc address people’s expectation to live in safe neighborhoods.
The City’s Strong Neighborhoods Initiative (SNI) program, for example, can establish recreational, fire safety, public safety, and character building programs for schools. This program to create supportive environments includes initiatives discussed in previous elements – parks and recreational programs, neighborhood development, stabilizing social fabric, and many others. Direct partnerships with schools can also be extremely effective. The City can initiate strong connections between schools and the business community to improve education, training, and retraining. Finally, a city that includes 27 school districts and has helped fund projects in many of them can help initiate regional cooperation and some sharing of responsibilities.
Facilitate communication among the 23 school districts in order to develop more arts education opportunities for the children in our community.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Coordinate with Strong Neighborhoods Initiative to provide recreational, fire safety, public safety, and character building programs in schools.
Identify ways to establish/strengthen relationships and partnerships between schools and the business community as one method to improve student education and outcomes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Oklahoma City has many desirable and recognizable places that attract visitors, residents, and businesses.
We will design and implement a bicycle route system based on getting people to priority destinations. The current Bicycle Transportation Plan provides a two-phased network of potential bike routes. This network is based on evaluating various streets for bicycle suitability, and provides a solid foundation for implementation. The system should now be refined by considering destinations and designing routes that assemble on-street segments and trails into an entire network that serves multiple destinations.
We will incorporate appropriate support features such as bike parking and wayfinding signage into the system. On and off-street facilities function best with relatively inexpensive support facilities like parking and information graphics. Zoning ordinances and cost-sharing programs can both require, and encourage through incentives, bike parking for appropriate land uses, like major commercial, multi-family, and mixed use development. Desirable city actions include installing bike parking in public parking structures and business districts and encouraging bike “corrals” in which one parking space is dedicated to bike parking in neighborhood business districts.
Identify areas that could be used to establish a greenbelt network throughout the City that connect major employment centers, commercial sites, parks, and key locations within major residential neighborhoods. Use the greenbelt as the backbone for a bicycle trails network which all other bicycle trails feed into.
Create and implement a citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan that addresses riders of all levels.
Require the placement of secure, properly positioned bicycle parking within multi-family and commercial development, and in all public parking garages.
We will design or retrofit trails to provide convenient and barrier-free access to adjacent streets and major destinations. A trail that provides miles but does not connect to its surroundings may provide benefits to people seeking workouts, but it fails in its transportation mission to move people to places. In addition, poor access or visibility to and from surroundings can create public safety problems as well. We must design new trails and retrofit existing trails to provide frequent and comfortable access to wayside destinations and streets, with clear signage that helps orient users to their location.
Create a standards for trails based on industry standards, “Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design” principles, expected use, and surrounding land uses.
Acquire easements in new and existing developments to develop and connect trails.
Establish connections between parks, residential areas, and other points of interest by constructing additional bike routes, trails and pedestrian paths to meet the growing demands for recreation and alternative transportation routes.
Require that new development tie into the park and trail system by providing linkages to existing parks or dedicating new park land. Connect existing parks and neighborhoods to create a continuous system of open spaces, for example along stream corridors.
We will develop and implement a strategic plan for the city’s pedestrian network, building on the foundation of the 2013 Sidewalk Master Plan for MAPS 3. The 2013 Sidewalk Master Plan was a significant step forward, including an analysis of pedestrian demand in different parts of the city. However, its primary purpose was to identify priority projects for a specific sidewalk construction category of MAPS 3. Many of these projects supply new sidewalks along major corridors with high demand, based on a systematic rating system. These are extremely important, but many other problems remain, including:
- Neighborhood sidewalks on local streets that provide access to destinations such as schools and transit stops.
- Barriers to pedestrian travel such as major intersections, long arterial street crossings, and signal timing.
- Relationship of sidewalks to other parts of the active transportation network, including multi-modal streets, bicycle facilities, transit, connections to adjacent development, and trail access.
These issues require an expanded pedestrian system plan that:
- Identifies a Complete Streets Network prioritizing pedestrian corridors that should be developed and funded as part of the city’s transportation program. The MAPS 3 and previous bond issue study provide a starting point for this network.
- Establishes standards for local sidewalk coverage and a process to evaluate pedestrian service on a neighborhood by neighborhood basis. An example of such a standard would be provision of a complete and well-maintained web of sidewalks within a 1/2 mile walking radius of elementary and middle schools.
- Identifies key pedestrian barriers that obstruct access for important user groups, including children and older adults. This effort should include standards and techniques to minimize these barriers.
- Relates other active modes or facilities to the sidewalk network.
- Provides a phased implementation program that may include individual categories of funding, such as neighborhood target areas and major network investments.
Enhance the safety and walkability of the sidewalk network through:
- Establishing a citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan that includes an inventory of sidewalk locations and conditions, and priorities for enhancement.
- Implementing sidewalk improvements through future bond issues, CIP projects or other sources of funding as prioritized in the citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan.
- Maintaining currency of the citywide bicycle and pedestrian master plan.
- Explore the feasibility of the City assuming responsibility for sidewalk maintenance.
Establish requirements for providing alternate pedestrian routes when construction activity prohibits use of existing facilities.
We will implement sidewalk requirements for both land use typology areas (LUTAs) and street typology standards in city development ordinances and standard practice. Different LUTAs will have different levels of pedestrian activity. Thus, different solutions may be applied to achieve the overall goal of providing appropriate pedestrian service. For example, a loop of local streets in an Urban-Low Intensity LUTA and a street grid in an Urban High-Intensity area will require different approaches to achieve areawide service. Different types of streets also have different sidewalk requirements based on their function and context. City design standards and implementing ordinances should reflect these differences in width, setback, connection, density, and presence of alternatives like trails or other off-street paths.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Prioritize street maintenance projects in the Capital Improvement Plan based on the Public Works Department’s street condition data and traffic volumes.
We will update and improve the city’s landscape ordinances. Improvements will address the objectives of improving community appearance, minimizing land use incompatibilities, improving air quality, and managing the city’s micro-climate. These ordinances also must address the long-term by including maintenance in their requirements. This starts with requiring native trees and plants that are adapted to the central Oklahoma climate. Use of native and drought tolerant plants lowers irrigation requirements, lowers cost, and conserves water.
We will educate the public on the use of native materials and proper maintenance. Preconceived notions of an aesthetically pleasing landscape often lead to the use of high-maintenance materials like non-native grasses. To overcome these inclinations, educational materials, demonstration gardens, and targeted corridor improvement projects should advertise both the beauty and benefits of proper installation and maintenance of native landscapes.
We will develop better procedures for reporting, citing and enforcement of violations. The current system for enforcement of landscaping requirements is complaint based, resulting in inconsistent maintenance on private properties and along many public rights-of-way. Improved procedures for code enforcement affecting private properties and additional funding sources for public areas should establish a clear level of expectation across the city.
Routinely assess the City’s development standards, design guidelines, and development review procedures to ensure that they reflect current trends in best-practice and allow for innovative design techniques and evolving methods in low-impact development.
Enhance existing development standards and establish design guidelines for areas outside of the City’s existing Design Review Overlay Districts. Development standards and design guidelines could include the following provisions:
- Minimize views and prominence of parking lots in relation to structures on a site.
- Sense of proportion (street width to building height, human scale)
- Pedestrian orientation of structures and architectural detailing/fenestration
- Terminated vistas
- Reduce the predominance of residential garages in the design of the front facades of single-family residences.
- Inclusion of front porches into the design of residential structures.
- Internal orientation of parking facilities and garages in multi-family developments.
- Improved pedestrian safety and enhanced pedestrian access through parking lots.
Develop distinctive standards for different types and categories of walls and fences, emphasizing durability, aesthetics, and visual continuity in materials and design with particular consideration of zoning classification.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Incorporate natural features (such as ponds, lakes, streams, rock outcroppings, stands of mature trees, and/or sizable individual trees) into the design of all residential, commercial, and industrial projects rather than eliminating, hiding, or limiting access to those features.
Establish streetscape standards requiring attractive entry features and the provision of accessible common open space in new neighborhoods.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Develop and adopt new standards to minimize the detrimental appearance of accessory utility equipment (i.e. transformers, cable cabinets, telephone cabinets, utility meters, valves, etc.) by integrating them into less prominent areas of the site design or by screening them with landscaping, artistic features, or architectural materials compatible with the primary structures. If not encouraged, artistic embellishment (creating urban ambiance with imaginatively designed/painted screens) should not be prohibited. Ensure that such facilities are situated so that they do not impede pedestrian access.
Enhance the City’s Landscape Ordinance by accomplishing the following objectives:
- Add guidelines and recommendations for landscape design that minimizes the need for supplemental irrigation.
- Clarify responsibilities and standards for landscape maintenance, including within public rights-of-way.
- Incentivize the use of drought-tolerant and native plants.
- Restrict the use of turf grass to the greatest extent feasible.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards for parking lots and consider making revisions that would result in more landscape buffering on parking lot fringes and more internal landscaping.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards to determine whether new standards should be adopted to help screen or buffer parking structures.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards in comparison to best practices and peer cities to determine whether minimum site landscaping standards should be revised and/or restructured to result in increased landscaping.
Consider the adoption of improved requirements to screen parked vehicles from view with enhanced landscaping, berming, low screen walls, and existing or proposed buildings, or some combination of those elements.
Establish a funded beautification program and source of funding to provide facade and landscaping enhancements along targeted industrial corridors.
Improve landscape design, installation, and landscape maintenance compliance through the following actions:
- Produce informational materials and work with local media to publicize the benefits of limiting turf areas (e.g. reduced water use, less mowing) and highlight the positive effects on property values and aesthetics that result from proper installation and maintenance of landscaping.
- Develop a program, including informational outreach, to inform property owners of their responsibilities to maintain right-of-way areas, the procedures for enforcement, and the applicable fines.
- Identify specific corridors with the worst landscape maintenance conditions and initiate coordinated clean-up programs in those locations.
- Install demonstration gardens/landscapes in select civic/public locations to provide practical examples of how to integrate drought tolerant and low maintenance plants in commercial and residential installations.
- Improve efficiency and effectiveness of the process for reporting, citing, and proactive enforcement violations for maintenance and compliance with landscape requirements.
- Explore the establishment of landscape improvement/maintenance districts where property owners are assessed a pro-rata share of the costs to properly and uniformly maintain landscaping within the district boundaries.
Develop a Master Streetscape Program to improve the appearance along major arterial streets. The program should outline methods for establishing a uniform streetscape appearance (with distinctive designs for individual streets or classifications of streets) through appropriate tree placement, species, and spacing, and coordinating the location of street trees in proximity to utilities, sidewalks, street lights and structures, and appropriate sidewalk designs. Differentiation in streetscape designs could be designated by street typology, designated areas, or other factors.
Using performance standards related to flow quantity, quality, and pattern, modify development regulations, codes, and policies to support the use of green infrastructure/low impact development techniques to mimic natural systems for developments within aquifer recharge zones with moderate or high vulnerability or in areas where streams and riparian areas have been channelized or developed (primarily in the Downtown, UH, and UM LUTAs). Low impact development techniques include but are not limited to:
- Onsite treating or filtering of stormwater contaminants.
- Discharging run-off as sheet-flow after passing through grassy or vegetated open space areas, rather than discharging run-off through concentrated outfalls.
- Creating attractive open space amenities that double as stormwater detention, retention, and / or filtering systems.
- Utilizing pervious pavement, pavers, or asphalt in appropriate locations (i.e. sidewalks, parking spaces, trails, patios, etc.).
- Utilizing planters (at grade or raised), vegetated landscape strips adjacent to roads and parking areas, and alternative curbing designs (allowing stormwater to easily move from impervious areas to pervious areas), to encourage stormwater infiltration and temporary detention.
- Rain Gardens
- Bioswales
- Green streets and alleys
- Green roofs
- Rooftop collection
- Underground detention
- Increased tree canopy preservation/tree planting
- Land/open space conservation
- Cluster development
Revise development regulations to require the following factors to be addressed in development and redevelopment proposals:
- Preservation of existing natural resources, such as wooded areas, habitat areas, and floodplains.
- Utilization of natural treatments and methods to stabilize or rehabilitate stream and river banks as a means to preserve downstream habitats.
- Integration of a variety of native or compatible non-native, non-invasive plant species.
- Mitigation of impacts of development on habitat, wildlife corridors, riparian and littoral areas, and water quality, through actions such as restoration or re-vegetation of disturbed natural areas and replacement of trees/habitat on-site or off-site.
- Management of invasive plant and animal species.
- Management and maintenance of natural areas, common areas and drainage areas.
- Impact on surface and groundwater supply.
- Impact on water quality caused by land uses and activities.
- Impacts on floodplains, riparian and littoral areas and wetlands and areas with significant landforms.
Revise the landscape ordinance to include the following:
- Define terms such as invasive species, exotic/non-native species, and native/indigenous species
- Require removal of invasive species from existing sites, and prohibit such species from being planted or maintained in new development.
- Provide a reference list of native plants and drought-tolerant plants.
- Provide incentives for using native and drought-tolerant plants and disincentives for using high-water plants and turf grass.
- Establish requirements for using design practices that minimize the need for supplemental irrigation.
Preserve natural habitat, maintain wildlife food sources, and reduce the risk of propagating invasive plant species by utilizing vegetation native to Oklahoma, preferably central Oklahoma, for all mitigation and habitat restoration efforts associated with new development and redevelopment projects, public and private, to the greatest extent possible.
Establish an Urban Forestry Program and City Urban Forester position to achieve the following:
- Measure and monitor tree canopy coverage and habitat on a regular basis so that any policies, programs, and regulations may be adjusted accordingly as situations change. Establish a process to maintain current data.
- Develop and maintain regulations, policies, processes, and programs that focus on protection and preservation of native trees.
- Provide assistance with proper tree selection, location, and maintenance to prevent power outages, reduce property damage, and coordinate emergency response during natural disaster events (excessive snow and ice, tornadoes, etc.), address the urban heat island effect, and reduce energy costs, etc.
- Establish programs such as tree give-aways, neighborhood planting programs, and education workshops.
- Provide resources to the public about tree selection, management, and care.
- Seek grant funding for community tree planting to improve City parks, publicly maintained rights-of-way and other areas of the city.
- Inventory the City’s street trees and develop a tree replacement program.
- Partner with volunteer and nonprofit organizations to recruit volunteers for tree planting and maintenance and to coordinate community-wide tree planting efforts.
Develop and adopt a tree preservation ordinance that achieves the following:
- Defines methods of preservation;
- Defines situations where preservation of trees is mandatory versus optional;
- Establishes incentives for tree preservation;
- Establishes mitigation options if preservation cannot be accomplished; and
- Establishes penalties for unauthorized tree removal.
Pursue methods to reduce the impact of the urban heat island effect on Oklahoma City by:
- Establishing a minimum canopy coverage requirement over paved surfaces such as parking lots.
- Instating a “continuous canopy” requirement for new streets and street reconstruction projects.
- Promoting the use of building and roofing materials that reduce heat island effects.
Modify development and subdivision regulations, and City policies to minimize alteration of natural landforms and native vegetation and maximize retention of distinctive natural features for public and private projects.
Establish development regulations that help improve air quality, including:
- Specifying construction controls that reduce airborne dust;
- Increasing landscaping and tree planting to absorb carbon dioxide and air pollutants; and
- Encouraging development patterns and densities that support alternative modes of transportation in the urban LUTAs.
We will reinforce the city’s existing cultural districts and expand the network into new areas. The city’s cultural districts have specific zoning and urban design regulations. They are “experience centers” that strengthen their surrounding neighborhoods. This program should be enhanced in two ways:
- Reinforcing existing districts through small-scale public realm projects (identifying graphics, sidewalk and streetscape improvements, wayfinding); cross-marketing; and integration into an “active loop,” linking the nodes with pedestrian and bicycle routes.
- Expanding the program to new cultural districts, including the four pending districts and others that might be identified through the historic preservation plan and other neighborhood planning processes.
Ultimately, the culture districts should be viewed as, and evolve, into a connected network of attractions.
Ensure that public art is integrated into the planning and implementation for key initiatives such as Core to Shore, Project 180, MAPS 3 and other City projects as well as downtown, neighborhoods, cultural districts, and commercial districts.
Make it easier for arts and cultural projects to navigate the City’s design review, zoning, licensing, and permit processes.
Provide a centralized area(s) for artists to live and work (e.g. Paseo, Film Row) by targeting districts within the city that have become centers for all types (performing, visual, literary, etc.) of art.
Coordinate efforts to educate the public regarding the location of all public art installations and potential locations for future installations. Such efforts could include:
- Producing educational materials for each newly commissioned work in the City’s Public Art collection and making these available to the publiC.
- Providing educational materials detailing the locations of public art installations, such as walking tour guides, podcasts, physical markers, or web-based maps.
- Developing and adopting a Physical Master Plan to promote public art “districts” for key areas, including the Riverfront, downtown, the airport.
- Establishing a collection management system for public art to catalogue artist, location, condition, value and other details of public interest.
Identify the economic value of cultural resources in attracting tourism and reinvest a share of tourism revenue to sustain and expand these resources.
Showcase local talent by incorporating the work of artists into City activities such as wall displays, public information efforts, and special events.
Explore the implementation of the following efforts to increase the economic impact of cultural activities and arts programs:
- Efforts organized by Oklahoma City Office of Arts and Cultural Affairs:
- Formalize neighborhood-based cultural economic development plans
- Work with groups interested in establishing a vacant storefronts program with artists
- Establish a public art program to include local artists
- Coordinate a master list of artist opportunities
- Convene organizers of events and festivals to share knowledge and resources
- Coordinate use of publicly-owned space for use by artists.
- Efforts coordinated by Cultural Development Corporation of Central OK (CDCOK):
- Clarify roles among arts service entities
- Expand business skills training for artists
- Build capacity among nonprofits for fiscal/project sponsorship
- Strengthen partnerships and engagement with higher education resources
- Provide artist fellowships in partnership with philanthropies
- Evolve CDCOK into an economic development entity
- Efforts led by artists:
- Build a multi-disciplinary artist network
- Conduct an Annual Artist Summit
- Pilot art sales program based on the Community Supported Art model
- Recognize outstanding contributions by artists to the region
Use light fixtures and street furniture in the public right-of-way that complement established or evolving cultural or design districts.
Create a public outreach program designed to explain and promote the benefits of urban design principles and design review districts.
Develop and adopt a Cultural Heritage Plan with the objective of reviving, explaining, commemorating, and integrating the City’s cultural history through its cultural districts, landmarks, and facilities. The plan could be used to accomplish the following:
- Develop a cultural map of the City identifying the location of all cultural resources, landmarks, and cultural districts. Convert this information into maps and guides for residents and visitors so they may visit Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites using their preferred transportation method (walking tours, bike tours, river tours, transit routes, driving routes, etc.).
- Develop an effective and attractive cultural signage program, including kiosk type directories in pedestrian areas, coordinated and designed to direct residents and visitors to major art and cultural sites or districts in the City. The program may also include such items as markers and temporary seasonal or event-based banners.
- Examine opportunities to maintain and expand existing art and cultural facilities and to attract new ones. Coordinate a cultural needs assessment to determine future space needs, cultural variety potential, and potential sites to accommodate improvements.
- Protect and facilitate the enhancement of existing and emerging arts and cultural districts throughout the City to preserve the unique character of these diverse neighborhoods.
- Assess the accessibility of the City’s art and cultural facilities and resources to determine if improvements are necessary. Recommend ways to enhance access and linkages to art and cultural facilities and resources via new sidewalks, trails, and pedestrian amenities and/or expanded transit service.
Establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city. The program should promote the economic and quality-of-life benefits of place-making investments and should:
- Establish and maintain partnerships between the City, the private sector, and “place management” organizations.
- Provide funding and City staff support for “place management” organizations.
Create specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to enhance the diversity and perceptions of the city. Identify appropriate areas and create master plans with urban design guidelines specialized to the cultural history on display. For example, one special district could be themed for the Hispanic/Latino community. Such a district would include associated thematic infrastructure, amenity, design, public art, and streetscape improvements.
We will update and enhance design standards and guidelines that apply to areas outside existing Design Review Districts. The Community Appearance Survey identified residents’ support for pedestrian-oriented amenities and human-scaled development. Appealing living spaces combine ingredients such as street and sidewalk environments, properly scaled buildings, visual interest, well-placed and designed furniture, and other elements. Updated standards will address the lessons and results of the Community Appearance Survey and provide practical and cost-effective design guidance and choices. They will address scale, materials, variety, visual quality, signs and graphics, and environmental sensitivity. The effort to update and enhance these standards will involve all stakeholders. They will also be routinely reviewed against best practices, allowing innovative design techniques and incorporating new techniques in low-impact development.
We will remove obstacles to greater design variety within residential construction. Community Appearance Survey participants strongly supported residential designs that included front porches and minimized garage exposure. These findings and the Housing Demand Study results both indicated interest in smaller lots and greater housing product variety, especially among younger households. Both the sustainokc and liveokc elements speak to the need for more diverse housing types. Design guidelines should illustrate ways to achieve higher densities in configurations that are consistent with citizen preferences. In addition, city standards and regulations that discourage design features like rear-loaded garages or mixed density housing should be modified.
We will improve regulation of sign scale, number, and placement. Sign images were the lowest rated urban design element in the Community Appearance Survey. New sign regulations will be fashioned as part of land development ordinance revisions to reduce clutter and increase legibility. Code direction will include limits on the number of permitted signs, increased use of ground signs, location standards, better overall size limitations, and requirements for sign master plans for large projects.
We will develop a Great Streets Program to improve the appearance of major arterial streets. Oklahoma City has implemented a Downtown Streetscape Master Plan, and should extend the concept of cohesive standards for landscaping, lighting, street furniture, sidewalk and crosswalk design, utility placement and treatment, and other elements to other streets of civic importance. This effort is related to the street typology concept presented in Chapter Two. The master planning effort will identify corridors of visual significance and establish vocabularies of materials and treatments that will be applied during widenings or reconstruction projects or on a stand-alone basis.
Routinely assess the City’s development standards, design guidelines, and development review procedures to ensure that they reflect current trends in best-practice and allow for innovative design techniques and evolving methods in low-impact development.
Enhance existing development standards and establish design guidelines for areas outside of the City’s existing Design Review Overlay Districts. Development standards and design guidelines could include the following provisions:
- Minimize views and prominence of parking lots in relation to structures on a site.
- Sense of proportion (street width to building height, human scale)
- Pedestrian orientation of structures and architectural detailing/fenestration
- Terminated vistas
- Reduce the predominance of residential garages in the design of the front facades of single-family residences.
- Inclusion of front porches into the design of residential structures.
- Internal orientation of parking facilities and garages in multi-family developments.
- Improved pedestrian safety and enhanced pedestrian access through parking lots.
Establish a list of preferred and discouraged building materials for all zoning districts.
Develop distinctive standards for different types and categories of walls and fences, emphasizing durability, aesthetics, and visual continuity in materials and design with particular consideration of zoning classification.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Make it easier for arts and cultural projects to navigate the City’s design review, zoning, licensing, and permit processes.
Establish new incentives and raise awareness of existing incentives that stimulate the preservation and rehabilitation of historic resources. Incentives could include:
- Preservation easements, low-interest or forgivable rehabilitation loans, and Tax Increment Financing Districts for historic buildings, sites, and districts.
- Tools and practices for public/private partnerships to ensure the preservation and retention of top-priority historic resources whose deterioration or demolition would present an irreparable and highly significant loss to the City and beyond.
- Existing city, state, and federal tools and incentives for rehabilitation, including state and federal tax credits for certified rehabilitation.
- Expedited review process for projects involving infill sites.
Develop and implement a Comprehensive Public Art Master Plan to:
- Establish goals and a framework for the rational development of a public art program for Oklahoma City
- Integrate public art into each of the City’s key development initiatives and community sectors with a plan for both permanent and temporary placement processes that facilitate new public art coordination and investment.
- Create an administrative and financial structure (with roles and responsibilities) to efficiently and effectively facilitate multi-departmental and multi-agency public art partnerships.
- Evaluate the current development/design/art review processes and make recommendations for improved and streamlined public art policies and procedures for both permanent and temporary public art (including murals).
- Involve the community in the process of public art selection to build consensus for the program.
- Include an educational component to reinforce the value of public art in the public realm for all ages and cultures.
- Provide a plan for maintaining the value and physical integrity of the City’s public art collection.
Allow the reuse of vacant storefronts as exhibition space for local artists.
Protect the unique character of National Register-listed properties or districts and local Historic Districts and ensure that development and redevelopment is compatible with historic resources and character.
Revise ordinances for design districts and design review procedures to ensure consistency in the treatment of historic properties, including the assessment of demolition proposals, the identification of historic or significant properties, and the consideration of the impact that the alteration or demolition of individual properties has on the context and continuity of the surrounding environment.
Provide incentives for private development projects that include public art.
Incorporate natural features (such as ponds, lakes, streams, rock outcroppings, stands of mature trees, and/or sizable individual trees) into the design of all residential, commercial, and industrial projects rather than eliminating, hiding, or limiting access to those features.
Establish streetscape standards requiring attractive entry features and the provision of accessible common open space in new neighborhoods.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines to promote new residential subdivision designs that orient residential neighborhoods toward adjacent complementary uses or features such as parks, schools, open space, and neighborhood serving commercial sites, promoting improved direct accessibility and more seamless community integration.
Develop and adopt new standards to minimize the detrimental appearance of accessory utility equipment (i.e. transformers, cable cabinets, telephone cabinets, utility meters, valves, etc.) by integrating them into less prominent areas of the site design or by screening them with landscaping, artistic features, or architectural materials compatible with the primary structures. If not encouraged, artistic embellishment (creating urban ambiance with imaginatively designed/painted screens) should not be prohibited. Ensure that such facilities are situated so that they do not impede pedestrian access.
Facilitate and coordinate burial of overhead power and communications distribution lines.
Enhance the City’s Landscape Ordinance by accomplishing the following objectives:
- Add guidelines and recommendations for landscape design that minimizes the need for supplemental irrigation.
- Clarify responsibilities and standards for landscape maintenance, including within public rights-of-way.
- Incentivize the use of drought-tolerant and native plants.
- Restrict the use of turf grass to the greatest extent feasible.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards for parking lots and consider making revisions that would result in more landscape buffering on parking lot fringes and more internal landscaping.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards to determine whether new standards should be adopted to help screen or buffer parking structures.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards in comparison to best practices and peer cities to determine whether minimum site landscaping standards should be revised and/or restructured to result in increased landscaping.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines that result in improvements to parking structure design including the following potential measures:
- Design parking structures to be architecturally integrated with adjoining primary structure(s).
- Include integrated storefronts or other active uses on the ground floors of parking structures that are adjacent to public sidewalks and other pedestrian plazas.
- Enhanced exterior façades of structures by integrating architectural features and materials that complement the character of the surrounding area, or screening with vegetation.
Develop standards/guidelines that require architectural articulation, variety, and interest on large structures adjacent to public streets by limiting long stretches of unbroken wall planes.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Consider the adoption of improved requirements to screen parked vehicles from view with enhanced landscaping, berming, low screen walls, and existing or proposed buildings, or some combination of those elements.
Use light fixtures and street furniture in the public right-of-way that complement established or evolving cultural or design districts.
Create a public outreach program designed to explain and promote the benefits of urban design principles and design review districts.
Develop a Master Streetscape Program to improve the appearance along major arterial streets. The program should outline methods for establishing a uniform streetscape appearance (with distinctive designs for individual streets or classifications of streets) through appropriate tree placement, species, and spacing, and coordinating the location of street trees in proximity to utilities, sidewalks, street lights and structures, and appropriate sidewalk designs. Differentiation in streetscape designs could be designated by street typology, designated areas, or other factors.
Establish development standards and design guidelines for new cultural, civic, and sporting facilities that address site design, architecture, compatibility, pedestrian-orientation and access, landscaping, and the inclusion of public art.
Using performance standards related to flow quantity, quality, and pattern, modify development regulations, codes, and policies to support the use of green infrastructure/low impact development techniques to mimic natural systems for developments within aquifer recharge zones with moderate or high vulnerability or in areas where streams and riparian areas have been channelized or developed (primarily in the Downtown, UH, and UM LUTAs). Low impact development techniques include but are not limited to:
- Onsite treating or filtering of stormwater contaminants.
- Discharging run-off as sheet-flow after passing through grassy or vegetated open space areas, rather than discharging run-off through concentrated outfalls.
- Creating attractive open space amenities that double as stormwater detention, retention, and / or filtering systems.
- Utilizing pervious pavement, pavers, or asphalt in appropriate locations (i.e. sidewalks, parking spaces, trails, patios, etc.).
- Utilizing planters (at grade or raised), vegetated landscape strips adjacent to roads and parking areas, and alternative curbing designs (allowing stormwater to easily move from impervious areas to pervious areas), to encourage stormwater infiltration and temporary detention.
- Rain Gardens
- Bioswales
- Green streets and alleys
- Green roofs
- Rooftop collection
- Underground detention
- Increased tree canopy preservation/tree planting
- Land/open space conservation
- Cluster development
Revise development regulations to require the following factors to be addressed in development and redevelopment proposals:
- Preservation of existing natural resources, such as wooded areas, habitat areas, and floodplains.
- Utilization of natural treatments and methods to stabilize or rehabilitate stream and river banks as a means to preserve downstream habitats.
- Integration of a variety of native or compatible non-native, non-invasive plant species.
- Mitigation of impacts of development on habitat, wildlife corridors, riparian and littoral areas, and water quality, through actions such as restoration or re-vegetation of disturbed natural areas and replacement of trees/habitat on-site or off-site.
- Management of invasive plant and animal species.
- Management and maintenance of natural areas, common areas and drainage areas.
- Impact on surface and groundwater supply.
- Impact on water quality caused by land uses and activities.
- Impacts on floodplains, riparian and littoral areas and wetlands and areas with significant landforms.
Revise the landscape ordinance to include the following:
- Define terms such as invasive species, exotic/non-native species, and native/indigenous species
- Require removal of invasive species from existing sites, and prohibit such species from being planted or maintained in new development.
- Provide a reference list of native plants and drought-tolerant plants.
- Provide incentives for using native and drought-tolerant plants and disincentives for using high-water plants and turf grass.
- Establish requirements for using design practices that minimize the need for supplemental irrigation.
Establish an Urban Forestry Program and City Urban Forester position to achieve the following:
- Measure and monitor tree canopy coverage and habitat on a regular basis so that any policies, programs, and regulations may be adjusted accordingly as situations change. Establish a process to maintain current data.
- Develop and maintain regulations, policies, processes, and programs that focus on protection and preservation of native trees.
- Provide assistance with proper tree selection, location, and maintenance to prevent power outages, reduce property damage, and coordinate emergency response during natural disaster events (excessive snow and ice, tornadoes, etc.), address the urban heat island effect, and reduce energy costs, etc.
- Establish programs such as tree give-aways, neighborhood planting programs, and education workshops.
- Provide resources to the public about tree selection, management, and care.
- Seek grant funding for community tree planting to improve City parks, publicly maintained rights-of-way and other areas of the city.
- Inventory the City’s street trees and develop a tree replacement program.
- Partner with volunteer and nonprofit organizations to recruit volunteers for tree planting and maintenance and to coordinate community-wide tree planting efforts.
Pursue methods to reduce the impact of the urban heat island effect on Oklahoma City by:
- Establishing a minimum canopy coverage requirement over paved surfaces such as parking lots.
- Instating a “continuous canopy” requirement for new streets and street reconstruction projects.
- Promoting the use of building and roofing materials that reduce heat island effects.
Modify development and subdivision regulations, and City policies to minimize alteration of natural landforms and native vegetation and maximize retention of distinctive natural features for public and private projects.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Ensure that new publicly financed developments – those which directly use or receive public dollars – with more than 100 units or with densities greater than 10 units/acre are located where they have easy access to frequent transit service.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Adopt design standards applicable to both new and remodeled libraries focusing on integrating the building and the site into existing neighborhoods and urban fabric, reducing their dependence on automobiles and increasing their access by other modes, especially walking, biking, and transit.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Require all new utility lines to be buried and bury existing utility lines when possible (e.g., when roads are widened).
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
In order to promote compatibility between different uses, establish standards and guidelines that ensure all developments are pedestrian-friendly and human scale at street frontages and property lines.
Develop design standards and guidelines for industrial development. Standards and guidelines should address: sensitive design and placement of buildings; screening or prohibiting outdoor storage; parcel sizes which allow for long term expansion for individual users; special landscaping requirements addressing screening and landscaping adjacent to residential areas and along highway and arterial streets; standards for the suitable location, orientation and screening of loading bays; and buffering treatments for truck access points.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will increase landscaping and design requirements in parking areas. Tree plantings and landscaping in parking lots have multiple benefits. Trees shade parking areas and decrease the heat island effect, help orient customers in large parking lots, manage circulation, and can be integrated into design elements that provide safe paths for pedestrians. In addition, parking lots should provide safe and pleasant paths from public walks and paths and transit stops to the front door of major projects and destinations. In some cases, parking lots can be designed for multiple purposes, acting as public spaces or markets during specific events. New parking design standards for Oklahoma City should incorporate contemporary practices for improved parking lot design.
We will integrate parking structures into primary structures. In appropriate high intensity settings, parking structures should be used to the maximum degree possible. When located along streets, parking structures should be activated at street level by storefronts, public art, or other details to avoid blank walls. The exterior facades of structures should be enhanced and complement the architectural features and materials of the surrounding area as a means to disguise the function of the structure and to minimize the detrimental aesthetic impacts of such facilities.
Enhance existing development standards and establish design guidelines for areas outside of the City’s existing Design Review Overlay Districts. Development standards and design guidelines could include the following provisions:
- Minimize views and prominence of parking lots in relation to structures on a site.
- Sense of proportion (street width to building height, human scale)
- Pedestrian orientation of structures and architectural detailing/fenestration
- Terminated vistas
- Reduce the predominance of residential garages in the design of the front facades of single-family residences.
- Inclusion of front porches into the design of residential structures.
- Internal orientation of parking facilities and garages in multi-family developments.
- Improved pedestrian safety and enhanced pedestrian access through parking lots.
Enhance the City’s Landscape Ordinance by accomplishing the following objectives:
- Add guidelines and recommendations for landscape design that minimizes the need for supplemental irrigation.
- Clarify responsibilities and standards for landscape maintenance, including within public rights-of-way.
- Incentivize the use of drought-tolerant and native plants.
- Restrict the use of turf grass to the greatest extent feasible.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards for parking lots and consider making revisions that would result in more landscape buffering on parking lot fringes and more internal landscaping.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards to determine whether new standards should be adopted to help screen or buffer parking structures.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards in comparison to best practices and peer cities to determine whether minimum site landscaping standards should be revised and/or restructured to result in increased landscaping.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines that result in improvements to parking structure design including the following potential measures:
- Design parking structures to be architecturally integrated with adjoining primary structure(s).
- Include integrated storefronts or other active uses on the ground floors of parking structures that are adjacent to public sidewalks and other pedestrian plazas.
- Enhanced exterior façades of structures by integrating architectural features and materials that complement the character of the surrounding area, or screening with vegetation.
Consider the adoption of improved requirements to screen parked vehicles from view with enhanced landscaping, berming, low screen walls, and existing or proposed buildings, or some combination of those elements.
Develop a Master Streetscape Program to improve the appearance along major arterial streets. The program should outline methods for establishing a uniform streetscape appearance (with distinctive designs for individual streets or classifications of streets) through appropriate tree placement, species, and spacing, and coordinating the location of street trees in proximity to utilities, sidewalks, street lights and structures, and appropriate sidewalk designs. Differentiation in streetscape designs could be designated by street typology, designated areas, or other factors.
Using performance standards related to flow quantity, quality, and pattern, modify development regulations, codes, and policies to support the use of green infrastructure/low impact development techniques to mimic natural systems for developments within aquifer recharge zones with moderate or high vulnerability or in areas where streams and riparian areas have been channelized or developed (primarily in the Downtown, UH, and UM LUTAs). Low impact development techniques include but are not limited to:
- Onsite treating or filtering of stormwater contaminants.
- Discharging run-off as sheet-flow after passing through grassy or vegetated open space areas, rather than discharging run-off through concentrated outfalls.
- Creating attractive open space amenities that double as stormwater detention, retention, and / or filtering systems.
- Utilizing pervious pavement, pavers, or asphalt in appropriate locations (i.e. sidewalks, parking spaces, trails, patios, etc.).
- Utilizing planters (at grade or raised), vegetated landscape strips adjacent to roads and parking areas, and alternative curbing designs (allowing stormwater to easily move from impervious areas to pervious areas), to encourage stormwater infiltration and temporary detention.
- Rain Gardens
- Bioswales
- Green streets and alleys
- Green roofs
- Rooftop collection
- Underground detention
- Increased tree canopy preservation/tree planting
- Land/open space conservation
- Cluster development
Revise development regulations to require the following factors to be addressed in development and redevelopment proposals:
- Preservation of existing natural resources, such as wooded areas, habitat areas, and floodplains.
- Utilization of natural treatments and methods to stabilize or rehabilitate stream and river banks as a means to preserve downstream habitats.
- Integration of a variety of native or compatible non-native, non-invasive plant species.
- Mitigation of impacts of development on habitat, wildlife corridors, riparian and littoral areas, and water quality, through actions such as restoration or re-vegetation of disturbed natural areas and replacement of trees/habitat on-site or off-site.
- Management of invasive plant and animal species.
- Management and maintenance of natural areas, common areas and drainage areas.
- Impact on surface and groundwater supply.
- Impact on water quality caused by land uses and activities.
- Impacts on floodplains, riparian and littoral areas and wetlands and areas with significant landforms.
Revise the landscape ordinance to include the following:
- Define terms such as invasive species, exotic/non-native species, and native/indigenous species
- Require removal of invasive species from existing sites, and prohibit such species from being planted or maintained in new development.
- Provide a reference list of native plants and drought-tolerant plants.
- Provide incentives for using native and drought-tolerant plants and disincentives for using high-water plants and turf grass.
- Establish requirements for using design practices that minimize the need for supplemental irrigation.
Establish an Urban Forestry Program and City Urban Forester position to achieve the following:
- Measure and monitor tree canopy coverage and habitat on a regular basis so that any policies, programs, and regulations may be adjusted accordingly as situations change. Establish a process to maintain current data.
- Develop and maintain regulations, policies, processes, and programs that focus on protection and preservation of native trees.
- Provide assistance with proper tree selection, location, and maintenance to prevent power outages, reduce property damage, and coordinate emergency response during natural disaster events (excessive snow and ice, tornadoes, etc.), address the urban heat island effect, and reduce energy costs, etc.
- Establish programs such as tree give-aways, neighborhood planting programs, and education workshops.
- Provide resources to the public about tree selection, management, and care.
- Seek grant funding for community tree planting to improve City parks, publicly maintained rights-of-way and other areas of the city.
- Inventory the City’s street trees and develop a tree replacement program.
- Partner with volunteer and nonprofit organizations to recruit volunteers for tree planting and maintenance and to coordinate community-wide tree planting efforts.
Pursue methods to reduce the impact of the urban heat island effect on Oklahoma City by:
- Establishing a minimum canopy coverage requirement over paved surfaces such as parking lots.
- Instating a “continuous canopy” requirement for new streets and street reconstruction projects.
- Promoting the use of building and roofing materials that reduce heat island effects.
Modify development and subdivision regulations, and City policies to minimize alteration of natural landforms and native vegetation and maximize retention of distinctive natural features for public and private projects.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Amend the landscape ordinance to increase the number of trees and landscaped islands required in parking lots.
Provide incentives for developers to build parking garages in high density areas. Include design requirements for projects receiving incentives.
We will establish programs for the rehabilitation or redevelopment of deteriorated structures. Vacant and abandoned properties threaten good community appearance. liveokc presents policies that address vacant buildings. When vacant properties have historic or architectural significance, preservation incentives should be especially focused on their reuse.
We will expand efforts to increase public awareness and participation in neighborhood clean-up efforts. These efforts may include training in property maintenance skills, development of volunteer programs (i.e. adopt a street), or publicizing such programs as Bulk Waste Days. Community education programs and materials should increase access to resources and knowledge, and publicize the level of property maintenance expected of citizens of Oklahoma City.
Enhance existing development standards and establish design guidelines for areas outside of the City’s existing Design Review Overlay Districts. Development standards and design guidelines could include the following provisions:
- Minimize views and prominence of parking lots in relation to structures on a site.
- Sense of proportion (street width to building height, human scale)
- Pedestrian orientation of structures and architectural detailing/fenestration
- Terminated vistas
- Reduce the predominance of residential garages in the design of the front facades of single-family residences.
- Inclusion of front porches into the design of residential structures.
- Internal orientation of parking facilities and garages in multi-family developments.
- Improved pedestrian safety and enhanced pedestrian access through parking lots.
Establish a list of preferred and discouraged building materials for all zoning districts.
Develop distinctive standards for different types and categories of walls and fences, emphasizing durability, aesthetics, and visual continuity in materials and design with particular consideration of zoning classification.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Initiate efforts to educate the public regarding programs that provide assistance for neighborhood clean-up efforts. Such efforts could include the following:
- Provide assistance to residents to make housing and neighborhood improvements and provide training in property maintenance skills.
- Develop and organize volunteer programs (such as adopt-a-street, adopt-a-park, and neighborhood clean-up days) and/or coordinate efforts to obtain grant funding to establish community clean-up programs in neighborhoods where inadequate property maintenance is prevalent.
- Publicize Bulk Waste Days and/or explore the possibility of adding more days/increased frequency.
- Develop a list of outside funding sources that could be used for property maintenance and make this information available to all citizens, especially those in targeted low-income areas.
- Establish public educational programs and advertising campaigns to discourage littering. Education should begin at the elementary level and continue through the adult level.
Intensify code enforcement in areas where specific and/or chronic violations have detrimental impacts on community appearance. Such efforts could include:
- Implement stricter enforcement of property maintenance regulations and consider more significant penalties for violations.
- Increase emphasis on the enforcement of littering laws. Impose fines against littering in a uniform and consistent manner to reinforce a public perception that littering does carry a definite risk.
- Immediately report and ensure expedient removal of graffiti that is visible from interstate highways and other important/designated viewshed corridors.
Revise ordinances for design districts and design review procedures to ensure consistency in the treatment of historic properties, including the assessment of demolition proposals, the identification of historic or significant properties, and the consideration of the impact that the alteration or demolition of individual properties has on the context and continuity of the surrounding environment.
Incorporate natural features (such as ponds, lakes, streams, rock outcroppings, stands of mature trees, and/or sizable individual trees) into the design of all residential, commercial, and industrial projects rather than eliminating, hiding, or limiting access to those features.
Establish streetscape standards requiring attractive entry features and the provision of accessible common open space in new neighborhoods.
Enhance the City’s Landscape Ordinance by accomplishing the following objectives:
- Add guidelines and recommendations for landscape design that minimizes the need for supplemental irrigation.
- Clarify responsibilities and standards for landscape maintenance, including within public rights-of-way.
- Incentivize the use of drought-tolerant and native plants.
- Restrict the use of turf grass to the greatest extent feasible.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards for parking lots and consider making revisions that would result in more landscape buffering on parking lot fringes and more internal landscaping.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards to determine whether new standards should be adopted to help screen or buffer parking structures.
- Evaluate existing landscape standards in comparison to best practices and peer cities to determine whether minimum site landscaping standards should be revised and/or restructured to result in increased landscaping.
Define responsibilities and assurances for maintaining, repairing, or replacing community walls and fences. Consider creating programs for routine and consistent maintenance of fencing along arterial roadways that could include fencing assessment districts, long-term bonds, or assigned HOA maintenance of community fencing.
Establish a funded beautification program and source of funding to provide facade and landscaping enhancements along targeted industrial corridors.
Establish policy or adopt ordinance language to ensure that City-owned or controlled historic buildings are appropriately recognized, maintained and repaired, or rehabilitated. Potential methods to be considered could include:
- Attach a preservation restriction or easement to historic properties that are surplused by the City.
- Assess the historic status of City-owned or controlled properties in order to follow through with formal HP/HL zoning, National Register listing, or other historic designation as appropriate.
- Incorporate early and substantive review of city improvement projects to assess potential impacts on historic buildings, and adopt alternatives that minimize or eliminate the impacts when necessary.
Improve landscape design, installation, and landscape maintenance compliance through the following actions:
- Produce informational materials and work with local media to publicize the benefits of limiting turf areas (e.g. reduced water use, less mowing) and highlight the positive effects on property values and aesthetics that result from proper installation and maintenance of landscaping.
- Develop a program, including informational outreach, to inform property owners of their responsibilities to maintain right-of-way areas, the procedures for enforcement, and the applicable fines.
- Identify specific corridors with the worst landscape maintenance conditions and initiate coordinated clean-up programs in those locations.
- Install demonstration gardens/landscapes in select civic/public locations to provide practical examples of how to integrate drought tolerant and low maintenance plants in commercial and residential installations.
- Improve efficiency and effectiveness of the process for reporting, citing, and proactive enforcement violations for maintenance and compliance with landscape requirements.
- Explore the establishment of landscape improvement/maintenance districts where property owners are assessed a pro-rata share of the costs to properly and uniformly maintain landscaping within the district boundaries.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Increase proactive code enforcement efforts, including litter control, and graffiti clean-up in targeted areas (e.g., SNI areas, and special districts).
We will create public/private partnerships that fill critical demands like workforce housing that are not normally satisfied by the private market. The Housing Market Preference and Demand Study defined housing preferences for different age and income groups, including residential types and locations. This information provides valuable guidance to city agencies, community organizations, builders, and developers that can help all parties make policy and business decisions. However, these data rapidly become outdated. Regular updates, funded by a mutually beneficial partnership of public and private sectors, can ensure that this information remains relevant and useful.
But information must be put to use. The 2013 housing study identified a major demand for “workforce” housing – equity and rental units affordable to people in a range from 60% to 120% of the citywide median household income. The normal private market has difficulty producing housing for much of this income range because of perceived risk and small profit. Partnerships between the public, private, and nonprofit sectors, including employers, can develop programs that remove obstacles to workforce housing production and marketing. Options include site acquisition, landbanking, interim financing, appraisals, mortgage financing, neighborhood infrastructure, and streamlined development reviews.
Collaborate with local development and real estate professionals to prepare a city-wide Housing Demand Market Study every 5 years which includes analyses and recommendations related to:
- Projected demand and trends in supply;
- Special needs housing;
- Housing conditions;
- Work force housing and its associated program; and,
- Overall health of the housing market, including owner-occupied and renter-occupied.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Ensure that new publicly financed developments – those which directly use or receive public dollars – with more than 100 units or with densities greater than 10 units/acre are located where they have easy access to frequent transit service.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Incorporate preventive health care and wellness education into public schools, recreation centers, senior centers, and technical/trade schools.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
We will set neighborhood development priorities by using quantitative evaluation criteria. Available resources are never sufficient to address the problems of struggling neighborhoods. Setting priorities and policy focuses can be addressed by an evaluative process that considers such factors as economic opportunities, educational performance, housing quality, access to commercial and other support services, public safety, and presence of community organizations and institutions. The process should consider positive neighborhood factors that can create the foundations for success, including:
- Existing support capacity from neighborhood associations, local service providers, and area businesses;
- Community institutions like parks, schools, churches, or community centers; and,
- Connections to surrounding neighborhoods.
We will expand rehabilitation and redevelopment programs to stabilize the physical fabric of neighborhoods. The physical condition of a neighborhood and its buildings is critical to its ability to function as a community. Residential rehabilitation programs should be expanded to both meet the needs of existing residents and serve future generations. Rehabilitation should focus items that directly affect health and safety, secure the basic building envelope, and add economic value to the surrounding area. Programs in which community development corporations acquire, rehabilitate, and either sell or rent units on a “turnkey” basis at moderate costs have been particularly effective in adding value, preserving housing, and introducing new owners and potential leaders into a neighborhood.
But housing rehabilitation is only part of the picture. Vacant sites and dilapidated buildings depress both property values and community momentum. Programs to accelerate the redevelopment of dilapidated properties should be tied closely to the priority evaluation process. Funds should be targeted to areas and projects that create a critical mass that in turn catalyzes private market investment and creates a self-sustaining community. Mechanisms like landbanks and land trusts have also proven effective in gaining control over vacant properties and returning them to productive use. Often, a high priority or visibility project at a strategic location can produce an unexpectedly powerful private reaction as neighbors gain confidence in their future.
We will create, enhance, and maintain community spaces where residents interact positively and advance the social fabric. Successful neighborhoods include spaces where people see and greet each other, and work and play together in a common enterprise. These spaces open a neighborhood, and increase the level of positive interaction that is the essence of a living neighborhood. Yet, hidden or neglected public spaces have the opposite effect, attracting nuisances and sometimes crime, and being scary or off-putting places that people avoid. Good community spaces can take many forms – a well-maintained public park surrounded and watched over by residents; a community garden; the median of a parkway; or a school or community center site.
Strengthening these community places begins with inventorying and analyzing their operations. This can be done in cooperation with neighbors and community organizations. Volunteer work, business participation, and other public and private support can provide the means to reclaim existing spaces and develop new ones, and to provide adequate resources for continued support and maintenance.
Facilities like community gardens and groceries are particularly attractive as community spaces because they are self-supporting; become natural and productive attractors of people, and address other key concerns such as access to healthy food. Efforts at a neighborhood level to secure sites and organize gardens should be expanded and educational institutions should provide technical help to gardeners. Public development incentives should have a special focus on attracting grocery stores to skipped over areas with viable consumer markets, and should encourage inclusion of public space in project design.
We will coordinate public infrastructure projects and community revitalization. In an effort to create tangible catalysts for revitalizing urban communities, the City will use the analysis described in this section as well as those located throughout planokc, to inform its capital improvements program.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Prioritize neighborhoods for revitalization and re-investment in order to reverse the decline associated with poor maintenance of public infrastructure and other property by using the following objective criteria:
- Low economic opportunity;
- Low educational attainment;
- Poor health outcomes;
- Poor housing environments;
- Low neighborhood quality; and,
- Existing capacity to support the revitalization efforts; and other important indicators.
Increase the City’s capacity to participate in targeted programs that strengthen neighborhood infrastructure and other assets.
Increase and/or re-assign City staff to support targeted neighborhoods and coalitions.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
Create places and opportunities for neighborhood events that allow neighbors to interact.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Establish a working partnership between the City, Oklahoma City Public Schools, Putnam City Schools, Western Heights Schools, and other metro area school districts and educational entities to help school districts complete a variety of non-educational (or indirectly educational) functions such as planning for and siting new schools, working on shared use issues, and redeveloping closed schools. The partnership should coordinate efforts to seek funding and appropriate resources to accomplish the following:
- Establish multiuse recreational and exercise facilities in schoolyards to increase opportunities for physical activity and strengthen the relationship between schools and neighborhoods.
- Establish a program to increase the number of community members and schools that make effective use of Senate Bill 1882 (effective 11/1/2012) allowing shared use of school facilities for recreational purposes.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
We will develop new site and building design guidelines and regulations and increase property maintenance standards and enforcement. Better community appearance is largely based on raising people’s expectations of how they should both develop and maintain their own property. New standards will establish better minimum expectations for how buildings and sites should look and function. These new standards should not add burdens or excessive costs, but should establish new basic assumptions about how we build, whether our projects are small convenience stores or a large mixed use developments. We often judge community appearance by the routine rather than the unique.
The same holds true for private property maintenance. Maintenance quality is contagious – care produces more care, and neglect produces more neglect. Again, our standards, technical assistance programs, and ultimately enforcement should move toward a higher level of care in our own individual environments.
We will improve the appearance of our streets. The public environment, all too often viewed as nobody’s responsibility, should in fact lead the way in creating upgraded appearance standards. In the planokc Business Survey, local businesses overwhelmingly cited “improving the appearance of major commercial streets” as the most important way to improve the appearance of the city.
After 2007 Bond Election resurfacing projects are complete, the City will assess the need for additional funds for citywide road maintenance beyond average annual expenditures. The assessment will be based on citizen satisfaction surveys, traffic volumes, and street condition data maintained by the Public Works Department. The City will also explore the feasibility of burying existing utility lines where possible and requiring all new utility lines to be buried. These efforts toward improving the quality of basic street appearance will continue and will encourage adjacent property owners to follow suit.
We will reduce litter and graffiti. The City will enhance litter and graffiti control through public awareness efforts and stricter laws and enforcement. Active code enforcement should be increased in targeted areas, including retail plan areas, special districts, and areas that are part of the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative (SNI).
We will reduce the impact of sign pollution. The City will update the sign code to reduce the visual impact of signs. Good standards actually improve readability and communicate business messages better than a cacophony of competing signs. The City can also explore reduction of sign pollution through amortization (gradual elimination as the service lives of signs expires) of existing signs that do not conform with new requirements.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Initiate efforts to educate the public regarding programs that provide assistance for neighborhood clean-up efforts. Such efforts could include the following:
- Provide assistance to residents to make housing and neighborhood improvements and provide training in property maintenance skills.
- Develop and organize volunteer programs (such as adopt-a-street, adopt-a-park, and neighborhood clean-up days) and/or coordinate efforts to obtain grant funding to establish community clean-up programs in neighborhoods where inadequate property maintenance is prevalent.
- Publicize Bulk Waste Days and/or explore the possibility of adding more days/increased frequency.
- Develop a list of outside funding sources that could be used for property maintenance and make this information available to all citizens, especially those in targeted low-income areas.
- Establish public educational programs and advertising campaigns to discourage littering. Education should begin at the elementary level and continue through the adult level.
Intensify code enforcement in areas where specific and/or chronic violations have detrimental impacts on community appearance. Such efforts could include:
- Implement stricter enforcement of property maintenance regulations and consider more significant penalties for violations.
- Increase emphasis on the enforcement of littering laws. Impose fines against littering in a uniform and consistent manner to reinforce a public perception that littering does carry a definite risk.
- Immediately report and ensure expedient removal of graffiti that is visible from interstate highways and other important/designated viewshed corridors.
Incorporate natural features (such as ponds, lakes, streams, rock outcroppings, stands of mature trees, and/or sizable individual trees) into the design of all residential, commercial, and industrial projects rather than eliminating, hiding, or limiting access to those features.
Develop and adopt new standards to minimize the detrimental appearance of accessory utility equipment (i.e. transformers, cable cabinets, telephone cabinets, utility meters, valves, etc.) by integrating them into less prominent areas of the site design or by screening them with landscaping, artistic features, or architectural materials compatible with the primary structures. If not encouraged, artistic embellishment (creating urban ambiance with imaginatively designed/painted screens) should not be prohibited. Ensure that such facilities are situated so that they do not impede pedestrian access.
Facilitate and coordinate burial of overhead power and communications distribution lines.
Develop standards/guidelines that require architectural articulation, variety, and interest on large structures adjacent to public streets by limiting long stretches of unbroken wall planes.
Use light fixtures and street furniture in the public right-of-way that complement established or evolving cultural or design districts.
Establish a funded beautification program and source of funding to provide facade and landscaping enhancements along targeted industrial corridors.
Establish incentives such as a simplified permitting process, reduced application fees, and special recognition for projects that:
- Utilize best management practices or other low-impact development methods for storm water management.
- Bring buried streams to the surface and restore riparian habitat.
- Install bridge systems instead of culverts for stream crossings to help maintain the natural ecosystem associated with the stream.
Revise the landscape ordinance to include the following:
- Define terms such as invasive species, exotic/non-native species, and native/indigenous species
- Require removal of invasive species from existing sites, and prohibit such species from being planted or maintained in new development.
- Provide a reference list of native plants and drought-tolerant plants.
- Provide incentives for using native and drought-tolerant plants and disincentives for using high-water plants and turf grass.
- Establish requirements for using design practices that minimize the need for supplemental irrigation.
Develop and adopt a tree preservation ordinance that achieves the following:
- Defines methods of preservation;
- Defines situations where preservation of trees is mandatory versus optional;
- Establishes incentives for tree preservation;
- Establishes mitigation options if preservation cannot be accomplished; and
- Establishes penalties for unauthorized tree removal.
Preserve mature healthy trees and incorporate them into the design of new development or redevelopment projects to the greatest extent possible. Include provisions and best management practices to ensure proper tree protection throughout the construction process. Best management practices include but are not limited to:
- The use of proper pruning techniques;
- Appropriate watering;
- Installation of protective fencing at the drip lines of trees or groups of trees;
- Designated material storage areas; and
- Approved equipment and vehicle parking and maintenance areas.
Modify development and subdivision regulations, and City policies to minimize alteration of natural landforms and native vegetation and maximize retention of distinctive natural features for public and private projects.
Preserve overall landscape character and natural landforms (rolling hills, native vegetation, etc.) to the greatest extent possible.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Increase proactive code enforcement efforts, including litter control, and graffiti clean-up in targeted areas (e.g., SNI areas, and special districts).
Require all new utility lines to be buried and bury existing utility lines when possible (e.g., when roads are widened).
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
Commercial buildings should be built at the street rather than behind a parking lot in order to promote pedestrian circulation, multipurpose shopping trips, and walkable and attractive streetscapes. Large-scale commercial buildings with parking in front should screen parking lots with the coordinated development of out-parcels (pad sites) and with landscaping.
Amend the landscape ordinance to increase the number of trees and landscaped islands required in parking lots.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
We will continue to create and enhance amenities such as parks, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. The MAPS programs have generated tremendous momentum for our city, but we cannot rest on past accomplishments. Instead we must continue our efforts to create great places at neighborhood, citywide, and street levels. In the future, these amenities will include public spaces, street corridors, transit facilities, cultural and recreational attractions, special districts, and community gateways.
Connections like the Bricktown Canal connecting Bricktown and the riverfront, the SkyDance Bridge, the riverfront greenway and in the near future the modern streetcar and trails projects have been as important as individual destinations. Signature transportation corridors are also vital parts of the cityscape. To this end, the City will explore the feasibility of installing and maintaining landscaping and public art along key transportation corridors to enhance the City’s appearance, image, and sense of place. Features like gateways can mark the transition from one district to another, and help emphasize the distinctiveness of Oklahoma City’s special districts.
We will build on the success of our special districts to attract residents and businesses. Downtown, Bricktown, Midtown, the Plaza, Deep Deuce, the Paseo, Stockyards City, Automobile Alley, Heritage Hills, and others are important districts that contribute strongly to Oklahoma City’s sense of place and identity. Future districts like Core to Shore will contribute to Oklahoma City’s collection of urban places. The City will continue to invest in features that make these existing and future places centerpieces of our community by catalyzing development, increasing land use diversity, building quality of life amenities, and promoting family-friendly features.
Catalyzing development. Urban housing has proven to be a staple of downtown and urban district revitalization. Residential development not only creates a market for more local services but also creates a comfortable environment that brings other people in from around the city and region. The City will continue to guide housing development to urban districts to increase activity and support demand for new retailing. Special focuses will include Downtown and surrounding areas and the new Core to Shore neighborhood. The City should also place a priority on establishing a signature retail development or a retail/housing mixed-use development.
Diversifying land use. Increasing land use diversity in urban districts will help attract and retain visitors and support development momentum. For example, Bricktown’s first development phases concentrated on offices, bars, and restaurants. But the historic district has become more vital with nearby housing, retailing at different scales, and hospitality uses, and this type of diversification should accelerate. In special districts, City policy should attract a balance of retail, residential, employment, and recreational uses.
Investing in amenities and activities. The City can strengthen downtown’s and other districts’ senses of place and increase activity by encouraging and investing in more public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Building family-friendliness. We can help attract and retain a variety of households to downtown and other urban districts by promoting and enhancing them as family-friendly places to live and play. Attention to street design, land uses (particularly around the downtown school) and public safety can help promote this image.
We will establish a place-making program. The City will establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city and promote both the economic and quality-of-life value of place-making investments. The program will establish partnerships and provide funding on a regular basis, including attention to small, neighborhood-scaled projects.
A significant part of this program is communicating the message of Oklahoma City’s places to the outside world. This both benefits businesses directly through promotion and supports city marketing and talent recruitment efforts. The Chamber of Commerce and Convention and Visitors Bureau are major partners in this effort.
We will designate additional special districts. The City will foster more specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to promote diversity and improve perceptions of the city. For example, Capitol Hill could grow as the center of an emerging Hispanic/Latino district, with appeal to people throughout the region. New special districts would include thematic infrastructure, amenities, design, public art, and streetscape improvements. Appropriate areas should be identified for special districts, followed by preparation of plans that establish design guidelines and strategies to capitalize on cultural meaning.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city. The program should promote the economic and quality-of-life benefits of place-making investments and should:
- Establish and maintain partnerships between the City, the private sector, and “place management” organizations.
- Provide funding and City staff support for “place management” organizations.
Create specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to enhance the diversity and perceptions of the city. Identify appropriate areas and create master plans with urban design guidelines specialized to the cultural history on display. For example, one special district could be themed for the Hispanic/Latino community. Such a district would include associated thematic infrastructure, amenity, design, public art, and streetscape improvements.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
Attract and retain young professionals to downtown and its environs to support and enhance place-making efforts and investments.
- Explore the possibility of the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce contracting with the City to facilitate and promote civic engagement and social opportunities for young professionals.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Strengthen downtown’s sense of place and activity levels by encouraging more housing, retail, public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Encourage the use of special service districts with enhanced levels of service.
Ensure adequate funds to maintain enhanced levels of service (including staffing) in places that have been or will be designated as special districts.
Initiate an effort to create and publicize a brand and image for the city. Examples of specific outcomes include:
- Coordinate with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber to advertise the city’s quality of life to national and regional audiences during major events such as the NBA playoffs, and at other appropriate times and places, and in appropriate media.
- Overhaul of City logo (buses, police cars, streetcar)
- Overhaul of City Website
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Enhance Downtown Oklahoma City’s prominence by maintaining and increasing its role as the major business center, establishing it as a major urban residential center, and focusing on developing retail, office, entertainment, and arts and cultural uses.
Work to establish a critical mass of retail uses in the downtown area. A lifestyle center or mixed-use town center presents the most viable option for a major infusion of retail into downtown.
We will promote redevelopment of vacant or under-used sites. Infill development on vacant, under-utilized, and brownfield sites should receive special attention through changes to land use regulations, infrastructure upgrades in target neighborhoods, incentives, favorable tax policies, expedited processing, and greater flexibility. The City recently produced a study on vacant and abandoned buildings to help address this issue and will continue to pursue implementation of the recommendations of that study.
We will encourage diversity in our neighborhoods. The City should use its housing and land use policies to encourage neighborhoods that have a diverse range of home sizes and types, and avoid concentration of low income households. Diversity builds unique and resilient neighborhoods, increases community involvement, and expands support for neighborhood schools. From an economic development point of view, housing and price-point diversity provides solid, affordable residential areas for members of the labor force at all levels of income and tends to encourage upward mobility.
We will support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative. The City should continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and consider permanent funding for the Neighborhood Stabilization Program to help reverse decline and create valuable places.
We will require good neighborhood design. Good neighborhood design can increase citizens’ access to jobs, housing, schools, and daily needs. It will also contribute to positive perceptions of neighborhoods, thereby encouraging investment.
New citywide site design and building regulations should establish basic functional requirements for features that produce good urban places. These include encouraging active transportation; integrating residential areas and activity centers; implementing good basic standards for signage, building materials, and site planning; and developing public spaces designed for desirable person to person contact.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will place a priority on increasing the economic strength and growth of viable existing commercial nodes and corridors. Commercial development typically flees to the “next new thing,” leaving previous locations for new sites, usually in growth areas. While understandable, this trend leaves older commercial areas underutilized with more marginal businesses and vacancy, lower rents, and reduced upkeep and investment. While market conditions and age will inevitably make some areas less competitive, we must maintain the strength of our existing viable districts. This program may include:
- Improving the function and convenience of commercial areas with improved transportation access, including better local circulation, enhanced transit service, and internal and external pedestrian and bicycle linkages.
- Creating a better physical environment through streetscape and public space investments.
- Providing financial incentives like tax increment financing for site and building upgrades, and for introduction of new uses into single-use commercial areas.
- Creating new parking standards for mixed-use projects that recognize that different uses generate their highest parking demands at different times.
- Encouraging new commercial within redevelopment areas, benefitting existing retailing by introducing new nearby attractions.
We will implement strategies for the reuse and redevelopment of low-performing commercial areas. Cities don’t stand still and neither do retail markets. Some of the city’s commercial areas are no longer viable in their current form, but still siphon some commercial activity from other, stronger districts. We will implement strategies for revitalization of these underutilized but still important districts.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Incentives for new regional retail development should only be considered if the proposed project truly creates a new regional destination for the city and does not significantly cannibalize sales from existing Regional Districts.
Regional-, community-, and neighborhood-scale retail developments should provide an internal vehicle and pedestrian circulation system between new and existing centers and individual stores that draws on the following principles:
- Concentrate access for new retail development at shared primary entrance points. Primary entrance points should be aligned with access points immediately across intersecting roads. Limit curb cuts on primary highways and arterials.
- Provide pedestrian circulation, including sidewalks and median breaks along interior and exterior fronting roads and within parking lots.
- Encourage coordinated development of retail centers in order to facilitate internal pedestrian and vehicle circulation and optimal center performance.
Wayfinding mechanisms and other placemaking features should be strongly encouraged in new and existing commercial districts.
We will establish and execute design guidelines for new commercial projects that enhance appearance, access, and function, and strengthen their surrounding neighborhoods. It seems to many people that one specific priority seems to drive commercial design: getting cars as quickly as possible from the street to parking lots. This produces a common pattern of buildings (shopping centers, multi-tenant strips, free-standing structures) separated from the streets and surrounded by parking, with big signs located along the road for maximum visibility from cars. In fact, zoning and development codes generally focus much more on parking than on the uses and buildings that the parking serves. This generic approach, repeated everywhere, lacks innovation, reduces the customer experience to finding a place to park, and produces inefficient and unattractive commercial strips. However, some new commercial designs are successfully following other approaches, based on providing a good customer experience. Our commercial development standards should also move in this direction. They should guide projects in ways that serve the competitive interests of neighborhoods, developers, businesses, and the entire community.
These guidelines should not micromanage development but instead should follow a few fundamental principles:
- Organizing commercial development as districts to the maximum degree possible. “Districts” allow customers to accomplish several purposes with one trip, to park once and walk comfortably and safely from business to business, and to find features and public amenities that encourage personal interaction and a positive customer experience.
- Engaging commercial buildings and businesses with public streets and sidewalks rather than their parking lots.
- Relating commercial development to surrounding residential neighborhoods, encouraging direct and convenient local access without inviting outside traffic.
- Incorporating mixed land uses such as higher-density residential, services, and offices into commercial projects.
- Developing well-conceived signs and graphics that communicate and guide customers without excessive size and numbers.
- Using site features like landscaping, walkways, internal driveways, and drainage areas to make projects more attractive, secure, and easier for customers to use.
- Reducing the amount of surface area devoted to parking, or dividing parking lots into smaller blocks for circulation and orientation.
We will focus commercial development in nodes that have good transportation access and support the development of multiple uses. Commercial strip development disperses business, working against the creation of walkable, multi-purpose activity centers. Yet, commercial zoning is often granted along these corridors by default, as people assume that their appearance, traffic, and previous land use patterns make them unsuitable for other uses. Nodes are more conducive than strips to pedestrian, bicycle, and transit access and encourage public spaces that upgrade the customer experience. planokc can reshape the character of major corridors, making them good environments for multiple uses. They will also direct commercial development to nodes that provide both good transportation access and opportunities for retailers to reinforce each other. Nodes at intersections may adopt a mixed-use character when non-retail uses are incorporated into at least one quadrant of an intersection.
Establish regulations that require pedestrian connections between new commercial development and adjoining residential areas.
Share parking among contiguous developments.
Undertake targeted parking studies to determine existing parking capacity and develop appropriate parking standards based on land use, location, and demand.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Develop and adopt new standards/guidelines that result in improvements to parking structure design including the following potential measures:
- Design parking structures to be architecturally integrated with adjoining primary structure(s).
- Include integrated storefronts or other active uses on the ground floors of parking structures that are adjacent to public sidewalks and other pedestrian plazas.
- Enhanced exterior façades of structures by integrating architectural features and materials that complement the character of the surrounding area, or screening with vegetation.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Favor commercial development clustered in nodes at arterial or collector intersections or along brief “main street” style corridors over commercial development extending in a linear pattern for long distances along highway, arterial, or collector corridors.
Regional-, community-, and neighborhood-scale retail developments should provide an internal vehicle and pedestrian circulation system between new and existing centers and individual stores that draws on the following principles:
- Concentrate access for new retail development at shared primary entrance points. Primary entrance points should be aligned with access points immediately across intersecting roads. Limit curb cuts on primary highways and arterials.
- Provide pedestrian circulation, including sidewalks and median breaks along interior and exterior fronting roads and within parking lots.
- Encourage coordinated development of retail centers in order to facilitate internal pedestrian and vehicle circulation and optimal center performance.
Commercial buildings should be built at the street rather than behind a parking lot in order to promote pedestrian circulation, multipurpose shopping trips, and walkable and attractive streetscapes. Large-scale commercial buildings with parking in front should screen parking lots with the coordinated development of out-parcels (pad sites) and with landscaping.
Amend the landscape ordinance to increase the number of trees and landscaped islands required in parking lots.
New neighborhood-scale retail should be located within new residential growth areas to serve daily shopping needs and limit trip distances. In newly developing areas, this retail format is preferred to the existing linear development patterns along arterials.
Neighborhood-scale retail should be developed at the median breaks or intersections of major or minor connectors.
Wayfinding mechanisms and other placemaking features should be strongly encouraged in new and existing commercial districts.
Encourage unified planning for all adjoining land owned or controlled by a project’s developer to ensure proper circulation and land use relationships.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
We will continue the process of creating a mixed-use, intensively developed, human-scaled, and experience-rich downtown. American downtowns declined as the number of reasons that brought people downtown decreased. Recently, downtowns have achieved success as places to live and visit as well as work. This evolution in Oklahoma City began in Bricktown and surrounding areas, where the canal and ballpark anchored adaptive reuse of historic buildings and the addition of new restaurants, entertainment venues, hotels, offices, and homes. This transformation continued with the addition of one of the National Basketball Association’s premier franchises, the Civic Center restoration, major office projects, and new housing. While the growth and development of downtown will always be ongoing, these accomplishments provide the foundation for building a great 21st century downtown.
Land use and development targets and policies will be instrumental in guiding this future. Major land use focuses will include a range of housing types and costs to serve a complete cross-section of the Oklahoma City market; services and retailing that support a larger resident population, including child care, educational facilities, and neighborhood commercial uses like a grocery store; integration of multiple uses into new and existing buildings; and public parks and open spaces for both programmed and informal activity. Much of this future development will occur on currently under-used sites such as the Core to Shore redevelopment area, the future Boulevard on the former I-40 right-of-way; existing surface parking lots, and vacant sites. Initial steps in meeting these needs include revisions of regulations to accelerate desirable uses and market research to demonstrate and quantify markets for specific project types.
As Downtown continues to develop, it must also evolve as a great urban place that offers a superb experience to its residents, workers, and visitors. The history of the urban renewal era in Oklahoma City tells us that investment dollars and big projects alone do not create a living and vibrant city center. A secure, populated, human-scaled environment requires family-friendly amenities, windows on the street, buildings with details scaled to people, pedestrian environments that engage the eye and mind, and an overall sense of welcoming and even festivity. These features have the power to attract the life that is characteristic of great downtowns.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
Attract and retain young professionals to downtown and its environs to support and enhance place-making efforts and investments.
- Explore the possibility of the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce contracting with the City to facilitate and promote civic engagement and social opportunities for young professionals.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Strengthen downtown’s sense of place and activity levels by encouraging more housing, retail, public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
In order to promote compatibility between different uses, establish standards and guidelines that ensure all developments are pedestrian-friendly and human scale at street frontages and property lines.
Enhance Downtown Oklahoma City’s prominence by maintaining and increasing its role as the major business center, establishing it as a major urban residential center, and focusing on developing retail, office, entertainment, and arts and cultural uses.
Continue to pursue a full scale downtown grocery store or a natural food grocer by:
- Increasing the amount of downtown housing
- Conducting a market study to quantify existing and future potential
- Promoting downtown to potential store operators
- Providing incentives such as land, infrastructure, or sales tax rebates, and allowing for mixed-use (vertical) integration with other uses including, but not limited to, residential.
Encourage development of new educational and childcare facilities downtown to accommodate families with children that work and/or live downtown.
In Downtown and adjacent areas, encourage the development of affordable housing for moderate-income households through incentives or requirements such as:
- Requiring a percentage of units in all new apartment and condominium developments to be affordable to working households with incomes of 80 to 100 percent of the area median family income as defined by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Developments may be exempted through payment of an in-lieu fee to go towards development of affordable housing.
- Establishing a density bonus program where appropriate.
- Establishing financial incentives for development of affordable housing.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
We will create a high-density downtown by providing efficient parking, excellent automobile, bicycle, and pedestrian circulation, and development policies that promote density.
We know that private automobile transportation and the space that cars require work against high-density development. We also know that downtown must accommodate private cars to succeed, but should provide better alternatives for people moving between features within the district. High density development itself brings more things closer together, making walking, biking (including bike share systems), and transit circulators like modern streetcars the most efficient and pleasant ways to go.
We can institute this “virtuous cycle” by:
- Redeveloping surface parking lots with new development, providing new parking in parking structures, and integrating structured parking vertically into new projects.
- Developing enhanced transit to downtown and “density-friendly” circulation to points within downtown, including pedestrian and bicycle facilities (including bike share) and the modern streetcar circulator included in the MAPS 3 capital program.
- Preserving and restoring to the degree possible the urban grid of blocks in Downtown Oklahoma City, re-establishing pedestrian linkages lost during the superblock era of Downtown redevelopment.
- Revising development ordinances to limit surface parking, encourage mixed uses on at least the street level of parking garages, and increase overall development yields.
Maintain existing alleys or construct new alleys where feasible to provide trash collection service and parking behind primary buildings and minimize curb cuts along the primary street frontage.
Prohibit new single-use, on-street commercial surface parking lots from locating Downtown and create incentives for the redevelopment of existing commercial surface parking lots with appropriately-scaled infill development.
Provide incentives for developers to build parking garages in high density areas. Include design requirements for projects receiving incentives.
Evaluate existing regulations for effectiveness in promoting density and mixed-use development and in addressing surface parking. Develop a new urban design code for downtown and other key districts to promote healthy mixes of land uses that are compatible and complementary.
Oklahoma City’s reputation as a low-crime community attracts and retains residents and businesses.
We will enhance policing and crime prevention programs through partnerships between police and local communities. The term “community policing” has become controversial in some instances, but it is in fact a common sense approach to law enforcement that many cities and towns implement without fanfare. Police departments that practice community-based techniques recognize that police alone cannot deal with neighborhood safety and livability issues, but instead must partner with citizens, businesses, organizations, schools, churches, and others to build safe environments.
Community-based programs establish personal relationships and trust between police and residents. Some police departments describe this approach as a “value system” or even “a way of life” as opposed to a program. In Oklahoma City, effective neighborhood policing will involve greater outreach to residents and businesses, interaction with organizations, working relationships with property owners, and other cooperative efforts. A critical support element will involve direct work with at-risk youth and adequate funding for job training, education, and leadership development programs.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
We will incorporate design and maintenance practices to create safer environments in both established and new neighborhoods. Addressing the impact of the neighborhood environment on public safety will follow two tracks: 1) reviewing new projects (including subdivisions and major new developments) and incorporating safe environmental design standards into their design, and 2) auditing existing neighborhoods for unsafe conditions and correcting problem areas.
Safety evaluation of new projects will start with developing design standards and guidelines, using the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design as a starting point. Our public safety departments should develop specific areas of expertise in these principles and be fully integrated into the City’s project review and approval process.
Established neighborhoods present different challenges. Partnerships between City staff and community organizations will analyze the neighborhood environment and local crime patterns to identify and correct specific problems. The most common issues include overgrown lots, hidden spaces, and vacant and deteriorated buildings. We must be aggressive in such areas as vegetation control and demolition of buildings beyond feasible repair.
Response times when emergencies occur are also an important factor in the interaction between public safety and environmental design. Neighborhood designs should increase the efficiency of public safety operations and ensure that the greatest number of residents can be reached in the shortest amount of time by emergency responders. This should include strategic improvements in existing neighborhoods and efficient design in new neighborhoods.
Systematic evaluation and correction of design aspects of new projects and inherently unsafe environments in established areas will be necessary to ensure a safe environment for all residents of Oklahoma City.
We will correct unsafe building elements and design conditions in public facilities and outdoor spaces. The City should lead in providing safe and secure facilities and properties. This is especially important in distressed neighborhoods, where a public park or center may be seen as a refuge. All publicly accessed properties should be assessed for unsafe conditions, including but not limited to poor lighting, blind spots, and maintenance hazards. Once this inventory has been completed, priorities for repair should be set and incorporated into the capital program.
Graffiti and vandalism in public areas are special and persistent problems. Uncorrected incidents suggest neglect in a neighborhood, which in turn encourages both more vandalism and serious criminal activity. Graffiti can be controlled through an aggressive removal policy, best accomplished in partnership with neighborhood residents. Cooperative action for productive purposes has the secondary benefit of building a sense of neighborhood effectiveness and establishing credibility for improvement efforts all of which help reconstruct the social fabric.
Improve the functionality and efficiency of the street network by:
- Providing direct connections from residential developments to nearby places and to each other.
- Providing street and sidewalk stubs to adjacent vacant land in anticipation of future development.
- Connecting new development to existing street and sidewalk stubs, and to existing trail, open space, and bicycle networks.
- Reducing block sizes and use of dead-end streets.
- Maintaining the existing street grid to preserve connectivity and mobility options.
Revise subdivision regulations to include connectivity standards and guidelines that require greater street connectivity, and provide allowances for pedestrian and bicycle connections when street connectivity cannot be made.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Reverse the detrimental impact of vacant and abandoned buildings through the following efforts:
- Develop an Abandoned Buildings program geared toward a significant reduction in vacancies by creating incentives and/or penalties that discourage prolonged building abandonment and help the City to recoup the costs associated with vacated buildings. Use fees generated by this program to help fund redevelopment of abandoned buildings.
- Assess the feasibility of potential reuse options for dilapidated or abandoned buildings. Define and establish criteria to help identify buildings that are too far gone and/or too costly to feasibly rehabilitate, and consider a coordinated demolition program for those buildings.
- Seek changes in state legislation to enhance the City’s ability to maintain and improve its neighborhoods including:
- Laws which would speed up the demolition process for long-term dilapidated or abandoned properties that cannot be rehabilitated, and
- Laws which would strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Evaluate public facilities and public property for unsafe conditions such as poor lighting (quality and quantity); blind spots; poor maintenance conditions; and other unsafe conditions. Prioritize improvements to these facilities and properties based on the following criteria: a) Proximity and condition of nearby neighborhoods; and b) Cost/benefit associated with mitigating the unsafe condition and maintaining the improvement.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Utilize existing natural streams as amenities in public parks, and regularly monitor and maintain stream banks for safety of park users.
Revise subdivision regulations to require development adjacent to parks and public open spaces to maintain open sight lines to parks and public open space. Reduce/limit residential rear yards, fences, walls, and physical and visual enclosures around park and public open space perimeters. Encourage designs that allow homes to face into parks or where side yards are located near parks.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will support our schools in improving student performance. Low academic performance is a problem in our city, and especially within Oklahoma City Public Schools, as measured by the State Department of Education. Our entire community must address this issue aggressively. Some solutions involve long-term and continuing efforts, such as creating and sustaining healthy, mixed-income neighborhoods that provide the secure environments necessary to nurture learning and achievement. Recommendations that help create these types of neighborhoods are found throughout planokc, from land use initiatives to neighborhood reinvestment and housing variety. Other specific efforts, involving concerted action by the public and private sectors and school districts can provide more immediate results. These educational support programs can include scholarship programs that offer post-secondary grants to students in inner-city schools and districts, expanded early childhood education, after- school programs, mentoring, specialized educational tracks, teacher skills training, or financial incentives for high-performing schools and teachers.
The City will also assist the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce in efforts to adapt the education and training offered by local institutions to match the current and future needs of local companies. This includes both K-12 schools and secondary schools.
Educational issues and programs represent a convergence of different perspectives. This element approaches good educational programming from a workforce and economic development framework; liveokc from a neighborhood development viewpoint; and serveokc from a public service and community quality point of view. However, all point in the same direction, highlighting the importance of increasing achievement and learning.
Facilitate communication among the 23 school districts in order to develop more arts education opportunities for the children in our community.
Establish development standards and design guidelines for new cultural, civic, and sporting facilities that address site design, architecture, compatibility, pedestrian-orientation and access, landscaping, and the inclusion of public art.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Coordinate with Strong Neighborhoods Initiative to provide recreational, fire safety, public safety, and character building programs in schools.
Identify ways to establish/strengthen relationships and partnerships between schools and the business community as one method to improve student education and outcomes.
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Work with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce to recommend adaptations to local education and training opportunities to match the current and projected needs of local companies.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Avoid concentrations of apartment complexes. Instead, integrate multifamily units into neighborhoods with mixes of housing types or in mixed-use developments.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
We will develop new site and building design guidelines and regulations and increase property maintenance standards and enforcement. Better community appearance is largely based on raising people’s expectations of how they should both develop and maintain their own property. New standards will establish better minimum expectations for how buildings and sites should look and function. These new standards should not add burdens or excessive costs, but should establish new basic assumptions about how we build, whether our projects are small convenience stores or a large mixed use developments. We often judge community appearance by the routine rather than the unique.
The same holds true for private property maintenance. Maintenance quality is contagious – care produces more care, and neglect produces more neglect. Again, our standards, technical assistance programs, and ultimately enforcement should move toward a higher level of care in our own individual environments.
We will improve the appearance of our streets. The public environment, all too often viewed as nobody’s responsibility, should in fact lead the way in creating upgraded appearance standards. In the planokc Business Survey, local businesses overwhelmingly cited “improving the appearance of major commercial streets” as the most important way to improve the appearance of the city.
After 2007 Bond Election resurfacing projects are complete, the City will assess the need for additional funds for citywide road maintenance beyond average annual expenditures. The assessment will be based on citizen satisfaction surveys, traffic volumes, and street condition data maintained by the Public Works Department. The City will also explore the feasibility of burying existing utility lines where possible and requiring all new utility lines to be buried. These efforts toward improving the quality of basic street appearance will continue and will encourage adjacent property owners to follow suit.
We will reduce litter and graffiti. The City will enhance litter and graffiti control through public awareness efforts and stricter laws and enforcement. Active code enforcement should be increased in targeted areas, including retail plan areas, special districts, and areas that are part of the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative (SNI).
We will reduce the impact of sign pollution. The City will update the sign code to reduce the visual impact of signs. Good standards actually improve readability and communicate business messages better than a cacophony of competing signs. The City can also explore reduction of sign pollution through amortization (gradual elimination as the service lives of signs expires) of existing signs that do not conform with new requirements.
Initiate new efforts to reduce sign clutter and improve the aesthetics of signs, while allowing for adequate and visible business identification by the following potential measures:
- Restrict new billboards and eliminate or reduce the number of existing billboards.
- Require non-conforming signs to be removed or be brought into compliance with existing regulations within a specific timeframe.
- Consider new standards in the Sign Ordinance to improve limits on the size, height, and number of signs.
- Improve proactive enforcement of the City’s sign regulations to curtail the placement of illegal signs and ensure adequate maintenance of signs.
Initiate efforts to educate the public regarding programs that provide assistance for neighborhood clean-up efforts. Such efforts could include the following:
- Provide assistance to residents to make housing and neighborhood improvements and provide training in property maintenance skills.
- Develop and organize volunteer programs (such as adopt-a-street, adopt-a-park, and neighborhood clean-up days) and/or coordinate efforts to obtain grant funding to establish community clean-up programs in neighborhoods where inadequate property maintenance is prevalent.
- Publicize Bulk Waste Days and/or explore the possibility of adding more days/increased frequency.
- Develop a list of outside funding sources that could be used for property maintenance and make this information available to all citizens, especially those in targeted low-income areas.
- Establish public educational programs and advertising campaigns to discourage littering. Education should begin at the elementary level and continue through the adult level.
Intensify code enforcement in areas where specific and/or chronic violations have detrimental impacts on community appearance. Such efforts could include:
- Implement stricter enforcement of property maintenance regulations and consider more significant penalties for violations.
- Increase emphasis on the enforcement of littering laws. Impose fines against littering in a uniform and consistent manner to reinforce a public perception that littering does carry a definite risk.
- Immediately report and ensure expedient removal of graffiti that is visible from interstate highways and other important/designated viewshed corridors.
Incorporate natural features (such as ponds, lakes, streams, rock outcroppings, stands of mature trees, and/or sizable individual trees) into the design of all residential, commercial, and industrial projects rather than eliminating, hiding, or limiting access to those features.
Develop and adopt new standards to minimize the detrimental appearance of accessory utility equipment (i.e. transformers, cable cabinets, telephone cabinets, utility meters, valves, etc.) by integrating them into less prominent areas of the site design or by screening them with landscaping, artistic features, or architectural materials compatible with the primary structures. If not encouraged, artistic embellishment (creating urban ambiance with imaginatively designed/painted screens) should not be prohibited. Ensure that such facilities are situated so that they do not impede pedestrian access.
Facilitate and coordinate burial of overhead power and communications distribution lines.
Develop standards/guidelines that require architectural articulation, variety, and interest on large structures adjacent to public streets by limiting long stretches of unbroken wall planes.
Use light fixtures and street furniture in the public right-of-way that complement established or evolving cultural or design districts.
Establish a funded beautification program and source of funding to provide facade and landscaping enhancements along targeted industrial corridors.
Establish incentives such as a simplified permitting process, reduced application fees, and special recognition for projects that:
- Utilize best management practices or other low-impact development methods for storm water management.
- Bring buried streams to the surface and restore riparian habitat.
- Install bridge systems instead of culverts for stream crossings to help maintain the natural ecosystem associated with the stream.
Revise the landscape ordinance to include the following:
- Define terms such as invasive species, exotic/non-native species, and native/indigenous species
- Require removal of invasive species from existing sites, and prohibit such species from being planted or maintained in new development.
- Provide a reference list of native plants and drought-tolerant plants.
- Provide incentives for using native and drought-tolerant plants and disincentives for using high-water plants and turf grass.
- Establish requirements for using design practices that minimize the need for supplemental irrigation.
Develop and adopt a tree preservation ordinance that achieves the following:
- Defines methods of preservation;
- Defines situations where preservation of trees is mandatory versus optional;
- Establishes incentives for tree preservation;
- Establishes mitigation options if preservation cannot be accomplished; and
- Establishes penalties for unauthorized tree removal.
Preserve mature healthy trees and incorporate them into the design of new development or redevelopment projects to the greatest extent possible. Include provisions and best management practices to ensure proper tree protection throughout the construction process. Best management practices include but are not limited to:
- The use of proper pruning techniques;
- Appropriate watering;
- Installation of protective fencing at the drip lines of trees or groups of trees;
- Designated material storage areas; and
- Approved equipment and vehicle parking and maintenance areas.
Modify development and subdivision regulations, and City policies to minimize alteration of natural landforms and native vegetation and maximize retention of distinctive natural features for public and private projects.
Preserve overall landscape character and natural landforms (rolling hills, native vegetation, etc.) to the greatest extent possible.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Quickly repair damage caused by vandalism, including graffiti, to minimize negative impacts on neighborhoods. Coordinate the efforts of existing programs, such as the Police Department’s Removal Unit, the Public Works Department’s Removal Unit, and Oklahoma County’s “SHINE” program to increase responses in targeted areas and expand the area which can be covered. Increase participation by the business community, such as donations of paint and time.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Increase proactive code enforcement efforts, including litter control, and graffiti clean-up in targeted areas (e.g., SNI areas, and special districts).
Require all new utility lines to be buried and bury existing utility lines when possible (e.g., when roads are widened).
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
Commercial buildings should be built at the street rather than behind a parking lot in order to promote pedestrian circulation, multipurpose shopping trips, and walkable and attractive streetscapes. Large-scale commercial buildings with parking in front should screen parking lots with the coordinated development of out-parcels (pad sites) and with landscaping.
Amend the landscape ordinance to increase the number of trees and landscaped islands required in parking lots.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
We will continue to create and enhance amenities such as parks, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. The MAPS programs have generated tremendous momentum for our city, but we cannot rest on past accomplishments. Instead we must continue our efforts to create great places at neighborhood, citywide, and street levels. In the future, these amenities will include public spaces, street corridors, transit facilities, cultural and recreational attractions, special districts, and community gateways.
Connections like the Bricktown Canal connecting Bricktown and the riverfront, the SkyDance Bridge, the riverfront greenway and in the near future the modern streetcar and trails projects have been as important as individual destinations. Signature transportation corridors are also vital parts of the cityscape. To this end, the City will explore the feasibility of installing and maintaining landscaping and public art along key transportation corridors to enhance the City’s appearance, image, and sense of place. Features like gateways can mark the transition from one district to another, and help emphasize the distinctiveness of Oklahoma City’s special districts.
We will build on the success of our special districts to attract residents and businesses. Downtown, Bricktown, Midtown, the Plaza, Deep Deuce, the Paseo, Stockyards City, Automobile Alley, Heritage Hills, and others are important districts that contribute strongly to Oklahoma City’s sense of place and identity. Future districts like Core to Shore will contribute to Oklahoma City’s collection of urban places. The City will continue to invest in features that make these existing and future places centerpieces of our community by catalyzing development, increasing land use diversity, building quality of life amenities, and promoting family-friendly features.
Catalyzing development. Urban housing has proven to be a staple of downtown and urban district revitalization. Residential development not only creates a market for more local services but also creates a comfortable environment that brings other people in from around the city and region. The City will continue to guide housing development to urban districts to increase activity and support demand for new retailing. Special focuses will include Downtown and surrounding areas and the new Core to Shore neighborhood. The City should also place a priority on establishing a signature retail development or a retail/housing mixed-use development.
Diversifying land use. Increasing land use diversity in urban districts will help attract and retain visitors and support development momentum. For example, Bricktown’s first development phases concentrated on offices, bars, and restaurants. But the historic district has become more vital with nearby housing, retailing at different scales, and hospitality uses, and this type of diversification should accelerate. In special districts, City policy should attract a balance of retail, residential, employment, and recreational uses.
Investing in amenities and activities. The City can strengthen downtown’s and other districts’ senses of place and increase activity by encouraging and investing in more public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Building family-friendliness. We can help attract and retain a variety of households to downtown and other urban districts by promoting and enhancing them as family-friendly places to live and play. Attention to street design, land uses (particularly around the downtown school) and public safety can help promote this image.
We will establish a place-making program. The City will establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city and promote both the economic and quality-of-life value of place-making investments. The program will establish partnerships and provide funding on a regular basis, including attention to small, neighborhood-scaled projects.
A significant part of this program is communicating the message of Oklahoma City’s places to the outside world. This both benefits businesses directly through promotion and supports city marketing and talent recruitment efforts. The Chamber of Commerce and Convention and Visitors Bureau are major partners in this effort.
We will designate additional special districts. The City will foster more specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to promote diversity and improve perceptions of the city. For example, Capitol Hill could grow as the center of an emerging Hispanic/Latino district, with appeal to people throughout the region. New special districts would include thematic infrastructure, amenities, design, public art, and streetscape improvements. Appropriate areas should be identified for special districts, followed by preparation of plans that establish design guidelines and strategies to capitalize on cultural meaning.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
Establish a program to develop place-making capacity in the city. The program should promote the economic and quality-of-life benefits of place-making investments and should:
- Establish and maintain partnerships between the City, the private sector, and “place management” organizations.
- Provide funding and City staff support for “place management” organizations.
Create specialized districts for large cultural or ethnic groups to enhance the diversity and perceptions of the city. Identify appropriate areas and create master plans with urban design guidelines specialized to the cultural history on display. For example, one special district could be themed for the Hispanic/Latino community. Such a district would include associated thematic infrastructure, amenity, design, public art, and streetscape improvements.
Promote the downtown area as an attractive place to live and play for all household types, including families with children by:
- Requiring human scale site and building designs
- Focusing on pedestrian friendliness
- Adding family-friendly public amenities including parks, open space, greenways, plazas, bikeways, public art, etc.
- Limiting noise and protecting privacy
- Ensuring new buildings and sites are designed to be attractive and to enhance safety and the sense of safety.
- Encouraging employment and residential uses in close proximity
- Encouraging or requiring a percentage of condominium or apartment units to be 2 and 3 bedroom units
- Encouraging “child-friendly” development near schools and discouraging uses that could be detrimental to schools’ viability
- Instituting on-street police officers on foot or bicycle to maintain “eyes on the street” and enhance public safety and security
Attract and retain young professionals to downtown and its environs to support and enhance place-making efforts and investments.
- Explore the possibility of the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber of Commerce contracting with the City to facilitate and promote civic engagement and social opportunities for young professionals.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Strengthen downtown’s sense of place and activity levels by encouraging more housing, retail, public plazas, public art, parks, indoor recreation facilities, and arts and cultural facilities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Encourage the use of special service districts with enhanced levels of service.
Ensure adequate funds to maintain enhanced levels of service (including staffing) in places that have been or will be designated as special districts.
Initiate an effort to create and publicize a brand and image for the city. Examples of specific outcomes include:
- Coordinate with the Greater Oklahoma City Chamber to advertise the city’s quality of life to national and regional audiences during major events such as the NBA playoffs, and at other appropriate times and places, and in appropriate media.
- Overhaul of City logo (buses, police cars, streetcar)
- Overhaul of City Website
Increase tourism, publicize the city’s quality of life, and increase the city’s profile as a regional vacation destination by working with the Conventions and Visitors Bureau using the following strategies:
- Package vacations that highlight the city’s amenities and destinations.
- Conduct a tourism market study and plan to identify opportunities to increase visitation from in-state and out-of-state groups and households.
- Publicize information highlighting the city’s amenities, destinations and transportation options (e.g., Spokies, transit, walking tours, and river boat tours).
- Direct visitors (through maps, walking, biking, and river tours, and driving and streetcar routes) to Oklahoma City’s cultural and historic sites, and commercial districts.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Enhance Downtown Oklahoma City’s prominence by maintaining and increasing its role as the major business center, establishing it as a major urban residential center, and focusing on developing retail, office, entertainment, and arts and cultural uses.
Work to establish a critical mass of retail uses in the downtown area. A lifestyle center or mixed-use town center presents the most viable option for a major infusion of retail into downtown.
We will promote redevelopment of vacant or under-used sites. Infill development on vacant, under-utilized, and brownfield sites should receive special attention through changes to land use regulations, infrastructure upgrades in target neighborhoods, incentives, favorable tax policies, expedited processing, and greater flexibility. The City recently produced a study on vacant and abandoned buildings to help address this issue and will continue to pursue implementation of the recommendations of that study.
We will encourage diversity in our neighborhoods. The City should use its housing and land use policies to encourage neighborhoods that have a diverse range of home sizes and types, and avoid concentration of low income households. Diversity builds unique and resilient neighborhoods, increases community involvement, and expands support for neighborhood schools. From an economic development point of view, housing and price-point diversity provides solid, affordable residential areas for members of the labor force at all levels of income and tends to encourage upward mobility.
We will support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative. The City should continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and consider permanent funding for the Neighborhood Stabilization Program to help reverse decline and create valuable places.
We will require good neighborhood design. Good neighborhood design can increase citizens’ access to jobs, housing, schools, and daily needs. It will also contribute to positive perceptions of neighborhoods, thereby encouraging investment.
New citywide site design and building regulations should establish basic functional requirements for features that produce good urban places. These include encouraging active transportation; integrating residential areas and activity centers; implementing good basic standards for signage, building materials, and site planning; and developing public spaces designed for desirable person to person contact.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Establish a program or series of programs that significantly improve the quality, appearance, and perception of rental housing throughout the city. Program components should include: 1) owner, manager, and tenant education; 2) code enforcement and inspections; 3) design standards/considerations that promote safety; 4) high attention to property maintenance; and 5) other relevant best practices.
Provide tools and incentives for targeted housing and neighborhood revitalization through programs such as a housing trust fund, land bank, abatement of permit and connection fees, employer assisted housing, inclusionary housing development, tax abatements, credits or deductions, abatement of permit and connection fees, and an expedited review and approval processes.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Identify, evaluate, and mitigate challenges associated with neighborhoods where housing values are rising quickly in response to public investment.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Catalyze the rehabilitation of abandoned structures by amending codes to facilitate the adaptive reuse of existing buildings for residential use.
Develop a City program to rehabilitate or redevelop dilapidated properties, including a land bank to receive donated properties from property owners who can no longer maintain their properties.
Create regulations/standards/guidelines that focus on design and/or compatibility principles which are sensitive to the surrounding urban form, especially in areas that are stable or improving and whose character is well-established. These provisions should also help ensure compatibility between lower- and higher- intensity land uses.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Improve parking provisions in neighborhoods that are near vibrant commercial corridors/areas by improving parking and corridor design, non-vehicular networks, transit, and signage.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Facilitate the development of housing in the Downtown, Bricktown, and Core to Shore areas in order to increase activity levels and demand for retail and amenities.
Increase land use diversity in Bricktown to attract and retain visitors and development momentum. Specifically, encourage more retail, office, and recreational uses rather than additional bars and restaurants, so that visitors of all ages and interests will be motivated to visit and stay longer.
Adopt new citywide site design and building regulations that ensure new developments meet basic functional and aesthetic minimums related to:
- Walkability and bike-ability
- Internal and external street connectivity
- Integration of uses
- Signage
- Building location
- Building appearance
- Open space (passive and active)
Support diverse and high-achieving student bodies through the creation of mixed-income neighborhoods that encourage parental and community involvement by:
- Integrating home sizes and types at neighborhood and block scales,
- Avoiding concentrations of low-income households by encouraging income diversity within neighborhoods and by spending City housing funds in a manner that does not concentrate low income households in one development or neighborhood, but instead creates opportunities for these households to live in income-diverse neighborhoods, and
- Encouraging school districts to open schools and school grounds after school hours to support community engagement and more convenient opportunities for active recreation.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Rather than rely solely on federal CDBG funding, seek other sources to continue to support the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and Neighborhood Stabilization Program in order to enhance their ability to reverse decline and create valuable places.
Increase the viability of townhomes and condominiums as housing products by:
- Adopting and supporting new local and state laws to increase consumer protection for condos and townhomes (e.g., better funding mechanisms and maintenance enforcement for common areas).
- Requiring developers to demonstrate sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Support diversity and integration of housing unit types and sizes in all land use typology areas in order to meet the diverse needs of households of different sizes, generational needs, incomes, and preferences. New residential subdivisions should achieve a mixture of housing types within a unified development.
Amend the zoning ordinance to better accommodate the integration of various residential densities, building types, and styles.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
We will reduce crime and improve the sense of security throughout the city. We will establish and expand crime prevention partnerships with neighborhoods, visible patrols with a high degree of community contact and interaction in targeted areas, and youth programs. Other components of this effort should include regular evaluation of police staffing needs and expansion of such preventive measures as elimination of nuisances like abandoned buildings and integration of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design in the project review process. The liveokc and serveokc elements also provide initiatives that address public safety issues.
Enhance effective policing by:
- Developing and/or enhancing community policing programs, which involve residents and businesses in crime prevention strategies.
- Increasing business presence and participation in community policing.
- Improving public outreach.
- Increasing opportunities for the Oklahoma City Police Department community relations officers to interact with community organizations, neighborhoods groups, schools, recreational and/or athletic programs. This interaction should include increasing resources to allow real-time communication of safety concerns with these organizations.
Seek funding, sponsors, and partnerships to enhance and expand the following crime prevention strategies:
- Education and job training for at-risk youth.
- Community involvement programs such as Light Up The Night, Neighbors Night Out, and other similar activities and programs designed to strengthen neighborhoods.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure resources and funds remain dedicated to crime prevention programs, including but not limited to: block watches; graffiti removal; education and outreach associated with elder fraud, identity theft, and sexual predators; safe driver programs for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles; after-school and youth diversion programs that provide recreational and educational support (tutoring, homework help, etc.); and other crime prevention programs. Ensure planokc is maintained to support and reflect the City’s priorities to provide a safe and secure community.
Reinforce existing partnerships and create new partnerships with allied agencies and non-profits to intervene early and often with at-risk youth redirecting them from participation in criminal activities to educational opportunities, job training, community service projects, neighborhood and business improvement programs, and other community building projects and/or programs.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Develop methods for the City to aid school districts in bolstering student performance. Explore the following methods:
- A cooperative City and business-funded scholarship program for OKC residents in underperforming school districts following the same pattern as The Pittsburgh Promise, which offers post-secondary scholarships to academically qualified students who live in Pittsburgh and attend Pittsburgh public schools,
- Increased police presence for security and truancy prevention,
- City-funded after school facilities and programs,
- City-funded financial rewards to schools showing measurable improvement,
- City-funded financial or other rewards to high-performing teachers,
- City-funded teaching skills training.
Reduce crime and improve feelings of safety through long term efforts such as:
- Improving design regulations to maximize crime prevention through appropriate urban design,
- Developing community-based activities, programs, and facilities that reduce crime and develop life skills, such as after school and youth diversion programs and facilities for recreation and educational support (e.g., tutoring, homework help, etc.),
- Encouraging more compact development to increase effectiveness of individual officers by ensuring less travel time and more engagement,
- Implementing a “good landlord” program,
- Exploring enhancements to police operations such as:
- Committing to a certain number of officers per capita and/or per square mile of urbanized area,
- Increasing patrols (automobile, bicycle, or on foot) in targeted areas,
- Evaluating needs on a regular basis for increasing the number of key positions, such as detectives, to meet demands,
- Coordinating neighborhood improvement efforts (such as the Strong Neighborhoods Initiative and the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program) with policing efforts, and
- Supporting efforts to obtain more effective criminal justice law, such as stricter gang laws.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will provide incentives and investments that produce a favorable environment for private investment on underutilized sites. In Oklahoma City, we have tended to view land as an inexhaustible and disposable resource, reducing the desirability of older areas and decreasing land values, while expanding the city’s boundaries outward. The surveys and process of planokc show that this view is also changing, as citizens place a high value on using existing infrastructure and urban land effectively and rebuilding established neighborhoods. Preferences are also changing, as many families appreciate active urban places like Midtown and Automobile Alley that provide living, shopping, entertainment, and work places with good walking, bike, and transit access. Effective use of existing land resources is a central principle of Chapter Two’s land use vision.
Redevelopment and infill depend on major private investment. City policy and action can create the conditions that help this private investment occur.
Directions for these policies include:
- Site assembly. Multiple property owners, often absent or very difficult to find, can make it impossible to put together sites for redevelopment. The City can help private developers by helping them assemble sites.
- Infrastructure and street improvement. While redevelopment and infill sites usually have infrastructure, these facilities are sometime obsolete and require improvement. Redevelopment can provide the impetus for making necessary public investments in these assets.
- Public investments. Parks, schools, civic facilities, pedestrian and bicycle facilities, streetscapes, and other amenities can provide anchors that are proven to generate private development. The Bricktown Canal is an excellent example of a public amenity that has paid for itself many times over in private investment. Similarly, the new MAPS 3 Park will inevitably become the catalyst for the Core to Shore redevelopment.
- Code improvement and proactive enforcement. Poor property maintenance, unattractive and cluttered signs, and public or operating nuisances can degrade the value of surrounding property and discourage reinvestment. Updated ordinances and consistent, enforcement will minimize these disincentives and create momentum for new private development.
Establish new incentives and raise awareness of existing incentives that stimulate the preservation and rehabilitation of historic resources. Incentives could include:
- Preservation easements, low-interest or forgivable rehabilitation loans, and Tax Increment Financing Districts for historic buildings, sites, and districts.
- Tools and practices for public/private partnerships to ensure the preservation and retention of top-priority historic resources whose deterioration or demolition would present an irreparable and highly significant loss to the City and beyond.
- Existing city, state, and federal tools and incentives for rehabilitation, including state and federal tax credits for certified rehabilitation.
- Expedited review process for projects involving infill sites.
Support and incentivize the adaptive use of existing buildings, infill development, and brownfield development.
Modify codes and/or regulations to create opportunities for more income diversity and mixed-income neighborhoods by allowing a variety of housing ownership and leasing arrangements, diverse housing sizes and types – including accessory dwelling units, carriage homes, lofts, live-work spaces, cottages, and manufactured/modular housing. Modifications should allow an increase the variety of ownership opportunities to include condominiums, ownership cooperatives (such as mutual housing associations, limited equity cooperatives, etc.) by identifying and removing regulatory barriers. Recommend improvements to protections for owners, developers, and lenders.
Priority should be given to projects that achieve efficiencies described elsewhere in planokc, such as dwelling units that are located to have easy access to each other and to other daily needs including jobs, recreation, and schools.
Maximize the use of all appropriate state, federal, local, and private funding for the development, preservation, and rehabilitation of housing affordable to a variety of income groups, including those that integrate low-income housing units in otherwise market-rate housing developments and support the creation and/or expansion of mixed-income communities.
Integrate housing rehabilitation programs with neighborhood revitalization programs. These programs should include assistance to property owners to renovate the existing housing stock with improvements that reduce utility and maintenance costs for owners and occupants, conserve energy, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Establish new or expand existing financing methods and/or mechanisms available to new and redevelopment mixed-income projects in urban areas. These could include: direct investment of public housing funds, tax-increment financing, bonds, revolving loans, housing program funds and/or other proven public-private partnership models.
Create and/or enhance Community Development Corporations (CDCs) and Community Housing Development Organizations (CHDOs) to increase their capacity to provide mixed-income housing, especially in targeted infill areas.
Reuse brownfield, greyfield, and other vacant building sites to provide new opportunities for mixed-used and mixed-income housing.
Prevent concentration of low-income populations by providing housing opportunities for all income groups in targeted redevelopment areas of the city with a particular focus on mixed-income projects, especially on those projects that have a public funding component.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Add legislative priorities for state laws to:
- Strengthen the City’s ability to obtain specific performance of property owners cited for code violations.
- Speed up the demolition process for long-time boarded properties that cannot be rehabilitated.
- Strengthen the City’s ability to require property owners to rehabilitate or sell neglected, boarded-up properties.
- Expedite the clearing of properties involved in probate.
Strategically use subsidized housing programs along with other City services and programs to revitalize targeted areas of the city.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Mitigate negative impacts of compactness by:
- Updating nuisance code to better address noise, smell, vibration, property maintenance, panhandling, animal control, delivery hours limits, and other possible negative effects.
- Updating the sign ordinance to reduce visual clutter.
Prioritize and concentrate development where facilities, infrastructure, and services have capacity and in areas where the Police and Fire Departments are best able to respond. Guide the location and timing of development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
We will incorporate crime prevention principles into the City’s design regulations and guidelines. Previous elements of the plan, including playokc and liveokc, introduced the concept of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles (CPTED), which use common-sense design features to minimize opportunities for criminal activity. CPTED principles apply on a wide range of scales, from individual site vegetation choices to citywide development patterns.
Oklahoma City should incorporate CPTED principles into its design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. Some cities (including Wichita, Kansas) have established ordinances that officially integrate CPTED principles into their design standards, while others use them as guidelines and adapt for their own use.
The City can encourage the use of CPTED principles through:
- Encouraging land use planning that mixes uses and extends hours of activity and “eyes on the street.”
- Establishing neighborhood territoriality by which adjacent residents and businesses can monitor activity in the public realm. a mixture of uses in neighborhoods.
- Lighting and building design guidelines.
- Landscaping guidelines that avoid hidden places.
- Building code enforcement and resolution and elimination of chronic vacancy and structural deterioration.
The City’s project review and approval process should include Police Department participation to provide specific public safety recommendations. The department should maintain an officer on staff with a specialty in CPTED and its principles. This staff member should also provide outreach to the development community to provide special training to builders, developers, and design professionals on safe community design.
Create a standards for trails based on industry standards, “Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design” principles, expected use, and surrounding land uses.
Establish access management requirements that limit driveways on arterials and collectors and increase connections between uses to improve safety and traffic efficiency.
Limit driveways on arterials and collectors and increase connections between uses to improve safety and traffic efficiency.
Ensure proper access to and between subdivisions in order to offer a choice in routes for residents, multiple access points for emergency responders, and to reduce vehicle congestion at arterial intersections. Contiguous developments should share access whenever feasible.
Establish a process for existing neighborhoods to request traffic calming, including how to evaluate the request, select the appropriate type of calming treatment, and fund recommendations.
Require sidewalks on both sides of all streets in urban LUTAs and in the Rural Residential LUTA for subdivisions with densities greater than 1 unit per acre.
Target specific areas of the city for enhanced safety and proactive enforcement. Selection of target areas will be informed by the Intelligence Led Policing program, with coordinated involvement from Police, Code Enforcement, Public Works Department, Planning, and community-based organizations.
Establish a Crime-Free Multifamily Housing Program designed to keep multifamily housing developments safe from crime and perceptions of crime by:
- Supporting partnerships between the police, property managers, property owners, and tenants.
- Providing training to managers and owners about screening applicants, fire safety, fair housing, and other components of ‘active property management’.
- Providing a security assessment based on Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles.
- Conducting safety meetings with residents/tenants.
Ensure that safety is factored into the design of neighborhoods through the following policies:
- Incorporate development standards and guidelines into the Subdivision Regulations that integrate the principles of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and increase safety and social interaction.
- Create a pre-development checklist with criteria to evaluate how safety is designed into a project.
- Establish a pre-development process wherein safety is considered in the design of projects.
- Involve the Fire and Police Departments in reviewing proposed development and redevelopment to provide input on any safety-related design concerns.
Establish criteria for locating, designing, and improving public and private parks to enhance safety and security, including:
Locating new parks in areas that are highly visible and accessible from surrounding residential streets and utilize trails to increase activity and visibility in parks.
Utilizing Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design principles, which includes controlled access, visibility, lighting, etc. for new parks and retrofitting/redesign of existing parks.
Improve safety of users of the parks and trails system by:
- Providing good lighting, emergency call boxes, and regular police patrols along the trail system.
- Providing shelter structures along the trail networks and determining the appropriate spacing for such structures. Structures could be relatively small to keep costs down but should be sturdy and easy to maintain.
Incorporate Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) principles into city-wide design standards for development and redevelopment of public and private projects. CPTED principles include: 1) Territorially – physically define spaces as public or private and the appropriate use is obvious even to outside observers; 2) Access Control – deny access to soft targets; 3) Natural Surveillance – make it easy to observe all users of/in a particular territory/space; 4) Maintenance and Management – ensure equipment is functioning (lights, gates, etc.), landscape is kept neat especially to preserve surveillance.
Maximize fire safety through actions such as:
Modifying regulations and guidelines to prevent subdivisions with a single point of access – except those with fewer than 10 homes.
Developing a vegetation management program targeting the wildland/urban interface, including rights-of-way in rural areas, and incorporating recommendations from the National Fire Protection Association’s Firewise Communities initiative.
Requiring residential sprinklers for developments located in Rural Land Use Typologies.
Requiring exceptional, effective, and easy access to sites augmented by a thorough system of connections within and between developments.
Evaluate development proposals to assess design components that contribute to or detract from safety and analyze emergency response capacity and capability.
Ensure that planokc is periodically updated to coordinate/correspond with the City’s Emergency Operation Plan and vice versa.
Adopt design standards to enable emergency management resources to be highly effective, such as resilient buildings, interconnected transportation networks, and other design considerations that help ensure community safety and recovery.
Encourage the integration and mixing of land uses in urban areas.
In order to promote compatibility between different uses, establish standards and guidelines that ensure all developments are pedestrian-friendly and human scale at street frontages and property lines.
Oklahoma City has a growing tax base and a revenue structure designed to ensure efficient growth and fiscal stability.
We will provide reliable and diversified funding for park development, capital improvement, maintenance, and operations. In order to provide adequate resources for the park system, we must diversify funding sources beyond our current reliance on sales taxes. Because bonds and property taxes can be used for capital projects, the most immediate need is for additional maintenance and operation funding. But a complete program must use a spectrum of techniques and a variety of partners. Diversification must be equitable to all parts of the city and not burden low-income households or any one particular group or constituency.
The Parks Master Plan presents a variety of options for various aspects of park development and operation. Sources for maintenance and operations include endowments, stormwater utility and impact fees, dedicated sales taxes, user fees, and private support. Land acquisition and capital development techniques include land dedication requirements and payments based on impact and demand created by projects, private park development, bond issues, dedication of easements, and private philanthropy.
We will supplement public funding of park development and operations by building a network of partnerships with other public, nonprofit, and private agencies and organizations. Budget constraints, state law that limits revenue sources for operations, the need to catch up on maintenance and replacement and keep up with growth, and other factors mean that city funding alone probably cannot provide the resources necessary to build, maintain, and operate the park system that Oklahoma City needs. Partnerships can provide the extra support and assistance that the system needs – as the Parks Master Plan puts it, “they can help make the difference between a park system that struggles and one that sparkles.” The plan’s recommendations for partnerships include support organizations, corporate or health provider sponsorships, conservancies, a Parks Foundation, and advocacy groups. Conservancies have special value for iconic parks. A conservancy-like group supports Myriad Gardens. Other possibilities for conservancies include the four original parks for the 1910 Dunn Plan and the MAPS 3 Park in the Core to Shore district.
Explore public/private funding sources and management structures, including non-profit conservancies, to improve, operate, manage and maintain downtown parks and open spaces.
Establish partnerships and programs with neighborhood associations and other organizations to improve maintenance of parks by:
- Increasing participation in the OKC Beautiful’s “Adopt a Park” program. Participants can include nearby businesses, neighborhood associations, churches, schools, and nonprofit groups;
- Establishing incentives for participating in the“Adopt a Park” program, such as providing awards; and,
- Increasing volunteer park maintenance programs.
Increase the level of involvement and resources from agencies and other community groups to provide physical activity programming, such as after-school programs.
Reduce the City’s long term operations and maintenance costs by:
- Adapting more energy efficient technologies for park facilities;
- Using low water landscape palettes and recycled water for irrigation; and,
- Identifying and pursuing additional funding sources including: increased appropriations to the City’s Parks & Recreation Department; federal, state, or county funds; dedicated sales tax; impact fees/in lieu fees; private, corporate, and foundation grants; and business improvement or assessment districts.
Utilize private and public partnerships and determine appropriate locations and funding sources to build larger multi-generational centers that will replace existing, small, and outdated recreation centers.
Pursue all opportunities, including donations, conservation easements, inheritance trusts, naming rights, and developer incentives to accomplish the following:
- Acquiring new lands for parks, open space;
- Acquiring natural areas that provide greater opportunities for people to access nature;
- Maintaining existing and future parks, open space, and natural areas;
- Enhancing existing landscaping at parks and along trails by planting additional native vegetation.
Establish a parkland dedication program to ensure adequate provision of parks to serve future populations.
Use one or more of the following methods to ensure infrastructure and facility capacities are adequate for proposed development:
- Ongoing master planning to determine the necessary water, sewer, and road infrastructure to serve development.
- An impact fee system that collects funds for specific areas as they develop and installs needed infrastructure in a timely manner.
- Use of special service districts to ensure appropriate levels of service, sufficient revenue, and timely installation of infrastructure and facilities for each district.
- Require developers to construct or fully fund infrastructure or other improvements needed to serve their development, with reasonable accommodation for future adjacent or nearby development.
- Require developers to wait until the City (or the State as the case may be) constructs the infrastructure needed to serve their development.
- For development proposed in areas not currently within one-half mile of existing water infrastructure, require a service area study to first be completed to determine the best method for providing water to the service area.
We will create development-ready sites with access to infrastructure in strategic areas.
An adequate and ongoing supply of immediately developable land provides the ability to respond nimbly to economic opportunities. Meeting the recommendation of the Employment Land Needs Assessment and Action Plan for maintaining a constant inventory of 1,000 acres of development-ready land involves a two-part strategy that:
- Protects land appropriate for major employment development from short-term encroachment by other uses.
- Extends services and infrastructure to this land so that major employers can build with minimum delay.
The Employment (EM) LUTA is specifically designed to preserve the integrity of land best suited for large-scale employment growth. Through the development approval process, the City can avoid compromising these sites by approving uses that will prove incompatible with future major employment centers. This may require creation of public or community-based development groups with the patience and ability to hold large assemblages of land for industrial, business park, or office headquarters uses.
The other leg of the strategy involves preparing this land for timely development by financing and installing (or being immediately prepared to install) infrastructure. Accomplishing this will require mobilization of existing agencies such as the Urban Renewal Authority, the Oklahoma Industries Authority, and the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust. It will also require establishing a reliable and repeatable method of funding capital investments that may include tax increment financing, general obligation limited tax bonds, and other public sources.
We will continue to provide incentives to major employers, targeted to specific industry clusters and locations. The City will continue to provide direct financial incentives to attract and retain major employers. These incentives should be targeted to:
- Industrial and employer clusters whose requirements are matched to our attributes and who move in the direction of greater economic diversification. These natural affinities for Oklahoma City include aerospace, aviation, defense, bio-science and other high-technology industries, renewable energy, new-to-market company headquarters, and advanced manufacturing.
- Sites where major community investments have been made in land, infrastructure, amenities, and other capital improvements; major redevelopment areas; or other desirable sites where these facilities are already available.
We will update public incentive programs to provide maximum leverage per dollar spent. The City provides incentives to businesses through its Strategic Investment Program. This incentive structure will be reviewed and optimized to provide the greatest community benefit and return on investment. This update should include specific evaluation criteria and objective measures of benefit. Preferred investments should move in the direction of private, front-end investment with incentive reimbursement tied to meeting performance criteria such as job creation and greater retail activity.
We will support locally-owned businesses and existing assets. Locally-owned businesses can have greater multiplier effects on the local economy than similar businesses that are non-local. This includes even the smallest businesses, such as home businesses, mobile food vendors, pop-up retail or vendors at farmer’s markets. The City can support locally-owned businesses and entrepreneurs through favorable tax policies, flexible regulations, and partnerships with local educational institutions to support business incubators and other programs that encourage business start-ups. We must also look carefully at measures that level the playing field among retail entities and allow local retailers to compete on at least an equal footing with on-line and out-of-city competitors.
Strengthen existing businesses and business districts within and adjacent to established residential areas. Promote the development of new businesses to provide additional jobs and higher income opportunities for nearby residents.
Create and promote development-ready sites in Employment (EM) areas using the following strategies:
- Task the Oklahoma Industries Authority (OIA) and/or the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust (OCICFT) to help public and private entities create development-ready sites.
- Partner with the State School Land Trust to prepare their sites located in EM areas for development.
- Pursue public purchase or optioning of key properties in EM areas in cooperation with the Urban Renewal Authority, the Oklahoma Industries Authority (OIA), and/or the Oklahoma City Industrial and Cultural Facilities Trust (OCICFT).
- Conduct a market analysis and feasibility study for a new business park.
- Facilitate development of EM sites by providing:
- Infrastructure financing options, such as tax-increment financing,
- Prioritized delivery of infrastructure, and
- Accelerated or facilitated permitting.
Provide adequate infrastructure for new or expanding companies by giving priority to Capital Improvements in ER areas. Additionally, consider the implementation of impact fees for infrastructure in order to provide infrastructure in a timely manner and to better coordinate with private development.
Consider updating the City’s Strategic Investment Program and retail incentive guidelines to maximize public benefit and return on investment from business recruitment and retention incentive structures according to the following order of preference:
- The prospective company pays for infrastructure and/or amenities and is reimbursed by the City as performance standards are achieved.
- The City pays for infrastructure and/or amenities, which the prospective company must repay if performance standards are not met.
- Direct, performance-based payments are made to the prospective company.
Continue providing direct financial incentives on a limited basis to attract and retain large, well-paying employers in areas where public infrastructure and amenities are already adequate. Financial incentives may include:
- Payments from general obligation limited tax bonds
- Performance-based rebate of all or a portion of future impact fees (if implemented)
- Revolving loan fund for small business starts/expansions
- Industrial revenue bonds
Increase economic diversity by supporting development of industry clusters such as aerospace, aviation, defense, bioscience (and other high-technology industries), renewable energy, new-to-market company headquarters, and advanced manufacturing. Strategies can include:
- Prioritizing incentives administered by the Oklahoma City Economic Development Trust for these industries
- Prioritizing installation of infrastructure to support aviation-related industrial development on the east side of the Will Rogers Airport
- Engaging ODOT in discussions to make improvements to I-44 in the vicinity of the Will Rogers Airport to relieve congestion and improve access to the airport-owned lands from I-44
- Protecting Airports and Tinker Air Force Base from encroachment by incompatible uses by analyzing the effectiveness of current Airport Environs overlay zoning districts and implementing necessary changes
- Facilitating expansion of Tinker-related operations to the east and south by prioritizing improvements to transportation, water, and sewer infrastructure
- Coordinating with the Chamber of Commerce to prepare sector acceleration plans for targeted industries
Support locally-owned businesses and entrepreneurs, which have greater multiplier effects on the local economy, by the following actions:
- Establish online sales taxes to correct a competitive imbalance currently suffered by local “brick and mortar” merchants.
- Facilitate entrepreneurial growth by working with local companies and universities and supporting business incubators.
- Consider amending the Strategic Investment Program guidelines to give higher priority to locally-owned businesses.
- Consider creating incentives and/or easing regulations for small, locally-owned businesses such as home businesses, farmers’ markets, mobile food vendors, pop-up retail, etc.
Support development of land designated for large employers and employment centers within the Employment Reserve LUTA, using the following strategies:
- When major infrastructure is extended to allow specific properties to develop in an Employment Reserve area, the City should place a condition on the land (through a development agreement) limiting future development to employment uses.
- Guide employment land development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure to accomplish the large-site employment land inventory objectives outlined in the Employment Land Needs Assessment & Action Plan.
We will increase the City’s sales tax revenue by supporting growth in retail sales. Sales tax revenues account for over half of the City’s budget due to the state constitution, which does not permit the use of more stable property taxes for operations. The reliance on sales taxes makes cities in Oklahoma very sensitive to the economic cycle. In addition, Oklahoma cities often compete with each other for sales tax revenue because it is distributed to cities entirely based on point-of-sale. Some states or regions address this issue by using distribution formulas at least partially based on population or other factors. Until the distribution method changes, or until such time as the state constitution is amended to allow more flexibility in the use of various tax sources, Oklahoma City must pursue strategies that help increase retail sales. The City will work to attract more retail activity and improve existing retail corridors, to ensure their future viability. These strategies must:
- Reduce leakage of local consumer dollars to other jurisdictions and non-taxed sellers.
- Import consumer spending from outside by providing unique destinations and retail environments.
- Increase sales through community growth and investment.
- Require on-line sales to compete on an equal basis with brick and mortar sales.
We will increase the City’s property tax revenue by increasing property values. Many planokc initiatives involve reinvestment, neighborhood stabilization, and efficient growth policies that will ultimately raise property values. This is good for both property owners and the public sector. For the former, raising values raises individual net worth and the stability of people’s investment in the city. For the latter, it creates both greater overall revenue and greater revenue yield per square mile of urban area. Redevelopment of areas like Core to Shore, restoration and full use of areas with depressed valuation, and incremental improvement of urban neighborhoods all serve the dual goals of improving life in the city and improving the City’s ability to provide the excellent services citizens expect and deserve at affordable cost.
We will consider ways to make the tax structure more stable, resilient, and balanced. The City will explore and evaluate options such as greater flexibility in tax sources that can fund City operations, reducing unnecessary tax exemptions, considering sales or marginal taxes on some types of goods and services, and taxing on-line sales.
Identify the economic value of cultural resources in attracting tourism and reinvest a share of tourism revenue to sustain and expand these resources.
Support annexation or deannexation actions that improve City service efficiency; improve fiscal sustainability; and/or contribute to regional goals related to transportation systems or environmental resources.
Support infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites by:
- Allowing densities sufficient to incentivize infill in older areas
- Focusing resources on target neighborhoods to build positive momentum
- Evaluating and adjusting zoning in areas where infill is desired
- Reducing permit fees and processing time for infill development proposals
- Waiving the requirement for traffic impact analyses for infill development proposals
- Establishing an Abandoned Buildings Program and enhancing it over time by:
- Seeking changes in City ordinance and State statute where necessary to allow for cost recovery of police and fire services costs caused by vacant buildings
- Using revenue collected beyond Vacant and Abandoned Buildings program administration cost for neighborhood improvements
- Submitting land bank legislation to the State Legislature and establishing a land bank authorized to acquire, rehabilitate, and dispose of abandoned properties
- Offering temporary or short term catalyzing incentives for the first “infillers” in target neighborhoods. Incentives may include small grants and/or low interest loans from a revolving loan fund or for property improvements.
- Evaluating the possibility of basing property taxes on only land value and not improvements, thereby encouraging high intensity use of well-positioned land and discouraging underutilization and long–term vacancy.
Consider updating the City’s Strategic Investment Program and retail incentive guidelines to maximize public benefit and return on investment from business recruitment and retention incentive structures according to the following order of preference:
- The prospective company pays for infrastructure and/or amenities and is reimbursed by the City as performance standards are achieved.
- The City pays for infrastructure and/or amenities, which the prospective company must repay if performance standards are not met.
- Direct, performance-based payments are made to the prospective company.
Assess the need for additional funds for citywide road maintenance beyond past average annual expenditures. If additional funds are needed for street maintenance, explore the feasibility of:
- Implementing a transportation utility fee; or
- Increasing the proportion of G.O. Bond money spent on street maintenance over past levels.
Improve efficiency of City operations through the following means:
- To the extent possible, base fees and charges on the cost of services and goods provided depending on location.
- Investigate and implement technological approaches to improving local government efficiency and service quality.
Provide public services in the most cost-effective manner through efficient growth by:
- Implementing an impact fee structure that varies by district according to actual cost.
- Studying the impacts of altering the pricing of utilities to factor in how the location of a user impacts the cost of providing them utility services.
- Exploring the use of fee-based revenue methods for maintaining infrastructure, such as transportation facilities, utility systems, and other public infrastructure.
- Altering zoning ordinance and subdivision regulations to allow more efficient development patterns.
Consider ways to make Oklahoma City’s tax structure more stable, resilient, and balanced by exploring options such as:
- Changing state law to allow property taxes to be used for local government operations.
- Reducing the number of sales tax exemptions (which have increased in recent years).
- Increasing the number of basic services subject to sales tax.
- Taxation of internet sales to regain lost revenue while restoring the competitive imbalance suffered by local retailers.
- Enhancing the stability of the local economy by supporting economic diversification.
Strengthen property values in order to increase property tax revenues using the following strategies:
- Implement, support, and enhance the Vacant and Abandoned Buildings initiative.
- Improve maintenance of existing infrastructure.
- Increase urban intensity where appropriate to encourage infill and neighborhood revitalization.
Increase City sales tax revenue by:
- Attracting and retaining retail inside municipal boundaries using the following specific strategies from the Retail Plan:
- Strengthen and expand existing regional retail destinations.
- Continue to pursue one-in-the-market retailers with potential to attract shoppers from the entire metro area.
- Partner with Penn Square regional node property owners to develop a plan for retail expansion of the node.
- Plan for one new regional retail node in the city by 2030. This node should be planned for the downtown area in concert with efforts to attract a lifestyle or mixed-use town center.
- Attract another Hispanic-focused supermarket to serve the area south of I-40.
- Actively seek a natural foods grocer to serve the Midtown and Deep Deuce neighborhoods.
- Reaffirm, revitalize, or re-vision existing retail nodes and corridors by following the recommendations for each node or corridor in the Retail Plan.
- Hastening the creation of a fair and simple way to appropriately tax online purchases.
Support locally-owned businesses and entrepreneurs, which have greater multiplier effects on the local economy, by the following actions:
- Establish online sales taxes to correct a competitive imbalance currently suffered by local “brick and mortar” merchants.
- Facilitate entrepreneurial growth by working with local companies and universities and supporting business incubators.
- Consider amending the Strategic Investment Program guidelines to give higher priority to locally-owned businesses.
- Consider creating incentives and/or easing regulations for small, locally-owned businesses such as home businesses, farmers’ markets, mobile food vendors, pop-up retail, etc.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Identify priority areas where the City can maximize private investment by providing public infrastructure and amenities including:
- Transit;
- Parks, trails, sidewalks;
- Streets;
- Arts and cultural facilities.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Work to establish a critical mass of retail uses in the downtown area. A lifestyle center or mixed-use town center presents the most viable option for a major infusion of retail into downtown.
We will place a priority on increasing the economic strength and growth of viable existing commercial nodes and corridors. Commercial development typically flees to the “next new thing,” leaving previous locations for new sites, usually in growth areas. While understandable, this trend leaves older commercial areas underutilized with more marginal businesses and vacancy, lower rents, and reduced upkeep and investment. While market conditions and age will inevitably make some areas less competitive, we must maintain the strength of our existing viable districts. This program may include:
- Improving the function and convenience of commercial areas with improved transportation access, including better local circulation, enhanced transit service, and internal and external pedestrian and bicycle linkages.
- Creating a better physical environment through streetscape and public space investments.
- Providing financial incentives like tax increment financing for site and building upgrades, and for introduction of new uses into single-use commercial areas.
- Creating new parking standards for mixed-use projects that recognize that different uses generate their highest parking demands at different times.
- Encouraging new commercial within redevelopment areas, benefitting existing retailing by introducing new nearby attractions.
We will implement strategies for the reuse and redevelopment of low-performing commercial areas. Cities don’t stand still and neither do retail markets. Some of the city’s commercial areas are no longer viable in their current form, but still siphon some commercial activity from other, stronger districts. We will implement strategies for revitalization of these underutilized but still important districts.
Create and implement small area plans for neighborhoods or districts with special strategic importance or complications related to development or redevelopment.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Incentives for new regional retail development should only be considered if the proposed project truly creates a new regional destination for the city and does not significantly cannibalize sales from existing Regional Districts.
Regional-, community-, and neighborhood-scale retail developments should provide an internal vehicle and pedestrian circulation system between new and existing centers and individual stores that draws on the following principles:
- Concentrate access for new retail development at shared primary entrance points. Primary entrance points should be aligned with access points immediately across intersecting roads. Limit curb cuts on primary highways and arterials.
- Provide pedestrian circulation, including sidewalks and median breaks along interior and exterior fronting roads and within parking lots.
- Encourage coordinated development of retail centers in order to facilitate internal pedestrian and vehicle circulation and optimal center performance.
Wayfinding mechanisms and other placemaking features should be strongly encouraged in new and existing commercial districts.
Public services are provided in the most cost-effective manner.
We will develop and implement a comprehensive asset management and maintenance system with sufficient funding to improve the park user’s experience. A systematic assessment of maintenance needs and priorities will help ensure that funds for operations and maintenance are both adequate and targeted to address key needs. This assessment begins with developing and maintaining a thorough inventory of the condition, with maintenance and replacement needs, of existing parks and facilities. It then establishes a maintenance standard and sets criteria and investment priorities to reach this level. Finally, the assessment should evaluate the deployment of maintenance staff and make adjustments to realize efficiencies. The overall process establishes adequate annual funding through the city’s budget process to implement the management and maintenance program.
The Parks Master Plan recommends establishing a Mode II standard, as defined by the National Recreation and Parks Association. This standard, typical of peer cities, is associated with high-level maintenance of well developed park areas with reasonably high visitation.
We will adapt park landscapes and facilities to minimize costs that are not necessary for the successful operation of the park or service to users. High costs related to energy use, landscape maintenance, and obsolete facilities or materials do not benefit park users. In order to support increased maintenance funding, taxpayers must be convinced that funds are used in the most efficient way possible. This sometimes requires difficult choices, such as minimizing landscaped areas that unnecessarily require high cost and extensive maintenance, removing underutilized facilities, and disposing of unproductive parks so that resources can be concentrated in repairing facilities with highest use. Designed use of natural rather than manicured landscapes, climatically appropriate materials, and energy efficient technologies can reduce maintenance costs without compromising service to park users.
Create partnerships and programs involving civic groups, business organizations, governmental entities, coalitions, and non-profits to develop or enhance the following:
- School reading programs;
- Elementary school intramural sports leagues;
- Rehabilitation of school infrastructure and replacement of school equipment (athletic facilities, media center materials, computers, etc.);
- After-school programs that focus on mentoring or conflict resolution;
- Rehabilitation of City parks;
- Community involvement opportunities associated with public schools; and,
- Other projects or programs that improve neighborhood safety by working with children.
Explore public/private funding sources and management structures, including non-profit conservancies, to improve, operate, manage and maintain downtown parks and open spaces.
Develop a downtown park master plan that identifies the following:
- Opportunities for providing private parks and open space while still maintaining a dense, urban environment (such as vest pocket parks, rooftop gardens, plazas and courtyards);
- Linkages and connections between public and private parks;
- Programming and amenities that complement and support parks in the system; and
- Funding for operations and maintenance.
Establish partnerships and programs with neighborhood associations and other organizations to improve maintenance of parks by:
- Increasing participation in the OKC Beautiful’s “Adopt a Park” program. Participants can include nearby businesses, neighborhood associations, churches, schools, and nonprofit groups;
- Establishing incentives for participating in the“Adopt a Park” program, such as providing awards; and,
- Increasing volunteer park maintenance programs.
Reduce the City’s long term operations and maintenance costs by:
- Adapting more energy efficient technologies for park facilities;
- Using low water landscape palettes and recycled water for irrigation; and,
- Identifying and pursuing additional funding sources including: increased appropriations to the City’s Parks & Recreation Department; federal, state, or county funds; dedicated sales tax; impact fees/in lieu fees; private, corporate, and foundation grants; and business improvement or assessment districts.
Pursue all opportunities, including donations, conservation easements, inheritance trusts, naming rights, and developer incentives to accomplish the following:
- Acquiring new lands for parks, open space;
- Acquiring natural areas that provide greater opportunities for people to access nature;
- Maintaining existing and future parks, open space, and natural areas;
- Enhancing existing landscaping at parks and along trails by planting additional native vegetation.
We will provide an appropriate level of service to citizens of all parts of the city. The Parks Master Plan identified level of service standards and deficits experienced by each of its four tiers. These level of service goals recognize that park service expectations are not the same for each tier. For example, central city areas with higher population densities, lower average household incomes, and less access to alternative facilities require (and should expect) a different level of service from rural areas with very low population and less dependence on the public recreation system.
We will provide full local park service in existing urban areas by filling current level of service gaps. Existing local and regional parks will provide most park services in developed areas. The City’s new park focus in these neighborhoods will concentrate on filling service gaps. The City should conduct a site selection and acquisition process for new park sites within areas that lack adequate local park service. Park sites should be considered for access and their ability to stabilize neighborhoods and encourage new private investment. A partnership of public funds through bond issues and private philanthropic contributions may provide financing for development of parks within these established, under-served neighborhoods, particularly when they are very dependent on public park service.
We will concentrate on developing regional public parks in developing areas and establish local parks through other means. Developing areas also require park service, but new park acquisition and development is difficult with limited capital and operational budgets. In these areas, with their lower population densities, the City’s focus should be on regional parks, with their ability to serve a larger population. In developing areas, local parks should focus on joint use with school sites or along trails when using public funds for purchase and development. Local parks that serve specific neighborhood needs should be privately built and operated. Regional or public local park development in development areas may be funded in part through an impact fee, based on the proportionate park area demand generated by new households multiplied by a factor for acquisition and park development.
Determine whether existing parks and facilities are serving the specific needs of the community within the park’s service area. If the area has transitioned and the park no longer serves the needs of the surrounding community, either reprogram the park, declare park surplus, or seek redevelopment to a more fitting use.
Coordinate planning efforts with school districts to attempt concurrent land purchases for schools and parks.
Modify codes and regulations to establish separate dedication requirements for parkland that excludes areas otherwise necessary or dedicated for drainage or detention as these areas should not receive credit to serve both purposes.
Ensure all homes are within walking distance of a park based on level of service standards for each urban land use typology by updating codes and regulations for new construction and by improving connections and access between existing parks and neighborhoods.
Establish procedures for creating new joint school/park sites, including the division of maintenance responsibilities.
Increase the number of joint-use agreements that allow community access to school playgrounds outside of school hours to improve neighborhood access to recreational facilities.
Increase the level of involvement and resources from agencies and other community groups to provide physical activity programming, such as after-school programs.
Prioritize capital improvement to construct linkages and connections from the existing urban parks and open space system to neighborhoods, commercial areas, employment centers, and community facilities.
Locate, design and upgrade City facilities and infrastructure in a manner that supports neighborhood revitalization and redevelopment.
Continue to create and enhance “big league city” amenities such as parks, public spaces, roadways, transit, cultural and recreational facilities, special districts, and gateways. Two specific possibilities for amenity enhancement include:
- Explore the feasibility of City-supported, high-quality landscaping along key transportation corridors as a means of enhancing the city’s appearance, image, and sense of place.
- Create gateways using public art features.
We will improve efficiencies in City operations and in providing public services through efficient growth. Increased efficiency follows two tracks. First, basic City operations should provide maximum value to the taxpayers per dollar spent. Second, the city’s growth should be economical and efficient so that it contributes to rather than detracts from fiscal stability.
Maximizing efficiency in City operations means establishing and maintaining appropriate staff levels and ensuring that staff is fully utilized; introducing technology and other innovations; avoiding duplications through information sharing and consolidation of functions where possible; and increasing cost recovery where possible by establishing fees and charges that reflect the actual cost of services.
Maximizing the benefits and efficiencies of growth is a primary theme of planokc, and is reflected throughout this document. While a comparison of the three development scenarios and preference for the “efficiency” scenario as the future growth model has many benefits, the choice is ultimately economic. The efficiency scenario accommodates the same amount of growth for $82 million less per year than continuing present trends. New techniques of financing development such as impact fees should also be considered to ensure that future development pays equitably for the cost of infrastructure that it demands.
Prioritize neighborhoods for revitalization and re-investment in order to reverse the decline associated with poor maintenance of public infrastructure and other property by using the following objective criteria:
- Low economic opportunity;
- Low educational attainment;
- Poor health outcomes;
- Poor housing environments;
- Low neighborhood quality; and,
- Existing capacity to support the revitalization efforts; and other important indicators.
In conjunction with City regulatory changes, such as significant modifications to zoning ordinances, building codes, or subdivision regulations, assess the effects of the proposed modifications on housing development costs and overall housing affordability, considering the balance between housing affordability and other objectives such as environmental quality, urban design quality, maintenance of neighborhood character and protection of public health, safety and welfare. This assessment should be integrated into the code amendment process, identify barriers to housing affordability, and include recommended mitigation.
Use established mechanisms/tools to allow property owners to provide for the perpetual maintenance, repair and reconstruction of private roads, sidewalks, trails, utilities, and parks in new housing developments by requiring funding mechanisms such as:
- Maintenance bonds/escrows
- Special assessment districts, such as Business Improvement District or Special Improvement District
- Covenants requiring compulsory membership in an incorporated Property Owners Association whose members will be financially liable for any such maintenance, repair, or reconstruction costs.
Incorporate these financing options into the platting process (or zoning process in the case of PUDs).
Construct all private roads and utilities to comply with minimum design and paving standards as outlined in the City of Oklahoma City Subdivision Regulations, including those related to the appropriate Street Typology.
Evaluate public facilities and public property for unsafe conditions such as poor lighting (quality and quantity); blind spots; poor maintenance conditions; and other unsafe conditions. Prioritize improvements to these facilities and properties based on the following criteria: a) Proximity and condition of nearby neighborhoods; and b) Cost/benefit associated with mitigating the unsafe condition and maintaining the improvement.
Continue to ensure that rates to wholesale customers, for example, nearby jurisdictions, are based on up-to-date cost of service studies.
Form a working partnership with the library system, both the Metropolitan Library System and the Oklahoma Department of Libraries, to coordinate timing of facility expansions, improvements, and new facility siting with other types of civic resources, such as schools, fire stations, parks, and projected growth and demand for those resources. This should also include identifying a mechanism to provide library services in Canadian County.
Support annexation or deannexation actions that improve City service efficiency; improve fiscal sustainability; and/or contribute to regional goals related to transportation systems or environmental resources.
Locate, design and upgrade City facilities and infrastructure in a manner that supports neighborhood revitalization and redevelopment.
Study the impact of vacant parcels on places and special districts, and determine how best to mitigate any negative impacts.
Prioritize street maintenance projects in the Capital Improvement Plan based on the Public Works Department’s street condition data and traffic volumes.
Improve efficiency of City operations through the following means:
- To the extent possible, base fees and charges on the cost of services and goods provided depending on location.
- Investigate and implement technological approaches to improving local government efficiency and service quality.
Provide public services in the most cost-effective manner through efficient growth by:
- Implementing an impact fee structure that varies by district according to actual cost.
- Studying the impacts of altering the pricing of utilities to factor in how the location of a user impacts the cost of providing them utility services.
- Exploring the use of fee-based revenue methods for maintaining infrastructure, such as transportation facilities, utility systems, and other public infrastructure.
- Altering zoning ordinance and subdivision regulations to allow more efficient development patterns.
Prioritize and concentrate development where facilities, infrastructure, and services have capacity and in areas where the Police and Fire Departments are best able to respond. Guide the location and timing of development through the proactive and strategic installation of infrastructure.
Use one or more of the following methods to ensure infrastructure and facility capacities are adequate for proposed development:
- Ongoing master planning to determine the necessary water, sewer, and road infrastructure to serve development.
- An impact fee system that collects funds for specific areas as they develop and installs needed infrastructure in a timely manner.
- Use of special service districts to ensure appropriate levels of service, sufficient revenue, and timely installation of infrastructure and facilities for each district.
- Require developers to construct or fully fund infrastructure or other improvements needed to serve their development, with reasonable accommodation for future adjacent or nearby development.
- Require developers to wait until the City (or the State as the case may be) constructs the infrastructure needed to serve their development.
- For development proposed in areas not currently within one-half mile of existing water infrastructure, require a service area study to first be completed to determine the best method for providing water to the service area.
For development proposed in areas not currently within a sanitary sewer drainage basin, a drainage basin study should first be completed to determine the best method for sanitary sewer service.
Encourage redevelopment and infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas.
Encourage the integration of different land uses in urban areas through the following means:
- Promote the use of performance standards in place of existing zoning methods (which address incompatibility by separating uses). Performance-based regulations should focus on achieving compatibility between uses by addressing the following:
- Noise, odors and air quality
- Traffic and parking (allow flexible, but sufficient parking)
- Site layout and building design
- Waste
- Safety
- Lighting (glare control, placement, and shielding)
- Delivery hours
- Enhance transit service (bus and rail).
- Prevent large areas of concentration of any particular land use such as multi-family or commercial.
Catalyze infill development on vacant, underutilized, and brownfield sites in urbanized areas by:
- Investing in infrastructure improvements;
- Improving multi-modal transportation networks;
- Improving parks and open spaces;
- Improving schools and other civic resources;
- Exploring innovative methods such as:
- A public-private partnership to purchase problem properties in target areas and build or rehabilitate homes while improving infrastructure and amenities
- An infill house plan program similar to Sacramento or Milwaukee
- Identifying and removing barriers to rehabilitation and/or replacement of residential buildings.
- Establishing a position in the City to facilitate medium- and large-scale redevelopment projects through the development process by guiding interactions with City departments, allied agencies, and utility companies.
Encourage the adaptive reuse of underutilized structures and the revitalization of older, economically distressed neighborhoods.
Prioritize maintaining the strength of existing commercial nodes and corridors over providing new areas for commercial development.
Continue promoting the re-use, redevelopment, and revitalization of low-performing or declining commercial areas.
Enable increased densities as appropriate to individual land use typology areas by addressing financial incentives and disincentives through evaluating the feasibility of strategies such as:
- Impact fees and/or transportation utility fees that vary by district according to actual cost;
- Assessing solid waste charges according to actual cost;
- Private solid waste services where it is impractical for the City to provide service such as in rural areas.
Create design standards and guidelines for the design, materials, shared amenities, and accessibility of high density urban residential development. Standards and guidelines should promote privacy and livability in a high density, mixed-use environment.
Adopt subdivision regulations that ensure new neighborhoods meet the basic needs of residents while supporting an efficient development pattern. Regulations should cover:
- Open space (passive and active),
- Demonstration of sustainable funding levels for common area and facility maintenance costs,
- Walkability and bikeability,
- Internal and external street connectivity,
- Block length,
- Integration of uses,
- Integration of a variety of home sizes,
- Integration of a variety of unit types, and
- Preservation of Environmentally Sensitive Areas.
Regulations could be based on a point scale to allow flexibility, while still requiring basic minimum thresholds be met.
New regulations should remove the existing requirement for development in Rural LUTAs to connect to water and sewer systems and establish a minimum one-acre lot size for lots with on-site sewer treatment.
























 Download PDF
Download PDF